SIMULATED FROG DISSECTION KIT SIMULATED FROG
... together and finding out what the relationships are between them. When people cut a dead animal’s body apart in a scientific way we say that they are “dissecting” it. Your frog model can show you exactly what is going on inside a frog. You can see how all the organs and body parts relate to each oth ...
... together and finding out what the relationships are between them. When people cut a dead animal’s body apart in a scientific way we say that they are “dissecting” it. Your frog model can show you exactly what is going on inside a frog. You can see how all the organs and body parts relate to each oth ...
What Is a Mollusk?
... Snails secrete mucus along the base of the foot, and then move over surfaces using a rippling motion of the foot. The octopus draws water into the mantle cavity and then forces the water out through a siphon. Water leaving the body propels the octopus in the opposite direction. ...
... Snails secrete mucus along the base of the foot, and then move over surfaces using a rippling motion of the foot. The octopus draws water into the mantle cavity and then forces the water out through a siphon. Water leaving the body propels the octopus in the opposite direction. ...
11) VENTILATION AND ENDURANCE PERFORMANCE Do our
... expanding its volume causes air to rush into the lungs to fill the relative vacuum. When we inspire air, we do so by contracting the diaphragm, pulling it down (similar to pulling up on the plunger). If you are breathing "correctly" at rest, the main movement you will notice is your stomach bulging ...
... expanding its volume causes air to rush into the lungs to fill the relative vacuum. When we inspire air, we do so by contracting the diaphragm, pulling it down (similar to pulling up on the plunger). If you are breathing "correctly" at rest, the main movement you will notice is your stomach bulging ...
CHAPTER 2: The respiratory system
... • Within the human body gases such as O2 and CO2 move from high concentrations to lower concentrations due to the differences in partial pressure of these gases. 3) Which one of the following has the greatest stimulating effect on the respiratory centres in the brain? a. oxygen. b. carbon dioxide ...
... • Within the human body gases such as O2 and CO2 move from high concentrations to lower concentrations due to the differences in partial pressure of these gases. 3) Which one of the following has the greatest stimulating effect on the respiratory centres in the brain? a. oxygen. b. carbon dioxide ...
NAME: CLASS:______ Fetal Pig Dissection Pigs are placental
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
ch24b_wcr
... Absorptive State: Hormonal Control • Absorptive state primarily controlled by insulin • Insulin secretion stimulated by – Elevated blood levels of glucose and amino acids – Intestinal GIP and parasympathetic stimulation ...
... Absorptive State: Hormonal Control • Absorptive state primarily controlled by insulin • Insulin secretion stimulated by – Elevated blood levels of glucose and amino acids – Intestinal GIP and parasympathetic stimulation ...
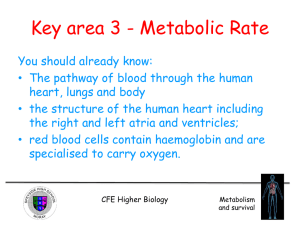
Unit 2 Key Area 3 - Metabolic Rate
... Also, the smaller animals have a greater surface area to volume ratio, so more heat is lost CFE Higher Biology ...
... Also, the smaller animals have a greater surface area to volume ratio, so more heat is lost CFE Higher Biology ...
The Respiratory System
... between air and blood occurs. 2. The effect on gas exchange when the respiratory membrane becomes thicker; an example is pulmonary edema. 3. The effect on gas exchange when the surface area of the respiratory membrane decreases; an example is emphysema. 4. The pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture ...
... between air and blood occurs. 2. The effect on gas exchange when the respiratory membrane becomes thicker; an example is pulmonary edema. 3. The effect on gas exchange when the surface area of the respiratory membrane decreases; an example is emphysema. 4. The pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture ...
The Human Body
... 84. Smooth muscle: An involuntary muscle found in walls of internal organs such as the stomach, intestine, bladder and blood vessels (excluding the heart). 85. Spinal cord: The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves in the peripheral nervous system 86. Stirrup - (als ...
... 84. Smooth muscle: An involuntary muscle found in walls of internal organs such as the stomach, intestine, bladder and blood vessels (excluding the heart). 85. Spinal cord: The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves in the peripheral nervous system 86. Stirrup - (als ...
Digestive System
... Animal Structures and Function Animals are composed of a variety of interdependent systems No one system can function entirely on its own In order to keep animals healthy, producers make sure that all systems function properly. ...
... Animal Structures and Function Animals are composed of a variety of interdependent systems No one system can function entirely on its own In order to keep animals healthy, producers make sure that all systems function properly. ...
Adventitious Breath Sounds Apnea
... • excessive increases in blood hematocrit raise the viscosity of the blood, in turn reducing cardiac output • excessive reductions in blood hematocrit (e.g. anemia) reduces O2 transport 3. Exercise • well-trained athletes can have up to 20 times the normal rate for O2 transport, partly due to increa ...
... • excessive increases in blood hematocrit raise the viscosity of the blood, in turn reducing cardiac output • excessive reductions in blood hematocrit (e.g. anemia) reduces O2 transport 3. Exercise • well-trained athletes can have up to 20 times the normal rate for O2 transport, partly due to increa ...
Science TAKS Students
... 2. Compare mechanical digestion to chemical digestion, and where most of each occurs. 3. Explain enzymes and give an example. 4. Discuss the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain their function. 5. Describe the function of villi and explain h ...
... 2. Compare mechanical digestion to chemical digestion, and where most of each occurs. 3. Explain enzymes and give an example. 4. Discuss the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain their function. 5. Describe the function of villi and explain h ...
respiratory system
... ventilatory process. On the other hand, pulmonary diseases that decrease the pulmonary compliance, or that increases airway resistance, or that increase the viscosity of the lung or chest wall can at times increase the work of breathing up to ...
... ventilatory process. On the other hand, pulmonary diseases that decrease the pulmonary compliance, or that increases airway resistance, or that increase the viscosity of the lung or chest wall can at times increase the work of breathing up to ...
COURSE
... objective. All items have been written to match the cognitive process of the remember verb in the objective. Questions require students to recall terms or words related to job seeking and keeping. These exact questions will not be used on the secured test, but questions in similar formats will be us ...
... objective. All items have been written to match the cognitive process of the remember verb in the objective. Questions require students to recall terms or words related to job seeking and keeping. These exact questions will not be used on the secured test, but questions in similar formats will be us ...
Turtle parts
... Coiled tubules where tails are added to sperm __________________________ epididymis ...
... Coiled tubules where tails are added to sperm __________________________ epididymis ...
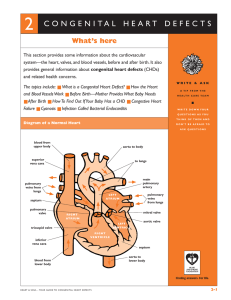
Congenital Heart Defects
... get undressed, and that the doctor will need to touch some areas on your child’s body, (such as the chest or groin) and that you will be there during the physical assessment. Gowns are available for older children. Parents may be present for infants and young children. Youth may prefer to go in by t ...
... get undressed, and that the doctor will need to touch some areas on your child’s body, (such as the chest or groin) and that you will be there during the physical assessment. Gowns are available for older children. Parents may be present for infants and young children. Youth may prefer to go in by t ...
BHS Anatomy and Physiology
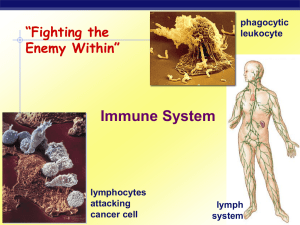
... and swollen. The inflamed nodes, called buboes (from which the disease gets its name), swell with pus to about the size of a chicken's egg. They soon turn black, split open, and ooze pus and blood onto the skin. The infection, rampant in the lymphatic system, quickly spreads throughout the body. Blo ...
... and swollen. The inflamed nodes, called buboes (from which the disease gets its name), swell with pus to about the size of a chicken's egg. They soon turn black, split open, and ooze pus and blood onto the skin. The infection, rampant in the lymphatic system, quickly spreads throughout the body. Blo ...
Human Body Systems - local
... Estrous: in mammals like cats and dogs, no blood, when it happens the female is in heat, hormones controlled by ovaries, feedback controlled by steroids in the ovaries Menstrual: in mammals like humans and some primates, monthly bleeding cycle, female can receive male at any time, hormones contr ...
... Estrous: in mammals like cats and dogs, no blood, when it happens the female is in heat, hormones controlled by ovaries, feedback controlled by steroids in the ovaries Menstrual: in mammals like humans and some primates, monthly bleeding cycle, female can receive male at any time, hormones contr ...
Chapter 8: Circulation
... nerve cells in the walls of some arteries sense changes in blood pressure. When pressure is higher or lower than normal, messages are sent to your brain by these nerve cells. Then messages are sent by your brain to raise or lower blood pressure—by speeding up or slowing the heart rate for example. T ...
... nerve cells in the walls of some arteries sense changes in blood pressure. When pressure is higher or lower than normal, messages are sent to your brain by these nerve cells. Then messages are sent by your brain to raise or lower blood pressure—by speeding up or slowing the heart rate for example. T ...
Animal Science - Lehi FFA
... Animal Structures and Function Animals are composed of a variety of interdependent systems No one system can function entirely on its own In order to keep animals healthy, producers make sure that all systems function properly. ...
... Animal Structures and Function Animals are composed of a variety of interdependent systems No one system can function entirely on its own In order to keep animals healthy, producers make sure that all systems function properly. ...
Regents Biology - I Heart Science
... Viruses enter body cells, hijack their organelles, and turn the cell into a virus making-factory. The cell will eventually burst, releasing thousands of viruses to infect new cells. ...
... Viruses enter body cells, hijack their organelles, and turn the cell into a virus making-factory. The cell will eventually burst, releasing thousands of viruses to infect new cells. ...
Now! - ambition classes
... Statement - 1 : Ear muscles of external ear in man are poorly developed. Statement - 2 : These muscles are useful which move external ear freely to detect sound efficiently. ...
... Statement - 1 : Ear muscles of external ear in man are poorly developed. Statement - 2 : These muscles are useful which move external ear freely to detect sound efficiently. ...
Pig Dissection - Milton
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
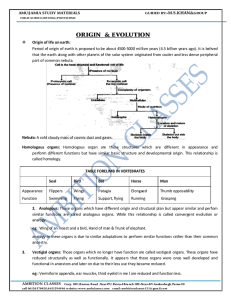
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.