Bio 520
... muscle. Be careful not to damage the diaphragm or the organs of each cavity. You may have to flush out your rat’s abdomen under flowing water in the sink to remove the fluid in the gastrovascular cavity. The abdominal organs may still be covered with a membrane, the peritoneum, (peritoneal membrane) ...
... muscle. Be careful not to damage the diaphragm or the organs of each cavity. You may have to flush out your rat’s abdomen under flowing water in the sink to remove the fluid in the gastrovascular cavity. The abdominal organs may still be covered with a membrane, the peritoneum, (peritoneal membrane) ...
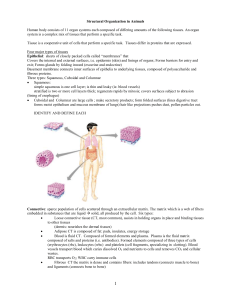
Structural Organization in Animals
... “acrosome” essentially a lysosome (contains hydrolytic enzymes that digest the cervical mucus and the protective coating around the egg). Testes descend from the body cavity into the scrotum during the ninth month of fetal life. Penis erection is accomplished by blood flowing into the spongy erectil ...
... “acrosome” essentially a lysosome (contains hydrolytic enzymes that digest the cervical mucus and the protective coating around the egg). Testes descend from the body cavity into the scrotum during the ninth month of fetal life. Penis erection is accomplished by blood flowing into the spongy erectil ...
The Cardiovascular System
... treatments like clot busters that work best within the first hour after onset of pain or discomfort. -Chewing an uncoated aspirin right away, at the first sign of chest discomfort or distress, can reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle during a heart attack. ...
... treatments like clot busters that work best within the first hour after onset of pain or discomfort. -Chewing an uncoated aspirin right away, at the first sign of chest discomfort or distress, can reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle during a heart attack. ...
Lesson 31 - Zoology, UBC
... which have no functional gills, is already oxygenated. Deoxygenated blood enters the sinus venosus, the right atrium, the right side of the ventricle and the opposite side of the spiral valve that delivers it to the posterior two gill arches. This blood then passes through the functional gills and c ...
... which have no functional gills, is already oxygenated. Deoxygenated blood enters the sinus venosus, the right atrium, the right side of the ventricle and the opposite side of the spiral valve that delivers it to the posterior two gill arches. This blood then passes through the functional gills and c ...
All About Blood - Spark Innovations
... much of their blood each part is, or during your demonstration. Talk about how one drop of blood contains a half a drop of plasma, 5 MILLION Red Blood Cells, 10 Thousand White Blood Cells and 250 Thousand Platelets. Write the numbers on the board next to your pie chart and ask them which one is the ...
... much of their blood each part is, or during your demonstration. Talk about how one drop of blood contains a half a drop of plasma, 5 MILLION Red Blood Cells, 10 Thousand White Blood Cells and 250 Thousand Platelets. Write the numbers on the board next to your pie chart and ask them which one is the ...
Chapter21 Lecture notes
... Preview: The classic example of homeostasis is the regulation of blood glucose levels. After a meal, when blood glucose levels rise, the body releases insulin to lower blood glucose levels by storing it as fat or glycogen. Between meals, when blood glucose levels have fallen, the body releases gluca ...
... Preview: The classic example of homeostasis is the regulation of blood glucose levels. After a meal, when blood glucose levels rise, the body releases insulin to lower blood glucose levels by storing it as fat or glycogen. Between meals, when blood glucose levels have fallen, the body releases gluca ...
Respiratory Overview
... The mechanics of breathing involve changing the volume and pressure of the thoracic cavity. By using the principles of Boyle's Law, one can see that the pressure in the thoracic cavity is inversely proportional to its volume. When the intercostal muscles contract the ribs are elevated. At the same t ...
... The mechanics of breathing involve changing the volume and pressure of the thoracic cavity. By using the principles of Boyle's Law, one can see that the pressure in the thoracic cavity is inversely proportional to its volume. When the intercostal muscles contract the ribs are elevated. At the same t ...
Unit 2 Summary Notes Cells, tissues and organs
... Tissues are groups of specialised cells which will carry out a particular function. Examples of animal tissues include: -Muscle -Blood -Nerves Examples of plant tissues include: -Vascular tissue (i.e. transport tissues such as xylem and phloem) -Palisade tissue (layer of palisade cells within the le ...
... Tissues are groups of specialised cells which will carry out a particular function. Examples of animal tissues include: -Muscle -Blood -Nerves Examples of plant tissues include: -Vascular tissue (i.e. transport tissues such as xylem and phloem) -Palisade tissue (layer of palisade cells within the le ...
Structural Organisation in Animals
... The squamous epithelium is made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved in a functions like forming a diffusion boundary. 1 The cuboidal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-l ...
... The squamous epithelium is made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved in a functions like forming a diffusion boundary. 1 The cuboidal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-l ...
Buffer System
... (interstitial fluid and plasma) but are very low in the intracellular fluid (cytoplasm) • K+ and HPO42- predominate in intracellular fluid (cytoplasm) but are in very low concentration in the extracellular fluids (interstitial fluid and plasma) • At body fluid pH, proteins [P-] act as anions; total ...
... (interstitial fluid and plasma) but are very low in the intracellular fluid (cytoplasm) • K+ and HPO42- predominate in intracellular fluid (cytoplasm) but are in very low concentration in the extracellular fluids (interstitial fluid and plasma) • At body fluid pH, proteins [P-] act as anions; total ...
Chapter 17
... – Most marine invertebrates are in osmotic equilibrium with their seawater environment. – With body surfaces permeable to water and salts, the internal and external concentrations are equal. – Such animals that cannot regulate osmotic pressure of their body fluids are called osmotic conforme ...
... – Most marine invertebrates are in osmotic equilibrium with their seawater environment. – With body surfaces permeable to water and salts, the internal and external concentrations are equal. – Such animals that cannot regulate osmotic pressure of their body fluids are called osmotic conforme ...
10/16/06
... Cvt = venous blood concentration Pt = tissue blood partition coefficient Vt = volume of tissue At = amount of chemical in tissue ...
... Cvt = venous blood concentration Pt = tissue blood partition coefficient Vt = volume of tissue At = amount of chemical in tissue ...
Emergency Medical Training Services
... a. Paired, rod-shaped organelles that lie at right angles to each other in a zone of cytoplasm (centrosome) (1 question on exam) It is here that energy, derived from the efficient metabolism of nutrients and oxygen via the Krebs cycle, is used to synthesize high-energy triphosphate bonds (e.g., aden ...
... a. Paired, rod-shaped organelles that lie at right angles to each other in a zone of cytoplasm (centrosome) (1 question on exam) It is here that energy, derived from the efficient metabolism of nutrients and oxygen via the Krebs cycle, is used to synthesize high-energy triphosphate bonds (e.g., aden ...
Animal Structure and Function Review
... 40. Describe the 5 types of signaling in figure 45.2 in your text. 41. What are the four classes of hormones and which ones are water soluble? 42. Describe the difference in how water soluble and lipid soluble hormones signal target cells. 43. One hormone can have multiple effects in the body. Give ...
... 40. Describe the 5 types of signaling in figure 45.2 in your text. 41. What are the four classes of hormones and which ones are water soluble? 42. Describe the difference in how water soluble and lipid soluble hormones signal target cells. 43. One hormone can have multiple effects in the body. Give ...
printer-friendly version
... heart (except pulmonary veins). Blood passes from arteries to capillaries then to veins where it returns to the heart. Capillaries are the thinnest and most numerous of blood vessels and are responsible for exchanging gasses and nutrients to the cells in exchange for their waste products. In the clo ...
... heart (except pulmonary veins). Blood passes from arteries to capillaries then to veins where it returns to the heart. Capillaries are the thinnest and most numerous of blood vessels and are responsible for exchanging gasses and nutrients to the cells in exchange for their waste products. In the clo ...
Chapter 17
... • Soil calcium produces a high blood calcium level; calciferous glands along the esophagus keep down the calcium ion concentration in the blood and are ion-regulatory rather than digestive in function. • Food passes the esophagus to be stored in a thin-walled crop. • The muscular gizzard grinds food ...
... • Soil calcium produces a high blood calcium level; calciferous glands along the esophagus keep down the calcium ion concentration in the blood and are ion-regulatory rather than digestive in function. • Food passes the esophagus to be stored in a thin-walled crop. • The muscular gizzard grinds food ...
Word Count: 963 The Liver: Facts, Functions, and Structure of Justin
... most main chemicals blood classified digestive system because bile produces bile produced stored gallbladder although contains digestive enzymes bile does dilute neutralize stomach acid increases efficiency digestion absorption that allows drink alcohol with help kidneys clears blood drugs alcohol o ...
... most main chemicals blood classified digestive system because bile produces bile produced stored gallbladder although contains digestive enzymes bile does dilute neutralize stomach acid increases efficiency digestion absorption that allows drink alcohol with help kidneys clears blood drugs alcohol o ...
Chapter 5 Gases
... • Fish have a one-circuit circulatory system. All other vertebrates have a short pulmonary circuit that carries blood to and from the lungs, and a longer systemic circuit that moves blood to and from the body’s other tissues. • A four-chambered heart evolved independently in birds and mammals. Such ...
... • Fish have a one-circuit circulatory system. All other vertebrates have a short pulmonary circuit that carries blood to and from the lungs, and a longer systemic circuit that moves blood to and from the body’s other tissues. • A four-chambered heart evolved independently in birds and mammals. Such ...
SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY
... such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments are tissues that attach bones to other bones. Tendons and ligaments help ...
... such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments are tissues that attach bones to other bones. Tendons and ligaments help ...
DO NOW - O. Henry Science
... Copy the following paragraph into your notebook on page 98. Use the word bank to help you fill in the blanks. Veins return __(1)__ blood back to the heart. The heart then pumps the oxygen poor blood to either the right or left __(2)__. There, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide at ...
... Copy the following paragraph into your notebook on page 98. Use the word bank to help you fill in the blanks. Veins return __(1)__ blood back to the heart. The heart then pumps the oxygen poor blood to either the right or left __(2)__. There, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide at ...
File
... ........................................................... cm3 (ii) Factors other than light intensity are limiting the rate of oxygen production above 2000 lux. Describe how a different factor can increase the volume of oxygen produced by this plant. ...
... ........................................................... cm3 (ii) Factors other than light intensity are limiting the rate of oxygen production above 2000 lux. Describe how a different factor can increase the volume of oxygen produced by this plant. ...
Lesson 2: Human Body Systems – The Circulatory System To
... oxygenated blood into the left atrium 6. When the heart contracts then the valve will open up allowing the oxygenated blood to flow into the left ventricle 7. Then a powerful contraction takes place to push the blood through another valve (called the aortic valve) to get into the aorta which is wher ...
... oxygenated blood into the left atrium 6. When the heart contracts then the valve will open up allowing the oxygenated blood to flow into the left ventricle 7. Then a powerful contraction takes place to push the blood through another valve (called the aortic valve) to get into the aorta which is wher ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.