The Human Body
... Made up of your brain, your spinal cord, and an enormous network of nerves that thread throughout your body, it's the control center for your entire body. Your brain uses information it receives from your nerves to coordinate all of your actions and reactions. ...
... Made up of your brain, your spinal cord, and an enormous network of nerves that thread throughout your body, it's the control center for your entire body. Your brain uses information it receives from your nerves to coordinate all of your actions and reactions. ...
In this unit, we have been exploring homeostasis, t
... Organs that eliminate wastes by filtering and cleansing ______________ to produce urine. Maintain fluid and chemical balances in body by filtering __________, salts, and other fluids. ___________________ regulate kidney function. o ___________________ ___________________: A saclike organ tha ...
... Organs that eliminate wastes by filtering and cleansing ______________ to produce urine. Maintain fluid and chemical balances in body by filtering __________, salts, and other fluids. ___________________ regulate kidney function. o ___________________ ___________________: A saclike organ tha ...
Bio 20 Reg - Holy Trinity Academy
... process also occurs in some yeast cells producing alcohol instead of lactic acid as an end product, called alcoholic fermentation. 2. If oxygen is present pyruvic acid enters Krebs cycle. This occurs inside the mitochondria Anaerobic Respiration (glucose lactic acid or alcohol) (fermentation) 1. o ...
... process also occurs in some yeast cells producing alcohol instead of lactic acid as an end product, called alcoholic fermentation. 2. If oxygen is present pyruvic acid enters Krebs cycle. This occurs inside the mitochondria Anaerobic Respiration (glucose lactic acid or alcohol) (fermentation) 1. o ...
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid–Base Balance
... Cannot protect ECF from changes in pH that result from elevated or depressed levels of CO2 2. Functions only when respiratory system and respiratory control ...
... Cannot protect ECF from changes in pH that result from elevated or depressed levels of CO2 2. Functions only when respiratory system and respiratory control ...
The Importance of the Respiratory System
... released is used to maintain cell processes, such as growth, movement, and the creation of new molecules. The concentration of oxygen in cells is much lower than in their environment because cells continuously use it for cellular respiration. Oxygen must be constantly replenished if a cell is to sur ...
... released is used to maintain cell processes, such as growth, movement, and the creation of new molecules. The concentration of oxygen in cells is much lower than in their environment because cells continuously use it for cellular respiration. Oxygen must be constantly replenished if a cell is to sur ...
Document
... 1. In the blood, hemoglobin binds with oxygen from the alveoli to form oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) 2. Carbon dioxide is carried primarily in the plasma of the blood in the form of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) ...
... 1. In the blood, hemoglobin binds with oxygen from the alveoli to form oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) 2. Carbon dioxide is carried primarily in the plasma of the blood in the form of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) ...
10-The Adrenal gland- Aldosterone 01-02-2016
... hyperplasia (CAH) are any of several autosomal recessive diseases resulting from mutations of genes for enzymes mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol from cholesterol by the adrenal glands (steroidogenesis). ...
... hyperplasia (CAH) are any of several autosomal recessive diseases resulting from mutations of genes for enzymes mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol from cholesterol by the adrenal glands (steroidogenesis). ...
Gas Exchange - Mrs. Feigenbaum`s Science Classes
... Gases move from high to low concentration. As O2 is used up inside organism, more diffuses in. When excess CO2 is formed inside, it diffuses out. More gases can diffuse if the respiratory surface is greater (meaning: a greater surface area) Small organisms (protists, hydra) can exchange gases direct ...
... Gases move from high to low concentration. As O2 is used up inside organism, more diffuses in. When excess CO2 is formed inside, it diffuses out. More gases can diffuse if the respiratory surface is greater (meaning: a greater surface area) Small organisms (protists, hydra) can exchange gases direct ...
Heart Dissection Introduction Mammals have four
... 1. Place a heart in a dissecting pan & rinse off with tap water. Pat the heart dry with paper towels. 2. Examine the heart to look for the thin membrane or pericardium that covers the heart. The pericardium may not be present if the butcher has removed it. The pericardium or pericardial sac, is a do ...
... 1. Place a heart in a dissecting pan & rinse off with tap water. Pat the heart dry with paper towels. 2. Examine the heart to look for the thin membrane or pericardium that covers the heart. The pericardium may not be present if the butcher has removed it. The pericardium or pericardial sac, is a do ...
Chapter 14—Respiratory System. I. The Respiratory System. a
... 1. Cortical influences allow conscious control of respiration that may be needed to avoid inhaling noxious gasses or water. 2. Breath holding is limited by the overriding stimuli of increased [H+] and [CO2] on the inspiratory area. 3. Levels of CO2 (especially) and oxygen (to a much lesser degree) i ...
... 1. Cortical influences allow conscious control of respiration that may be needed to avoid inhaling noxious gasses or water. 2. Breath holding is limited by the overriding stimuli of increased [H+] and [CO2] on the inspiratory area. 3. Levels of CO2 (especially) and oxygen (to a much lesser degree) i ...
Phylum Arthropoda
... striated strong muscle contractions – fast, active movements - muscle strength to body weight ratio of flea greater than that of humans! ...
... striated strong muscle contractions – fast, active movements - muscle strength to body weight ratio of flea greater than that of humans! ...
the respiratory system
... -reflex arcs initiated by stretch receptors in the lungs also play a role in respiration by notifying neural centers of excessive over inflation 2) PHYSICAL FACTOR: -increase body temperature, exercise, speech, singing And non-respiratory air movements modify both rate and depth of breathing 3) VOLI ...
... -reflex arcs initiated by stretch receptors in the lungs also play a role in respiration by notifying neural centers of excessive over inflation 2) PHYSICAL FACTOR: -increase body temperature, exercise, speech, singing And non-respiratory air movements modify both rate and depth of breathing 3) VOLI ...
CH1
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
MOLLUSCS
... • 31. Many gastropods have a single shell for protection. They are able to retreat inside when threatened. They may also have a rigid part of the foot called an operculum that closes like a door and seals them inside. ...
... • 31. Many gastropods have a single shell for protection. They are able to retreat inside when threatened. They may also have a rigid part of the foot called an operculum that closes like a door and seals them inside. ...
CO 2 - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... 4. MOIST: They are very moist and this helps gas exchange. 5. VERY RICH BLOOD SUPPLY: They have a close association with many blood capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged efficiently. 6. LINED WITH A LAYER OF LIPOPROTEINS (surfactant) on their inner surface. This helps to maintain ...
... 4. MOIST: They are very moist and this helps gas exchange. 5. VERY RICH BLOOD SUPPLY: They have a close association with many blood capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged efficiently. 6. LINED WITH A LAYER OF LIPOPROTEINS (surfactant) on their inner surface. This helps to maintain ...
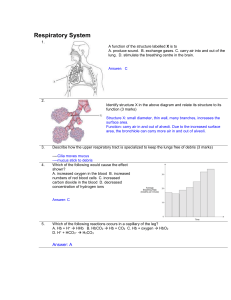
Respiratory System
... What is the relationship between the following terms as they related to respiratory function? a) medulla oblongata and diaphragm (2 marks) medulla oblongata send message to diaphragm that whether it should contract via the phrenic nerve b) intercostal muscles and inspiration (2 marks) intercostals m ...
... What is the relationship between the following terms as they related to respiratory function? a) medulla oblongata and diaphragm (2 marks) medulla oblongata send message to diaphragm that whether it should contract via the phrenic nerve b) intercostal muscles and inspiration (2 marks) intercostals m ...
The Respiratory System - Cal State LA
... – The diaphragm moves downward – The pressure around the lungs decreases – And air is drawn into the respiratory tract ...
... – The diaphragm moves downward – The pressure around the lungs decreases – And air is drawn into the respiratory tract ...
NEWS - Aniwell Veterinary Clinic
... virus multiplies on the skin of affected rabbits, causing puffy swellings of the eyes, usually leading to blindness. Affected rabbits become very ill, often suffering from pneumonia and sadly most will die over a period of 10-14 days. Viral Haemorrhagic Disease is another highly contagious and very ...
... virus multiplies on the skin of affected rabbits, causing puffy swellings of the eyes, usually leading to blindness. Affected rabbits become very ill, often suffering from pneumonia and sadly most will die over a period of 10-14 days. Viral Haemorrhagic Disease is another highly contagious and very ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.