AB Balance Lecture 1_2015
... An acid load, is associated with the uptake of excess H+ ions by bone which occurs in exchange for surface Na+ and K+ and by the dissolution of bone mineral, resulting in the release of buffer compounds, such as NaHCO3, CaHCO3, and CaHPO4. 40% of an acute acid load BONES ...
... An acid load, is associated with the uptake of excess H+ ions by bone which occurs in exchange for surface Na+ and K+ and by the dissolution of bone mineral, resulting in the release of buffer compounds, such as NaHCO3, CaHCO3, and CaHPO4. 40% of an acute acid load BONES ...
Lymphatic System - American Academy
... Warmup 10/31 Describe (without notes) using all the vocabulary words, the passageway air takes to get into the lungs…. (at least 8 vocab words) ...
... Warmup 10/31 Describe (without notes) using all the vocabulary words, the passageway air takes to get into the lungs…. (at least 8 vocab words) ...
- The Wonderful Hormone - INSULIN - UCO
... genetically altered bacteria was approved for use with insulin dependent patient – This form of insulin is an exact match to that which is made in the body ...
... genetically altered bacteria was approved for use with insulin dependent patient – This form of insulin is an exact match to that which is made in the body ...
Higher Biology - Unit 1 Cell Biology
... State that gas exchange takes place in the alveoli. Explain how the alveoli allow efficient gas exchange. Identify and name the organs of the digestive system. State that food moves along the digestive system by peristalsis. Describe the process of peristalsis. Describe the structure and function of ...
... State that gas exchange takes place in the alveoli. Explain how the alveoli allow efficient gas exchange. Identify and name the organs of the digestive system. State that food moves along the digestive system by peristalsis. Describe the process of peristalsis. Describe the structure and function of ...
Herpetology 483/583
... 74. What happens in the distal tubule? 75. How do aldosterone and vasopressin (ADH) work together to maintain fluid volume in the body? 76. How are the loop of Henle and collecting duct each involved in creating and maintaining the osmotic gradient that becomes more osmotic in the medial part of the ...
... 74. What happens in the distal tubule? 75. How do aldosterone and vasopressin (ADH) work together to maintain fluid volume in the body? 76. How are the loop of Henle and collecting duct each involved in creating and maintaining the osmotic gradient that becomes more osmotic in the medial part of the ...
Introduction to Anatomy, Chapter 1
... • Dorsal: Relating to the back side of the body; toward the back. Used synonymously with posterior in human anatomy. Ex: The vertebrae are dorsal to the heart. • Medial: Toward or at the midline of the body. Ex: The ulna is medial to the radius. • Lateral: Away from the midline of the body. Ex: The ...
... • Dorsal: Relating to the back side of the body; toward the back. Used synonymously with posterior in human anatomy. Ex: The vertebrae are dorsal to the heart. • Medial: Toward or at the midline of the body. Ex: The ulna is medial to the radius. • Lateral: Away from the midline of the body. Ex: The ...
Human Body
... 2a. Students know many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. 2b. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, ...
... 2a. Students know many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. 2b. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, ...
Document
... Dissection and examination of a pig heart 1 Identify the left and right sides, the dorsal and ventral sides, and the major blood vessels of a pig heart. ...
... Dissection and examination of a pig heart 1 Identify the left and right sides, the dorsal and ventral sides, and the major blood vessels of a pig heart. ...
NSC 104 - National Open University of Nigeria
... To be provided for each module by the facilitator in addition to the ones already spelt out in the course materials. SPECIFIC READING ASSIGNMENTS To be provided for each module COURSE OVERVIEW Human Physiology (I) Physiology is the scientific study of how the body works under normal conditions or in ...
... To be provided for each module by the facilitator in addition to the ones already spelt out in the course materials. SPECIFIC READING ASSIGNMENTS To be provided for each module COURSE OVERVIEW Human Physiology (I) Physiology is the scientific study of how the body works under normal conditions or in ...
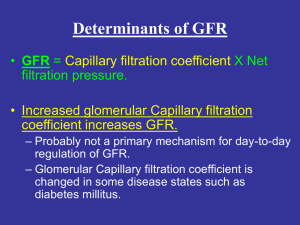
Determinants of GFR - BHS116.3 Physiology III
... Determinants of GFR • GFR = Capillary filtration coefficient X Net filtration pressure. • Increased hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule decreases GFR (inverse is also true). – Normally, not a primary mechanism for day-to-day regulation of GFR. – Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule can cha ...
... Determinants of GFR • GFR = Capillary filtration coefficient X Net filtration pressure. • Increased hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule decreases GFR (inverse is also true). – Normally, not a primary mechanism for day-to-day regulation of GFR. – Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule can cha ...
What Is the Purpose of the Embryonic Heart Beat? or How Facts Can
... That the unfailing beat of the heart is necessary for life is one of the few dogmas that enjoys equal popularity among both cardiovascular physiologists and the lay public. The convective flow of blood through the circulation provides the ceaseless transport of the respiratory gases and nutrients re ...
... That the unfailing beat of the heart is necessary for life is one of the few dogmas that enjoys equal popularity among both cardiovascular physiologists and the lay public. The convective flow of blood through the circulation provides the ceaseless transport of the respiratory gases and nutrients re ...
FREE Sample Here
... Body fluids are contained in two compartments. The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment contains the largest amount of water in the body and consists of all of the water and ions within the cells. The extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment contains the body fluids remaining outside the cells: either ...
... Body fluids are contained in two compartments. The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment contains the largest amount of water in the body and consists of all of the water and ions within the cells. The extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment contains the body fluids remaining outside the cells: either ...
ppt
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid
... Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to th ...
... Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to th ...
slide_6
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
2 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
... Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. because there is not enough time for heart to fill ...
SCF Class 2
... has alkaline enzymes, acids in the stomach that produces a semisolid liquid called chyme and alkaline and acid enzymes in the intestines. *If we don’t have enough acid, hydrochloric acid, in the stomach to dissolve the food before we eat, our body will produce it later in the intestines. This is one ...
... has alkaline enzymes, acids in the stomach that produces a semisolid liquid called chyme and alkaline and acid enzymes in the intestines. *If we don’t have enough acid, hydrochloric acid, in the stomach to dissolve the food before we eat, our body will produce it later in the intestines. This is one ...
Chapter 42 PowerPoint
... • Fluid, called lymph, reenters the circulation directly at the venous end of the capillary bed and indirectly through the lymphatic system • The lymphatic system drains into veins in the neck • Lymph nodes are organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body’s defense • Edema is swel ...
... • Fluid, called lymph, reenters the circulation directly at the venous end of the capillary bed and indirectly through the lymphatic system • The lymphatic system drains into veins in the neck • Lymph nodes are organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body’s defense • Edema is swel ...
Document
... the heart is not formed until after metamorphosis. The larva does not feed but swims around for some hours, during which time it is at first positively phototactic(趋光性) and negatively geotactic but later becomes negatively phototatic and positively geotactic. By its adhesive papi1lae it now fastens ...
... the heart is not formed until after metamorphosis. The larva does not feed but swims around for some hours, during which time it is at first positively phototactic(趋光性) and negatively geotactic but later becomes negatively phototatic and positively geotactic. By its adhesive papi1lae it now fastens ...
Reading Part 2: The Respiratory System
... The respiratory system—gas exchange Oxygen doesn’t dissolve well in water. It must be carried in red blood cells by the ...
... The respiratory system—gas exchange Oxygen doesn’t dissolve well in water. It must be carried in red blood cells by the ...
Gaseous Exchange in Animals
... to search for food and escape predators. As a result they need a large amount of oxygen and they release a large amount of carbon dioxide. ...
... to search for food and escape predators. As a result they need a large amount of oxygen and they release a large amount of carbon dioxide. ...
Lec 09 - Structure-Circulatory System
... acids, proteins, organic acids and other compounds. pH is usually acidic (6.7). Density is 1.01 to 1.06. Water content is 84-92 per cent. Inorganic ions present are `Na' in predators and parasites, `Mg' and `K'in phytophagous insects. Carbohydrate is in the form of trehalose sugar. Major proteins ar ...
... acids, proteins, organic acids and other compounds. pH is usually acidic (6.7). Density is 1.01 to 1.06. Water content is 84-92 per cent. Inorganic ions present are `Na' in predators and parasites, `Mg' and `K'in phytophagous insects. Carbohydrate is in the form of trehalose sugar. Major proteins ar ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.