* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
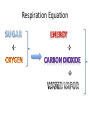
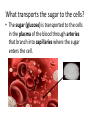
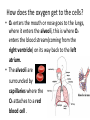
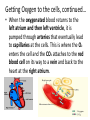
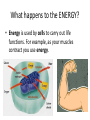
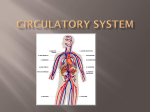
Cellular Respiration Respiration Equation How does the food get to the cells? How does this food…. Get here? Cells How does the oxygen (O2) get to the cells? How does the oxygen O2 get from here … to here? Cells What happens to the energy? How do we use the energy? Cells Cells Cells How does the carbon dioxide (CO2) get out of our body? Out here? How does the CO2 get from here….. Cells How does the water vapor (waste) get out of our body? How does the water vapor (waste) get from here….. Out here? Cells Remember the equation for cellular respiration! • It requires all 3 body systems for this to occur! Glucose + Oxygen ENERGY + Carbon Dioxide + Water Vapor • Occurs in all cells • Recall how each system contributes to each part of the equation. How does the sugar get to the cells? • Carbohydrates get broken down in the mouth to sugars by saliva (glucose comes from this). • Nutrients are absorbed in the small intestines through the villi and they go to the blood stream through capillaries. What transports the sugar to the cells? • The sugar (glucose) is transported to the cells in the plasma of the blood through arteries that branch into capillaries where the sugar enters the cell. How does the oxygen get to the cells? • O2 enters the mouth or nose goes to the lungs, where it enters the alveoli, this is where O2 enters the blood stream(coming from the right ventricle) on its way back to the left atrium. • The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries where the O2 attaches to a red blood cell . Getting Oxygen to the cells, continued… • When the oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium and then left ventricle, it is pumped through arteries that eventually lead to capillaries at the cells. This is where the O2 enters the cell and the CO2 attaches to the red blood cell on its way to a vein and back to the heart at the right atrium. Now how does the carbon dioxide and water vapor get out of the body? • As the capillaries branch back into veins the CO2 on the red blood cell and the water vapor return to the right atrium, then right ventricle which pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the alveoli the CO2 and water vapor leave the capillary and enter the alveoli, they are exhaled. What happens to the ENERGY? • Energy is used by cells to carry out life functions. For example, as your muscles contract you use energy.