Overview of Lecture: Circulation, gas exchange Read: Text. 34
... each cell is in direct contact w/ external environment & diffusion to and from the membrane is adequate Diffusion is inefficient over distances of more than a few millimeters;; diffusion time is proportional to the square of the distance: if it takes ~1 se ...
... each cell is in direct contact w/ external environment & diffusion to and from the membrane is adequate Diffusion is inefficient over distances of more than a few millimeters;; diffusion time is proportional to the square of the distance: if it takes ~1 se ...
To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document.
... pulmonary veins left atrium Atrium contracts: blood bicuspid valve left ventricle ...
... pulmonary veins left atrium Atrium contracts: blood bicuspid valve left ventricle ...
Homeostasis
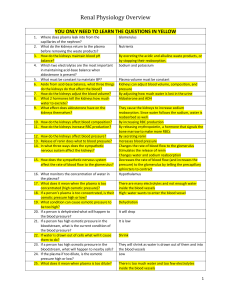
... • released when the solute concentration of the blood rises • makes the transport epithelium of the distal tubules and the collecting ducts more permeable to water • alcohol inhibits production of ADH Hormonal control of the kidney by negative feedback circuits ...
... • released when the solute concentration of the blood rises • makes the transport epithelium of the distal tubules and the collecting ducts more permeable to water • alcohol inhibits production of ADH Hormonal control of the kidney by negative feedback circuits ...
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... bone marrow to make more RBCs By secreting renin Increases blood pressure Changes the rate of blood flow to the glomerulus Stimulates the release of renin Changes water and sodium reabsorption Decreases the rate of blood flow (and increases the pressure) to the glomerulus by telling the precapillary ...
... bone marrow to make more RBCs By secreting renin Increases blood pressure Changes the rate of blood flow to the glomerulus Stimulates the release of renin Changes water and sodium reabsorption Decreases the rate of blood flow (and increases the pressure) to the glomerulus by telling the precapillary ...
Circulatory_Orange
... and one cell thick which permits exchanges of material between the contents of the capillary and the surrounding tissue. Red blood cells go through one at a time. ...
... and one cell thick which permits exchanges of material between the contents of the capillary and the surrounding tissue. Red blood cells go through one at a time. ...
cells
... • The sugar (glucose) is transported to the cells in the plasma of the blood through arteries that branch into capillaries where the sugar enters the cell. ...
... • The sugar (glucose) is transported to the cells in the plasma of the blood through arteries that branch into capillaries where the sugar enters the cell. ...
chapter 16 review game
... Occurs when the body cannot properly use the insulin it produces. Usually occurs in people that are overweight an don’t get enough exercise. ...
... Occurs when the body cannot properly use the insulin it produces. Usually occurs in people that are overweight an don’t get enough exercise. ...
the excretory system
... substances such as ions, water, glucose, and amino acids, easily pass through capillary walls. Large substances, such as proteins and blood cells, cannot pass through. Reabsorption- as the filtrate moves through the proximal convoluted tubule, some materials are reabsorbed. The small solutes, such a ...
... substances such as ions, water, glucose, and amino acids, easily pass through capillary walls. Large substances, such as proteins and blood cells, cannot pass through. Reabsorption- as the filtrate moves through the proximal convoluted tubule, some materials are reabsorbed. The small solutes, such a ...
Maintaining Homeostasis
... – It works in response to a change that counteracts another change. – Its output response that affects the initial input feedback decreases its effect – Works like a household thermostat: it can shut off the original stimulus, or reduces its intensity – Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms ...
... – It works in response to a change that counteracts another change. – Its output response that affects the initial input feedback decreases its effect – Works like a household thermostat: it can shut off the original stimulus, or reduces its intensity – Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms ...
Respiratory System
... Chronic bronchitis- Bronchial tubes get irritated and too much mucus is produced. The more the person coughs the more the cilia can be damaged and they are unable to move mucus, dirt and other particles. This occurs from smoking. Emphysema- The aveoli lose their ability to expand and contract. Bronc ...
... Chronic bronchitis- Bronchial tubes get irritated and too much mucus is produced. The more the person coughs the more the cilia can be damaged and they are unable to move mucus, dirt and other particles. This occurs from smoking. Emphysema- The aveoli lose their ability to expand and contract. Bronc ...
Document
... Spiracle: small opening located along the side of the body through which air enters and leaves the body Book lung: organ that has layers of respiratory tissue stacked like the pages of a book: used to exchange gases ...
... Spiracle: small opening located along the side of the body through which air enters and leaves the body Book lung: organ that has layers of respiratory tissue stacked like the pages of a book: used to exchange gases ...
body systems - lderewal
... Bodily fluid that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Made up of 4 components… ...
... Bodily fluid that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Made up of 4 components… ...
The Excretory System
... glycogen and transforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other animals. 3. The esophagus runs through the diaphragm and moves food from the mouth to the stomach. It is distinguished from the trachea by its lack of cartilage rings. ...
... glycogen and transforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other animals. 3. The esophagus runs through the diaphragm and moves food from the mouth to the stomach. It is distinguished from the trachea by its lack of cartilage rings. ...
TAKS Objective 2 (Blitz) The Human Body System
... the body can use. The nutrients are delivered to the blood stream through the the small intestines. • Mouth (tongue teeth, salivary glands), pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine • Accessory organs: liver, gall bladder, pancreas ...
... the body can use. The nutrients are delivered to the blood stream through the the small intestines. • Mouth (tongue teeth, salivary glands), pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine • Accessory organs: liver, gall bladder, pancreas ...
Cardiovascular System - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... blood cells mature. Some of these white blood cells stay in the lymphatic system where they attack invading pathogens. ...
... blood cells mature. Some of these white blood cells stay in the lymphatic system where they attack invading pathogens. ...
Circulation File
... tubes or pipes (arteries, capillaries, veins) • vertebrate circulation as closed circulation ...
... tubes or pipes (arteries, capillaries, veins) • vertebrate circulation as closed circulation ...
Year 11 Physiological Responses to Exercise - PE
... - e.g. The heart gets stronger and larger, resting and exercise heart rate decrease ...
... - e.g. The heart gets stronger and larger, resting and exercise heart rate decrease ...
Unit 3 powerpoint chapters 11 through 13
... – One muscle in the pair contracts to move the bone in one direction. – Then, the other muscle in the pair contracts to move the bone back ...
... – One muscle in the pair contracts to move the bone in one direction. – Then, the other muscle in the pair contracts to move the bone back ...
Human Body Study Guide (Key)
... 13) Which systems are involved in sending urine out of the body? Urinary or excretory and the muscular System 14) All organisms have one or more ________. cells 15) Which system regulates sugar levels in the blood? Endocrine System 16) What process helps lower or bring down a high body temperature? ...
... 13) Which systems are involved in sending urine out of the body? Urinary or excretory and the muscular System 14) All organisms have one or more ________. cells 15) Which system regulates sugar levels in the blood? Endocrine System 16) What process helps lower or bring down a high body temperature? ...
Amphibians and Mammals
... 2. Beetles, bees, and flies have a larval stage in their development in which the young organisms look very different than their adult counterparts. These insects then enter a pupal stage where marked changes in body form take place after which an adult emerges. This type of development is ...
... 2. Beetles, bees, and flies have a larval stage in their development in which the young organisms look very different than their adult counterparts. These insects then enter a pupal stage where marked changes in body form take place after which an adult emerges. This type of development is ...
MLS 211 Master Syllabus
... -Describe the circulatory pattern of CSF. -Identify the major components of the reflex arc and their function. -Classify the types of reflex arc according to development, response, processing site, and complexity of circuit. -Given a diagram of a spinal reflex arc, be able to determine its classifi ...
... -Describe the circulatory pattern of CSF. -Identify the major components of the reflex arc and their function. -Classify the types of reflex arc according to development, response, processing site, and complexity of circuit. -Given a diagram of a spinal reflex arc, be able to determine its classifi ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.