here
... PUNISHMENT What is punishment? “an aversive action or unpleasant sensation (not necessarily physical) applied either during or within on e second of a particular behaviour that reduces the likelihood of that behaviour being repeated in the future.” Differs from negative reinforcement (where t ...
... PUNISHMENT What is punishment? “an aversive action or unpleasant sensation (not necessarily physical) applied either during or within on e second of a particular behaviour that reduces the likelihood of that behaviour being repeated in the future.” Differs from negative reinforcement (where t ...
CH 29 Review Answer Key
... 2. What does the traditional phylogenetic tree (Fig 29.2) tell you about the evolution of the animals studied in this chapter? (pg 519) Strongly suggests that life evolved from simpler/less complex organisms into increasing more complex animals in incremental stages. 3. What features make sponges di ...
... 2. What does the traditional phylogenetic tree (Fig 29.2) tell you about the evolution of the animals studied in this chapter? (pg 519) Strongly suggests that life evolved from simpler/less complex organisms into increasing more complex animals in incremental stages. 3. What features make sponges di ...
PPSI 2002 Short Research Summaries
... Pilot data were presented for the VIA Inventory of Strengths for Youth (VIA-Y), a new selfreport measure of character strengths. Data was collected from a sample of over 300 adolescents. Reliability of each of the scales for the 23 strengths measured was fair to good. The validity of the measure, wi ...
... Pilot data were presented for the VIA Inventory of Strengths for Youth (VIA-Y), a new selfreport measure of character strengths. Data was collected from a sample of over 300 adolescents. Reliability of each of the scales for the 23 strengths measured was fair to good. The validity of the measure, wi ...
Behaviourist Approach Model Answers
... experiment, a method that studies cause and effect by manipulating one variable (the independent variable) to see its effect on another variable (the dependant variable). Since all other variables which might affect behaviour are controlled, it is possible to say with a high degree of accuracy what ...
... experiment, a method that studies cause and effect by manipulating one variable (the independent variable) to see its effect on another variable (the dependant variable). Since all other variables which might affect behaviour are controlled, it is possible to say with a high degree of accuracy what ...
chapter 26: animal evolution and diversity
... UNIT 12: ANIMAL EVOLUTION OUTLINE CHAPTER 25: INTRODUCTION TO ANIMALS Section 25.1: What is an Animal? ...
... UNIT 12: ANIMAL EVOLUTION OUTLINE CHAPTER 25: INTRODUCTION TO ANIMALS Section 25.1: What is an Animal? ...
Inherited Trait / Instinct
... Inherited traits are physical characteristics and behaviors that an organism gets from its parents. It is born with them. Eye color, hair color, freckles, skin color and dimples are all inherited traits in humans. Other animals and plants also have inherited traits…some might include fur color, ...
... Inherited traits are physical characteristics and behaviors that an organism gets from its parents. It is born with them. Eye color, hair color, freckles, skin color and dimples are all inherited traits in humans. Other animals and plants also have inherited traits…some might include fur color, ...
The Animal Kingdom
... Animals whose cells are arranged into two embryonic layers, an outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm are called diploblastic Often an undifferentiated layer of cells is found between these two layers and is called the mesoglia This type of arrangement is found in cnidarians ...
... Animals whose cells are arranged into two embryonic layers, an outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm are called diploblastic Often an undifferentiated layer of cells is found between these two layers and is called the mesoglia This type of arrangement is found in cnidarians ...
Kingdom Animalia
... 3. Coelom Formation a. Protostomes - coelom formation is called schizocoelous development Coelom forms by splitting of mesoderm b. Deuterostomes - coelom formation is called enterocoelous development Coelom forms as outpockets from the endoderm The Animal Phylogenetic Tree The relationships between ...
... 3. Coelom Formation a. Protostomes - coelom formation is called schizocoelous development Coelom forms by splitting of mesoderm b. Deuterostomes - coelom formation is called enterocoelous development Coelom forms as outpockets from the endoderm The Animal Phylogenetic Tree The relationships between ...
Colorado Lawyer Assistance Program How You Can Deal With
... maliciously sabotaging others, co-dependency, shaming, the list goes on. We need to understand the origins of these behaviors so we can respond in ways that are helpful, rather than hurtful, when communicating with others who might exhibit these traits. When we experience intense feelings, whether t ...
... maliciously sabotaging others, co-dependency, shaming, the list goes on. We need to understand the origins of these behaviors so we can respond in ways that are helpful, rather than hurtful, when communicating with others who might exhibit these traits. When we experience intense feelings, whether t ...
I. Innate vs. Learned Behavior
... A. Behavior Cycles - cycles in behavior in response to cycles in environment. Circadian rhythm in response to day and night, migration cycles in response to seasons. B. Courtship – behavior related to reproduction and reproductive strategy. (intrasexual competition, intersexual choice, courtship rit ...
... A. Behavior Cycles - cycles in behavior in response to cycles in environment. Circadian rhythm in response to day and night, migration cycles in response to seasons. B. Courtship – behavior related to reproduction and reproductive strategy. (intrasexual competition, intersexual choice, courtship rit ...
Affective Computing
... • Basic, distinct emotion circuits in the brain – Distinct emotional patterns can be evoked by stimulating electrically particular subcortical areas responsible for basic emotions • Cortical regions largely free of such effects ...
... • Basic, distinct emotion circuits in the brain – Distinct emotional patterns can be evoked by stimulating electrically particular subcortical areas responsible for basic emotions • Cortical regions largely free of such effects ...
File - Learning! Outside of Class!
... punishment influence the level of the resulting behaviour. ...
... punishment influence the level of the resulting behaviour. ...
Section 26.1 Summary – pages 693-697
... These are animals that make both sperm and eggs, but they do not fertilize themselves (there would be no point if they did because their offspring would be identical to them), so they swap sperm and eggs with other hermaphrodites to produce genetically different offspring. ...
... These are animals that make both sperm and eggs, but they do not fertilize themselves (there would be no point if they did because their offspring would be identical to them), so they swap sperm and eggs with other hermaphrodites to produce genetically different offspring. ...
The Feeling of Meaning
... illustrating the general theory of emotion and aesthetics — and idiographic — reflecting the specific perspective of the artist. As might be appropriate study of aesthetics, there are several ways that Cupchik’s book can be interpreted. The most straightforward way is what you might expect, and what ...
... illustrating the general theory of emotion and aesthetics — and idiographic — reflecting the specific perspective of the artist. As might be appropriate study of aesthetics, there are several ways that Cupchik’s book can be interpreted. The most straightforward way is what you might expect, and what ...
Introduction to Animals - Linn
... Focus on key features – Hallmark characteristics e.g. Mammals have fur. Symmetry Body Cavity Types Digestive system – how does it process food e.g. gastrovascular cavity vs. through gut. Special modes of reproduction e.g. internal vs external fertilization. Degrees of complexity – such as segmentati ...
... Focus on key features – Hallmark characteristics e.g. Mammals have fur. Symmetry Body Cavity Types Digestive system – how does it process food e.g. gastrovascular cavity vs. through gut. Special modes of reproduction e.g. internal vs external fertilization. Degrees of complexity – such as segmentati ...
Introduction to Animals
... Diploidy-two copies of each chromosomes All animals have two copies of each chromosome. One ...
... Diploidy-two copies of each chromosomes All animals have two copies of each chromosome. One ...
Cognitive Processes in Animal Behavior
... – Emphasizes observing animals under more-or-less natural conditions • with the objective of understanding species-specific behavioral repertoire ...
... – Emphasizes observing animals under more-or-less natural conditions • with the objective of understanding species-specific behavioral repertoire ...
PSY 402
... Guthrie proposed that no reinforcement was needed – just contiguity (closeness) in time ...
... Guthrie proposed that no reinforcement was needed – just contiguity (closeness) in time ...
Study Guide
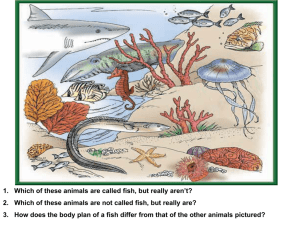
... 1. Explain the relationship between differentiation and specialization. ___________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. On what basis ...
... 1. Explain the relationship between differentiation and specialization. ___________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. On what basis ...
Name Class Date SECTION 32-1 Study Guide THE NATURE OF
... 1. Explain the relationship between differentiation and specialization. ___________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. On what basis ...
... 1. Explain the relationship between differentiation and specialization. ___________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. On what basis ...
Understanding Motivation
... start eating even if it has just consumed a full meal. Or if it is surgically removed, the animal will stop eating and starve to death. Ventromedial hypothalamus, acts as an off-switch that ...
... start eating even if it has just consumed a full meal. Or if it is surgically removed, the animal will stop eating and starve to death. Ventromedial hypothalamus, acts as an off-switch that ...
Self-Regulation
... for Emotion Regulation (Gross) Suppression 1. reducing expressive behavior: 2. “control your expression so that nobody could tell what you are feeling” ...
... for Emotion Regulation (Gross) Suppression 1. reducing expressive behavior: 2. “control your expression so that nobody could tell what you are feeling” ...
Invertebrate Notes
... __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ ___ ...
... __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ ___ ...
Emotion in animals

Emotions in animals are the subjective feelings and emotions experienced by nonhuman animals. Emotions may be described as subjective, conscious experiences characterized primarily by psychophysiological expressions, biological reactions, and mental states.Charles Darwin was one of the first scientists to write about the existence and nature of emotions in nonhuman animals. His observational and sometimes anecdotal approach has developed into a more robust, hypothesis-driven, scientific approach. General hypotheses relating to correlates between humans and non-human animals also support the claim that non-human animals may feel emotions and that human emotions evolved from the same mechanisms. Several tests, such as cognitive bias tests and learned helplessness models, have been developed. Cognitive biases (feelings of optimism or pessimism) have been shown in a wide range of species including rats, dogs, cats, rhesus macaques, sheep, chicks, starlings, pigs and honeybees.Some behaviourists claim stimulus–response models provide a sufficient explanation for animal behaviours that have been described as emotional, and that it is unnecessary to postulate that animals are conscious. Other behaviourists further question whether animals feel emotions on the grounds that emotions aren't universal even among humans, that interpretations of animal behaviour are anthropomorphic, and that definitions of emotions lack robustness.