* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TAKS Objective 2 (Blitz) The Human Body System
Survey
Document related concepts
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
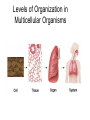
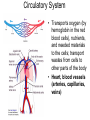
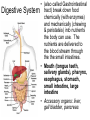
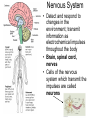
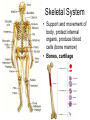
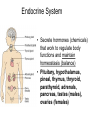
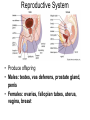
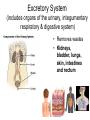
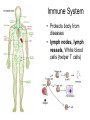
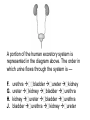
TAKS Objective 2 The Human Body System th (11 Grade Blitz) Levels of Organization in Multicellular Organisms Circulatory System • Transports oxygen (by hemoglobin in the red blood cells), nutrients, and needed materials to the cells; transport wastes from cells to other parts of the body • Heart, blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, veins) Circulatory System interacting with other systems Digestive Nervous Skeletal Endocrine Blood carries digested nutrients to body cells. The brain stem controls heart rate. Bone marrow produces blood cells, Blood carries hormones throughout the body. Reproductive Nutrients diffuse through the placenta and are carried to the embryo through blood vessels in the umbilical cord. Integumentary Platelets in the blood help close small cuts in the skin, Immune White blood cells attack pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Excretory Waste products are filtered from the blood in the kidneys. Muscular The heart is largely composed of muscle tissue. Respiratory Oxygen moves from the lungs to the blood, and carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the lungs. Digestive • (also called Gastrointestinal System tract) break down food chemically (with enzymes) and mechanically (chewing & peristalsis) into nutrients the body can use. The nutrients are delivered to the blood stream through the the small intestines. • Mouth (tongue teeth, salivary glands), pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine • Accessory organs: liver, gall bladder, pancreas Nervous System • Detect and respond to changes in the environment; transmit information as electrochemical impulses throughout the body • Brain, spinal cord, nerves • Cells of the nervous system which transmit the impulses are called neurons Skeletal System • Support and movement of body, protect internal organs, produce blood cells (bone marrow) • Bones, cartilage Endocrine System • Secrete hormones (chemicals) that work to regulate body functions and maintain homeostasis (balance) • Pituitary, hypothalamus, pineal, thymus, thryroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, testes (males), ovaries (females) Reproductive System • Produce offspring • Males: testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, penis • Females: ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, breast Integumentary System • Provide barrier between body and external environment; help maintain homeostasis • Skin, hair, nails Respiratory System Gas exchange (CO2 with O2) • Brings oxygen into the body and eliminates and carbon dioxide (gas exchange) between body and external environment. • The gases travels through the blood stream • Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, diaphragm Respiratory System interacting with other systems Digestive The pharynx serves as a passageway for both air and food. Nervous The brain stem regulates breathing. Skeletal The rib cage expands to help move air into the lungs. Endocrine Hormones can contribute to asthma attacks. Reproductive Breathing rate increases to provide the extra oxygen needed during labor. Integumentary Cells lining the nostrils produce mucus that keeps the nearby tissue from drying out Immune Mucus lining the respiratory passages helps trap pathogens. Excretory The respiratory system removes the waste gas carbon dioxide from the body. Muscular Contraction of the diaphragm helps move air into the lungs. Muscular System • Move body and pump blood throughout the body • Heart and other muscles of the body Pairs of opposing muscles work together to move bones and joints. (i.e. When the bicep muscle contracts, the triceps muscle relaxes and vice versa). Muscular System interacting with other systems Digestive Muscles churn the stomach to aid in digestion. Nervous Signals travel down the spinal cord to the muscles. Skeletal Endocrine Reproductive Integumentary The contraction and relaxation of skeletal muscles moves bones. Hormones cause males to put on more muscle mass during puberty. Muscle contractions in the uterus push the fetus out during labor. Muscles raise the hair on the arms and legs to help retain heat. Immune Sneezing involves involuntary muscle contractions. Excretory Muscle contractions are involved in emptying the urinary bladder. Respiratory Breathing rate increases during exercise to help meet the increased oxygen demand by skeletal muscles. Excretory System (includes organs of the urinary, integumentary respiratory & digestive system) • Removes wastes • Kidneys, bladder, lungs, skin, intestines and rectum Immune System • Protects body from diseases • lymph nodes, lymph vessels, White blood cells (helper T cells) Let’s try some practice questions! A portion of the human excretory system is represented in the diagram above. The order in which urine flows through the system is — F. G. H. J. urethra bladder ureter kidney ureter kidney bladder urethra kidney ureter bladder urethra bladder urethra kidney ureter Which body system is directly responsible for delivering nutrients to cells throughout the body? A. B. C. D. Circulatory system Integumentary system Endocrine system Respiratory system Red marrow is the principal tissue that produces red blood cells in humans. In which body system is red marrow found? F. Integumentary system G. Respiratory system H. Nervous system J. Skeletal system The diagram represents a human arm. Which structure is most responsible for moving the arm to a straighter position? A. B. C. D. Tendons of origin Biceps Radius Triceps Food is digested in the gastrointestinal tract to provide nutrients to the body. In addition, various hormones secreted from the lining of a few digestive organs allow other organs to function properly. According to this information, some organs of the gastrointestinal tract — A. B. C. D. fit in more than one organ system perform only one function at a time supply the body with platelets produce soluble vitamins In the diagram above, one cell creates and releases chemicals that travel to a second cell and quickly induce that cell into action. This diagram represents part of the — A. endocrine system B. skeletal system C. muscular system D. nervous system Hemoglobin carries oxygen to body cells. Which body system contains hemoglobin? A. Circulatory system B. Respiratory system C. Endocrine system D. Nervous system Nutrients from digested food move from the digestive system directly into the — A. B. C. D. circulatory system integumentary system excretory system endocrine system When a person is frightened by a wild animal, some organ systems immediately become active, while others are suppressed. Which of these systems is likely to be suppressed? F. G. H. J. Muscular system Respiratory system Endocrine system Digestive system How is the circulatory system related to the digestive system? F The brain stem controls the heart rate. G Blood carries nutrients to body cells. H Stomach muscles contract and expand. J The pharynx is a passageway for air and food. How is the excretory system most likely to respond when an animal is thirsty? F. G. H. J. By relaxing the smooth muscles By retaining body fluids By absorbing heat from lymph glands By releasing hormones Because chewing begins the breakdown of food before it is swallowed, digestion starts in the mouth and throat. Which of the following systems aids most in this early stage of digestion? A. B. C. D. Immune system Excretory system Muscular system Respiratory system