Mitochondria
... • The inner membrane, which encloses the matrix space, is folded to form cristae. The area of the inner membrane is about five times as great as the outer membrane. • This membrane is richly endowed with cardiolipin, a phospholipid that possesses four, rather than the usual two, fatty acyl chains. T ...
... • The inner membrane, which encloses the matrix space, is folded to form cristae. The area of the inner membrane is about five times as great as the outer membrane. • This membrane is richly endowed with cardiolipin, a phospholipid that possesses four, rather than the usual two, fatty acyl chains. T ...
1 Amino Acid Metabolism
... • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N compounds, energy (also via gluco ...
... • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N compounds, energy (also via gluco ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N compounds, energy (also via gluco ...
... • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N compounds, energy (also via gluco ...
$doc.title
... turns yellow. What conclusion is consistent with these observations? b. The bacteria can’t ferment sucrose because they lack an enzyme to digest it. ...
... turns yellow. What conclusion is consistent with these observations? b. The bacteria can’t ferment sucrose because they lack an enzyme to digest it. ...
Practice Exam III answers
... a). The enzyme lowers the activation energy of the rate-limiting step of the reaction. b). The reaction order changes from 1st order to 2nd order with respect to [E]. c). The efficiency of catalysis increases. d). All of the active sites of the enzyme are saturated with S at high [S]. e). The enzyme ...
... a). The enzyme lowers the activation energy of the rate-limiting step of the reaction. b). The reaction order changes from 1st order to 2nd order with respect to [E]. c). The efficiency of catalysis increases. d). All of the active sites of the enzyme are saturated with S at high [S]. e). The enzyme ...
Generalities Main amino acid reactions
... Proteins are the polypeptides formed by sequences of amino acids General formula of the a-amino acids NH2-CH-COOH R The amino acids occupy a central position in the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds ...
... Proteins are the polypeptides formed by sequences of amino acids General formula of the a-amino acids NH2-CH-COOH R The amino acids occupy a central position in the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds ...
fatty acid oxid final
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
... Glycogen synthase is allosterically inhibited by physiological concentrations of ATP, ADP and Pi. It is allosterically activated by glucose-6-phosphate. Like glycogen phosphorylase, allosteric controls are overridden by reversible covalent phosphorylation. In this case the phosphorylated glycogen sy ...
... Glycogen synthase is allosterically inhibited by physiological concentrations of ATP, ADP and Pi. It is allosterically activated by glucose-6-phosphate. Like glycogen phosphorylase, allosteric controls are overridden by reversible covalent phosphorylation. In this case the phosphorylated glycogen sy ...
Biology: Cellular Respiration Practice Problems
... 14. On average, how many ATP can be made from each NADH during the electron transport process? 15. On average, how many ATP can be made from each FADH2 during the electron transport process? 16. What would happen to the cellular respiration process if the enzyme for one step of the process were miss ...
... 14. On average, how many ATP can be made from each NADH during the electron transport process? 15. On average, how many ATP can be made from each FADH2 during the electron transport process? 16. What would happen to the cellular respiration process if the enzyme for one step of the process were miss ...
FEBS Letters
... Heterocysts supply vegetative cells with gluta- 1 mine formed by the nitrogenase/glutamine synthetase reactions. In exchange, a disaccharide and glutamate were said to be transported from vegetative cells to heterocysts [l-3]. The latter statement is not so well substantiated by experimental finding ...
... Heterocysts supply vegetative cells with gluta- 1 mine formed by the nitrogenase/glutamine synthetase reactions. In exchange, a disaccharide and glutamate were said to be transported from vegetative cells to heterocysts [l-3]. The latter statement is not so well substantiated by experimental finding ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... The Glyoxylate Cycle • Plant can use acetate as the only source of carbon for all the carbon compounds • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-producting steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the s ...
... The Glyoxylate Cycle • Plant can use acetate as the only source of carbon for all the carbon compounds • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-producting steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is utilized • Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are the s ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... • Other components are added to the VLDL in the blood. ...
... • Other components are added to the VLDL in the blood. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (b) pepsin (c) lysozyme (d) lipase (2) An example of enzyme regulation by covalent modification is (a) isomerization (b) trypsinization (c) substrate channeling (d) phosphorylation (3) Trypsinogen is activated by (a) chymotrypsin (b) trypsin ...
... (b) pepsin (c) lysozyme (d) lipase (2) An example of enzyme regulation by covalent modification is (a) isomerization (b) trypsinization (c) substrate channeling (d) phosphorylation (3) Trypsinogen is activated by (a) chymotrypsin (b) trypsin ...
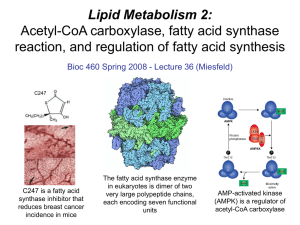
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
OVERVIEW OF LIPID METABOLISM
... 1) Glycogen breakdown provides glucose and protein breakdown provides alanine, which is converted to glucose in the liver. The blood glucose is used by the brain and red blood cells. Most other tissues, including resting muscle, are relying primarily on fatty acids as an energy source. Exercising mu ...
... 1) Glycogen breakdown provides glucose and protein breakdown provides alanine, which is converted to glucose in the liver. The blood glucose is used by the brain and red blood cells. Most other tissues, including resting muscle, are relying primarily on fatty acids as an energy source. Exercising mu ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
Enzymes of Clinical Significance
... b. Remain unchanged in the reaction, not consumed in the reaction c. Effect speed of reaction (not final concentration of substrate or products) d. Show greater degree of specificity than chemical catalysts e. Unstable and easily destroyed ...
... b. Remain unchanged in the reaction, not consumed in the reaction c. Effect speed of reaction (not final concentration of substrate or products) d. Show greater degree of specificity than chemical catalysts e. Unstable and easily destroyed ...
Mrs C`s Chem Lecture
... Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution (water, in living organisms). Glycine Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution (water, in living organisms). Glycine Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
k - upatras eclass - Πανεπιστήμιο Πατρών
... Archaea exhibit a great variety of chemical reactions in their metabolism and use many different sources of energy. These forms of metabolism are classified into nutritional groups, depending on the source of energy and the source of carbon. Some archaea obtain their energy from inorganic compounds ...
... Archaea exhibit a great variety of chemical reactions in their metabolism and use many different sources of energy. These forms of metabolism are classified into nutritional groups, depending on the source of energy and the source of carbon. Some archaea obtain their energy from inorganic compounds ...
CARBOHYDRATES B.SC Ist SEMESTER INTRODUCTION TO
... person suffer from lactose intolerance problem. •This problem occurs as most of mammals do not consume milk after weaning and mainly lactose intolerance is caused by deficiency of enzyme lactase which hydrolyze lactose. •In absence of this enzyme, lactose is not hydrolyzed into glucose and galactose ...
... person suffer from lactose intolerance problem. •This problem occurs as most of mammals do not consume milk after weaning and mainly lactose intolerance is caused by deficiency of enzyme lactase which hydrolyze lactose. •In absence of this enzyme, lactose is not hydrolyzed into glucose and galactose ...
Chapter 25 LIPID METABOLISM
... Major form of energy: triacylglycerol/fat/triglycerides o 90% of dietary lipid o oxidized to CO2 and H2O o 6 times more energy/weight of glycogen o water insoluble o digestion at lipid/water interface o emulsified by bile salts/bile acids in small intestine o cut at pos 1 and 3 by lipase (triacylgly ...
... Major form of energy: triacylglycerol/fat/triglycerides o 90% of dietary lipid o oxidized to CO2 and H2O o 6 times more energy/weight of glycogen o water insoluble o digestion at lipid/water interface o emulsified by bile salts/bile acids in small intestine o cut at pos 1 and 3 by lipase (triacylgly ...
14e8d39db06b481
... Suggest the possible alterations in glucose storage and break down that might occur in this clinical problem. Inhibition of glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis) Stimulation of glycogenolysis (glycogen degradation) ...
... Suggest the possible alterations in glucose storage and break down that might occur in this clinical problem. Inhibition of glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis) Stimulation of glycogenolysis (glycogen degradation) ...
Biochemistry 3 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... Which of the following is a Catacholemine synthesized from Tyrosine? EPINEPHRINE How many essential Amino Acids are Aromatic? (PHENYLALANINE & TRYPTOPHAN) Thyroxine is derived from ____________. TYROSINE (also epinephrine) The enzyme which catalases the interconversion of UDP-Galactose with UDP Gluc ...
... Which of the following is a Catacholemine synthesized from Tyrosine? EPINEPHRINE How many essential Amino Acids are Aromatic? (PHENYLALANINE & TRYPTOPHAN) Thyroxine is derived from ____________. TYROSINE (also epinephrine) The enzyme which catalases the interconversion of UDP-Galactose with UDP Gluc ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑