* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
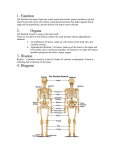
STANDARD 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central Concepts: The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. STANDARD 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central Concepts: The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.1 Explain generally how the digestive system converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules Parts of the Digestive System in order that food moves through them: 4.1 Explain generally how the digestive system converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules Parts of the Digestive System in order that food moves through them: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ In the ___________________, food is (1)mechanically digested using teeth and (2)carbohydrates are chemically digested using enzymes. In the ___________________, food is (1)mechanically digested using teeth and (2)carbohydrates are chemically digested using enzymes. ______________________ moves food from the mouth to the stomach. ______________________ moves food from the mouth to the stomach. ______________________ (1) uses muscles to mechanically digest and mix food and (2) enzymes to chemically digest proteins. ______________________ (1) uses muscles to mechanically digest and mix food and (2) enzymes to chemically digest proteins. ______________________ absorbs nutrients through tiny structures called villi. ______________________ absorbs nutrients through tiny structures called villi. _______________________ uses enzymes to complete chemical digestion of all carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. _______________________ uses enzymes to complete chemical digestion of all carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. ______________________ absorbs water. Undigested food waste passes through the _______ and _________before leaving the body. ______________________ absorbs water. Undigested food waste passes through the _______ and _________before leaving the body. 4.2 Explain how the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes cell wastes. 4.2 Explain how the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes cell wastes. ______________ has 4 chambers and pumps blood through the body. ________________ carry blood away from the heart to the body’s cells. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ connect arteries and veins and are the blood vessels where oxygen and nutrients diffuse into cells. ______________ has 4 chambers and pumps blood through the body. ________________ carry blood away from the heart to the body’s cells. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ connect arteries and veins and are the blood vessels where oxygen and nutrients diffuse into cells. **Kidney (rinones) and liver (higado) filter and clean the blood.** **Kidney (rinones) and liver (higado) filter and clean the blood.** 4.3 Explain how the respiratory system provides exchange of O2 and CO2. 4.3 Explain how the respiratory system provides exchange of O2 and CO2. WORD BANK: oxygen, carbon dioxide, mouth, nose, lungs, alveoli, blood, gas exchange WORD BANK: oxygen, carbon dioxide, mouth, nose, lungs, alveoli, blood, gas exchange 1. Air is inhaled through the ____________ and ______________. 2. Air passes moves down the trachea towards the _____________. 3. The bronchi brings the air to the left and right lungs. 4. At the end of the bronchi, tiny balloon-like structures called _______________ fill with air. 5. _____________ from inhaled air diffuses from the __________into the ___________. ___________________ from the blood diffuses into the alveoli, which will be exhaled. This is the process of ____________________. 4.4 Explain how the nervous system mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION 1. Air is inhaled through the ____________ and ______________. 2. Air passes moves down the trachea towards the _____________. 3. The bronchi brings the air to the left and right lungs. 4. At the end of the bronchi, tiny balloon-like structures called _______________ fill with air. 5. _____________ from inhaled air diffuses from the __________into the ___________. ___________________ from the blood diffuses into the alveoli, which will be exhaled. This is the process of ____________________. 4.4 Explain how the nervous system mediates communication among different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION Brain Brain Spinal cord Neuron Sensory neuron Motor neuron Neurotransmitters -Transmits impulse to the muscles -Cells that are the basic unit of the nervous system used to transmit electrical impulses -Central processing center -Connects the brain to the other nerves in body -Sense changes in the environment and transmit signal to spinal cord and brain -Chemicals used to transmit impulse between neurons Spinal cord Neuron Sensory neuron Motor neuron Neurotransmitters -Transmits impulse to the muscles -Cells that are the basic unit of the nervous system used to transmit electrical impulses -Central processing center -Connects the brain to the other nerves in body -Sense changes in the environment and transmit signal to spinal cord and brain -Chemicals used to transmit impulse between neurons 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system works to allow for movement. MUSCULOSKELTAL SYSTEM FUNCTION 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system works to allow for movement. MUSCULOSKELTAL SYSTEM FUNCTION Skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscles Bones Tendons Cartilage Ligaments Skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscles Bones Tendons Cartilage Ligaments -Provide support to body, produce red blood cells -Connects muscle to bones -Connects bone to bone -Soft, flexible cushion at joints between the bones -Types of muscles -Provide support to body, produce red blood cells -Connects muscle to bones -Connects bone to bone -Soft, flexible cushion at joints between the bones -Types of muscles **Muscular/Skeletal system purpose is to support the body and allow movement** **Red blood cells are produced in the bones (huesos).** **Muscles are connected to bones using tendons. When muscles contract, they pull on bones, causing them to move.** **Muscular/Skeletal system purpose is to support the body and allow movement** **Red blood cells are produced in the bones (huesos).** **Muscles are connected to bones using tendons. When muscles contract, they pull on bones, causing them to move.** 4.8 Recognize that the body’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. **Homeostasis: maintenance of constant internal conditions; matenimiento de condiciones internas constants Example: breathing faster during exercise to get more oxygen to cells** 4.8 Recognize that the body’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. **Homeostasis: maintenance of constant internal conditions; matenimiento de condiciones internas constants Example: breathing faster during exercise to get more oxygen to cells**