Notes
... A group of different kinds of tissues that coordinate their actions into a main primary function is called an organ. A group of organs and tissues that work together to maintain homeostasis in the body are called a system. ...
... A group of different kinds of tissues that coordinate their actions into a main primary function is called an organ. A group of organs and tissues that work together to maintain homeostasis in the body are called a system. ...
PE Revision – Powerpoint of whole specification 2012
... speed and terrain over which you run, cycle or ski. It improves both anaerobic and aerobic fitness. ...
... speed and terrain over which you run, cycle or ski. It improves both anaerobic and aerobic fitness. ...
turtle dissection lab
... Like amphibians, the circulatory system in reptiles consists of a CLOSED TWO LOOP SYSTEM and a THREE CHAMBER HEART surrounded by a PERICARDIAL MEMBRANE. (1) Locate the RIGHT ATRIUM, LEFT ATRIUM, and VENTRICLE. Look for the SINUS VENOSUS and CONUS ARTERIOSUS. The CONUS ARTERIOSUS forms the base of th ...
... Like amphibians, the circulatory system in reptiles consists of a CLOSED TWO LOOP SYSTEM and a THREE CHAMBER HEART surrounded by a PERICARDIAL MEMBRANE. (1) Locate the RIGHT ATRIUM, LEFT ATRIUM, and VENTRICLE. Look for the SINUS VENOSUS and CONUS ARTERIOSUS. The CONUS ARTERIOSUS forms the base of th ...
A quick summary: The skeletal system is made up of bones
... acute and chronic medical problems, diseases, infections, that can easily disrupt this stability. There are also day-to-day changes in food and fluid requirements, different levels of physical activity, and constant variations in the needs of the organs and tissue for oxygen, blood flow, and nutrie ...
... acute and chronic medical problems, diseases, infections, that can easily disrupt this stability. There are also day-to-day changes in food and fluid requirements, different levels of physical activity, and constant variations in the needs of the organs and tissue for oxygen, blood flow, and nutrie ...
A quick summary: The skeletal system is made up of bones
... acute and chronic medical problems, diseases, infections, that can easily disrupt this stability. There are also day-to-day changes in food and fluid requirements, different levels of physical activity, and constant variations in the needs of the organs and tissue for oxygen, blood flow, and nutrie ...
... acute and chronic medical problems, diseases, infections, that can easily disrupt this stability. There are also day-to-day changes in food and fluid requirements, different levels of physical activity, and constant variations in the needs of the organs and tissue for oxygen, blood flow, and nutrie ...
Part 1 Structure and function of the respiratory system
... Breathing Rate • At rest: 10-20 breaths / minute • During exercise: 40 - 45 at maximum exercise in adults ...
... Breathing Rate • At rest: 10-20 breaths / minute • During exercise: 40 - 45 at maximum exercise in adults ...
Introduction to the Human Body - cK-12
... Specialized cells are organized into tissues. A tissue is a group of specialized cells of the same kind that perform the same function. There are four basic types of human tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues. The four types are shown in Figure 1.2. • Connective tissue consis ...
... Specialized cells are organized into tissues. A tissue is a group of specialized cells of the same kind that perform the same function. There are four basic types of human tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues. The four types are shown in Figure 1.2. • Connective tissue consis ...
11. Circulatory and resp
... Arteries have thick walls that can expand when blood enters under pressure. Blood pressure moves blood in arteries and arterioles. Veins have weak walls and valves that prevent blood from falling back. When skeletal muscles contract, they press against the venules and veins, keeping the blood moving ...
... Arteries have thick walls that can expand when blood enters under pressure. Blood pressure moves blood in arteries and arterioles. Veins have weak walls and valves that prevent blood from falling back. When skeletal muscles contract, they press against the venules and veins, keeping the blood moving ...
Respiration and Circulation Blood
... What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements to see if you have changed your mind. Before ...
... What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements to see if you have changed your mind. Before ...
Directed Reading
... the heart and veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. hypertension anemia The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide from the body. lungs The diaphragm is a muscular dome below the lungs which causes inhalation and expiration. an infection of the lungs in ...
... the heart and veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. hypertension anemia The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide from the body. lungs The diaphragm is a muscular dome below the lungs which causes inhalation and expiration. an infection of the lungs in ...
File
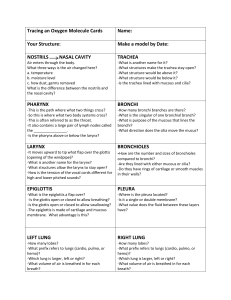
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
File - Berwick PDHPE Stage 6
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
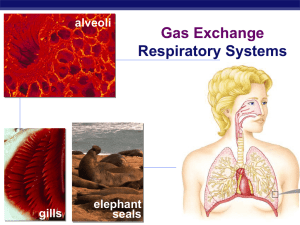
Gas Exchange print ppt
... blood alone could not provide enough O2 to animal cells hemocyanin in insects = copper (bluish/greenish) hemoglobin in vertebrates = iron (reddish) ...
... blood alone could not provide enough O2 to animal cells hemocyanin in insects = copper (bluish/greenish) hemoglobin in vertebrates = iron (reddish) ...
The Excretory System - Doral Academy High School
... aorta and carotids that oxygen is low in the blood. Brain signals diaphragm, a muscle below the lungs, and respiratory muscles to tighten which causes inhalation to occur when the muscles relax. Inhalation- Oxygen is breathed in through upper airways into the lower airways, and then into the gas exc ...
... aorta and carotids that oxygen is low in the blood. Brain signals diaphragm, a muscle below the lungs, and respiratory muscles to tighten which causes inhalation to occur when the muscles relax. Inhalation- Oxygen is breathed in through upper airways into the lower airways, and then into the gas exc ...
doc - NSW Department of Education
... are and which glands release them. They find out which glands regulate bodily functions such as energy levels, digestion, calcium, growth and puberty. ...
... are and which glands release them. They find out which glands regulate bodily functions such as energy levels, digestion, calcium, growth and puberty. ...
Survey of Animals from the Phylum Chordata
... – Internal Amniotic Egg: develops inside of mother and contains amnion/amniotic fluid – External Amniotic Egg: develops outside of mother and contains amnion/amniotic fluid – Aquatic Egg: contains no amnion and develops in a liquid (aquatic) environment ...
... – Internal Amniotic Egg: develops inside of mother and contains amnion/amniotic fluid – External Amniotic Egg: develops outside of mother and contains amnion/amniotic fluid – Aquatic Egg: contains no amnion and develops in a liquid (aquatic) environment ...
Requirements of Animals Ch 5 Pt D - SandyBiology1-2
... Protein breakdown( metabolism) results in nitrogenenous waste • This then is excreted as either ammonia, urea or uric acid ...
... Protein breakdown( metabolism) results in nitrogenenous waste • This then is excreted as either ammonia, urea or uric acid ...
1 The Cell Membrane Exchanged Materials cytoplasm: the cell
... molecules move from high to low concentrations due to their kinetic energy – molecules are in constant motion and the movement of each molecule is random but there are more molecules in an area of higher concentration the molecules will move and spread out to lower concentrations the entropy of a ...
... molecules move from high to low concentrations due to their kinetic energy – molecules are in constant motion and the movement of each molecule is random but there are more molecules in an area of higher concentration the molecules will move and spread out to lower concentrations the entropy of a ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.