AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... Animal cells require O2 for aerobic respiration. If cells are not directly exposed to the outside environment, then some mechanism must provide gas exchange to internal cells—delivering O2 and removing waste CO2. ...
... Animal cells require O2 for aerobic respiration. If cells are not directly exposed to the outside environment, then some mechanism must provide gas exchange to internal cells—delivering O2 and removing waste CO2. ...
Urinary System - Department of Zoology, UBC
... Henle resorb more fluid and salt => the filtrate flow and the osmolarity in the tubule will be low => the macula densa cells are inhibited from releasing the vasoconstrictive substance => afferent arteriole will dilate => increase in net filtration and GFR ...
... Henle resorb more fluid and salt => the filtrate flow and the osmolarity in the tubule will be low => the macula densa cells are inhibited from releasing the vasoconstrictive substance => afferent arteriole will dilate => increase in net filtration and GFR ...
circulatory system
... 1. Function: to break down food into forms the cells can use for energy 2. The parts of the digestive system where food actually enters: Mouth to Esophagus to Stomach to Small Intestine to Large Intestine to Anus 3. The parts of the digestive system where food does not enter: Liver, Gall Bladder and ...
... 1. Function: to break down food into forms the cells can use for energy 2. The parts of the digestive system where food actually enters: Mouth to Esophagus to Stomach to Small Intestine to Large Intestine to Anus 3. The parts of the digestive system where food does not enter: Liver, Gall Bladder and ...
blood cells - School
... As urea is toxic, it must be removed from the body as quickly as possible! The blood now has to help the body do this. ...
... As urea is toxic, it must be removed from the body as quickly as possible! The blood now has to help the body do this. ...
Mix and Match Human Body Systems
... Protection of organs, movement, support, muscle attachment, breathing, making blood cells, sound transmission and growth ...
... Protection of organs, movement, support, muscle attachment, breathing, making blood cells, sound transmission and growth ...
Circulatory System of a Mammal
... lungs 2. Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart 3. Carries deoxygenated blood away from the liver 4. The first main blood vessel that an oxygen molecule reaches after being absorbed from an alveolus 5. Has the highest blood pressure ...
... lungs 2. Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart 3. Carries deoxygenated blood away from the liver 4. The first main blood vessel that an oxygen molecule reaches after being absorbed from an alveolus 5. Has the highest blood pressure ...
3 - Suffolk County Community College
... b) cells that remove water from the air c) a counter current mechanism to extract oxygen d) a trachea connecting directly to the alveoli 10. Air flows in only one direction through the lungs of which animals? a) frogs b) birds c) mammals d) insects 11. Human respiration rate is usually regulated by: ...
... b) cells that remove water from the air c) a counter current mechanism to extract oxygen d) a trachea connecting directly to the alveoli 10. Air flows in only one direction through the lungs of which animals? a) frogs b) birds c) mammals d) insects 11. Human respiration rate is usually regulated by: ...
THE STRUCTURE OF THE BODY Cells Tissue Organs Systems The
... Bones, joints. Provides a rigid framework which supports the body. 2. THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Muscles, tendons. Moves limbs and drives blood around the body. 3. THE SKIN SYSTEM Skin, nails, hair. Provides a barrier that protects the body and control temperature. 4. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain, spinal cord, ...
... Bones, joints. Provides a rigid framework which supports the body. 2. THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Muscles, tendons. Moves limbs and drives blood around the body. 3. THE SKIN SYSTEM Skin, nails, hair. Provides a barrier that protects the body and control temperature. 4. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain, spinal cord, ...
mechanisms assist it with gas exchange
... Blood distributes oxygen around body cells (via haemoglobin) and collects carbon dioxide from cells to return to the gills Blood is contained within a closed circulatory system Diffusion occurs in very thin walled blood vessels (capillaries) ...
... Blood distributes oxygen around body cells (via haemoglobin) and collects carbon dioxide from cells to return to the gills Blood is contained within a closed circulatory system Diffusion occurs in very thin walled blood vessels (capillaries) ...
Tissues in the lungs
... Explain the meaning of the terms single and double circulatory systems with reference to the circulatory systems of fish and animals. Large animal transport systems All living cells need a supply of oxygen and nutrients to survive. They also need to remove waste products to prevent their build up ...
... Explain the meaning of the terms single and double circulatory systems with reference to the circulatory systems of fish and animals. Large animal transport systems All living cells need a supply of oxygen and nutrients to survive. They also need to remove waste products to prevent their build up ...
O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 - Cloudfront.net
... • blood gets O2 from lungs • drops off CO2 to lungs • brings O2-rich blood from lungs to heart – Circulation to body (systemic) • pumps O2-rich blood to body • picks up nutrients from digestive ...
... • blood gets O2 from lungs • drops off CO2 to lungs • brings O2-rich blood from lungs to heart – Circulation to body (systemic) • pumps O2-rich blood to body • picks up nutrients from digestive ...
1. Blood a. Fluid connective tissue i. Consists of cells suspended in
... a. Hemocytoblast divides and differentiates. Its nucleus and organelles are discarded while Hb stores are built up to tremendous levels. b. Requires iron and vitamin B12. RBC levels a. # of RBCs in blood is remarkably constant and maintained via negative feedback. b. Too few RBCs compromises O2 tran ...
... a. Hemocytoblast divides and differentiates. Its nucleus and organelles are discarded while Hb stores are built up to tremendous levels. b. Requires iron and vitamin B12. RBC levels a. # of RBCs in blood is remarkably constant and maintained via negative feedback. b. Too few RBCs compromises O2 tran ...
Body Systems
... •Organic nutrients include carbohydrates, fats, proteins or amino acids, and vitamins. Inorganic chemical compounds such as minerals; water and oxygen may also be considered nutrients. •A nutrient is essential to an organism if it cannot be synthesized by the organism in sufficient quantities and mu ...
... •Organic nutrients include carbohydrates, fats, proteins or amino acids, and vitamins. Inorganic chemical compounds such as minerals; water and oxygen may also be considered nutrients. •A nutrient is essential to an organism if it cannot be synthesized by the organism in sufficient quantities and mu ...
Lesson Smoking Fact File
... it. However carbon monoxide also links to haemoglobin but doesn’t let it go. If a red blood cell becomes full of carbon monoxide it cannot carry oxygen. This makes the blood of smokers less efficient, this is why smokers get breathless when they run. They are not very good at getting oxygen to thei ...
... it. However carbon monoxide also links to haemoglobin but doesn’t let it go. If a red blood cell becomes full of carbon monoxide it cannot carry oxygen. This makes the blood of smokers less efficient, this is why smokers get breathless when they run. They are not very good at getting oxygen to thei ...
Physiology of blood. Erythrocytes.Respiratory pigments. Blood types
... metabolic diseases (congenital and acquired porphyria, etc.) It may be the reserve pigments, which give the tissue oxygen in a small oxygen condition. ...
... metabolic diseases (congenital and acquired porphyria, etc.) It may be the reserve pigments, which give the tissue oxygen in a small oxygen condition. ...
Word Bank: diaphragm capillaries oxygen ATP alveoli blood CO 2
... IX. Interactions between body systems A) The different systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis. For example: 1. Nutrients from the __________system are transported to cells by the __________system. 2. Wastes from the ________system are removed by the _________system. 3. The _______ ...
... IX. Interactions between body systems A) The different systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis. For example: 1. Nutrients from the __________system are transported to cells by the __________system. 2. Wastes from the ________system are removed by the _________system. 3. The _______ ...
human body systems
... Functions: to get rid of wastes and toxins that could damage systems and to regulate the fluid levels in the body. example: kidneys filter blood and then send to bladder to be expelled from the body Urine can be tested for many diseases (diabetes, kidney disease or heart failure) Diseases of this sy ...
... Functions: to get rid of wastes and toxins that could damage systems and to regulate the fluid levels in the body. example: kidneys filter blood and then send to bladder to be expelled from the body Urine can be tested for many diseases (diabetes, kidney disease or heart failure) Diseases of this sy ...
Standard 4
... through the body. ________________ carry blood away from the heart to the body’s cells. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ connect arteries and veins and are the blood vessels where oxygen and nutrients diffuse into cells. ...
... through the body. ________________ carry blood away from the heart to the body’s cells. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ connect arteries and veins and are the blood vessels where oxygen and nutrients diffuse into cells. ...
3.2 Organ Systems - SCIENCE WITH MR Z
... Arteries carry blood from the heart to all body parts. Veins carry blood from body parts back to the heart. Capillaries are extremely small, allow oxygen to diffuse from blood into cells, ...
... Arteries carry blood from the heart to all body parts. Veins carry blood from body parts back to the heart. Capillaries are extremely small, allow oxygen to diffuse from blood into cells, ...
EXCRETION
... In the course of the biochemical activities of the cell, nutrients are oxidized, releasing energy for life processes and producing numerous new substances. Some of these materials are useful, but others, if allowed to accumulate, are poisonous and interfere with normal metabolic reactions. Excretion ...
... In the course of the biochemical activities of the cell, nutrients are oxidized, releasing energy for life processes and producing numerous new substances. Some of these materials are useful, but others, if allowed to accumulate, are poisonous and interfere with normal metabolic reactions. Excretion ...
Blood
... 12. For each of the following structures, indicate its function in the fetus. Circle the blood vessel that carries the most oxygenrich blood. ...
... 12. For each of the following structures, indicate its function in the fetus. Circle the blood vessel that carries the most oxygenrich blood. ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint
... Lymph node: an organ that filters lymph and that is found along the lymphatic vessels. Small and bean shaped. Contain lymphocytes (also called killer t cells) surround and destroy pathogens. Other lymphocytes are called B cells (produce antibodies that attaches to pathogens—serve as markers. Swollen ...
... Lymph node: an organ that filters lymph and that is found along the lymphatic vessels. Small and bean shaped. Contain lymphocytes (also called killer t cells) surround and destroy pathogens. Other lymphocytes are called B cells (produce antibodies that attaches to pathogens—serve as markers. Swollen ...
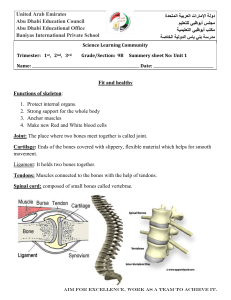
Abu Dhabi Education Council - baniyas international private school
... Strong support for the whole body Anchor muscles Make new Red and White blood cells ...
... Strong support for the whole body Anchor muscles Make new Red and White blood cells ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.