Body System QR Code
... Connected to almost all other systems. Works very closely with the respiratory system and the immune system. ...
... Connected to almost all other systems. Works very closely with the respiratory system and the immune system. ...
CHAP 21a - Dr. Gerry Cronin
... • For example, during emergencies, the autonomic nervous system will vasodilate the precapillary sphincters of metarterioles in the skeletal muscles, lungs, and brain, while constricting the precapillary sphincters found in tissues such as the skin, GI tract, and kidneys. • This sends the majority o ...
... • For example, during emergencies, the autonomic nervous system will vasodilate the precapillary sphincters of metarterioles in the skeletal muscles, lungs, and brain, while constricting the precapillary sphincters found in tissues such as the skin, GI tract, and kidneys. • This sends the majority o ...
WHS Rat Review PPT
... 6. Toward the belly (underside of body) Ventral 7. Closest to the point of attachment Proximal 8. Toward the head Cranial ...
... 6. Toward the belly (underside of body) Ventral 7. Closest to the point of attachment Proximal 8. Toward the head Cranial ...
Ch. 42 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... homeostatic mechanisms reflect continuity due to common ancestry and/or divergence due to adaptation in different environments. LO 2.27 The student is able to connect differences in the environment with the evolution of homeostatic mechanisms. LO 4.8 The student is able to evaluate scientific questi ...
... homeostatic mechanisms reflect continuity due to common ancestry and/or divergence due to adaptation in different environments. LO 2.27 The student is able to connect differences in the environment with the evolution of homeostatic mechanisms. LO 4.8 The student is able to evaluate scientific questi ...
The Lymphatic System A. 1.
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
Internal Environment
... core body temperature blood glucose concentration water levels in body tissues ph (hydrogen ion concentration) ions, such as sodium, calcium and chloride ions blood oxygen concentration carbon dioxide concentration blood volume blood pressure ...
... core body temperature blood glucose concentration water levels in body tissues ph (hydrogen ion concentration) ions, such as sodium, calcium and chloride ions blood oxygen concentration carbon dioxide concentration blood volume blood pressure ...
excretion hand outs – urinary system
... Each kidney is composed of about a million nephrons. A nephron is the filtering unit of the kidney. At the end, most of the water, sugar, vitamins and salts have been reabsorbed ...
... Each kidney is composed of about a million nephrons. A nephron is the filtering unit of the kidney. At the end, most of the water, sugar, vitamins and salts have been reabsorbed ...
Cardiovascular _ Respiratory Systems Ch_ 16
... The heart and the brain are perhaps the most important organs in your body The heart is made of the myocardium which is what makes it pump Your heart rate increases or decreases automatically based on your physical activity ...
... The heart and the brain are perhaps the most important organs in your body The heart is made of the myocardium which is what makes it pump Your heart rate increases or decreases automatically based on your physical activity ...
human body systems- thesis
... Purpose: to remove infectious diseases and other pathogens from the human body Major Organs and Their Functions Skin – also called the integumentary system, the skin is the body’s first line of defense White Blood Cells – recognize disease agents (antigens) and create antibodies to tag and remove th ...
... Purpose: to remove infectious diseases and other pathogens from the human body Major Organs and Their Functions Skin – also called the integumentary system, the skin is the body’s first line of defense White Blood Cells – recognize disease agents (antigens) and create antibodies to tag and remove th ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... g) proximal - nearest the point of attachment h) distal - farthest from point of attachment i) superficial – close to the surface j) deep – more internal ...
... g) proximal - nearest the point of attachment h) distal - farthest from point of attachment i) superficial – close to the surface j) deep – more internal ...
脊椎动物的结构与机能
... EXCRETION AND HOMEOSTASIS • kidney function • The kidneys of man and other vertebrates play a critical role in the body's economy. As vital organs their failure means death, in this respect they are neither more nor 1ess important than are the heart, lungs, or liver. The kidney is part of many inte ...
... EXCRETION AND HOMEOSTASIS • kidney function • The kidneys of man and other vertebrates play a critical role in the body's economy. As vital organs their failure means death, in this respect they are neither more nor 1ess important than are the heart, lungs, or liver. The kidney is part of many inte ...
1030ExamIV
... C. The wrong VSU student ID! D. Only the printed number, no bubbles! E. My VSU student ID, printed and bubbled in Extra Credit — you’ve been asking for this all semester long! This is the only absolutely fair way that I could think of to do this, since most everybody is here taking this test, and yo ...
... C. The wrong VSU student ID! D. Only the printed number, no bubbles! E. My VSU student ID, printed and bubbled in Extra Credit — you’ve been asking for this all semester long! This is the only absolutely fair way that I could think of to do this, since most everybody is here taking this test, and yo ...
B Natural Vitamins Article
... produce healthy red blood cells and prevent anemia. Folic acid helps prevent hair loss. Vitamin B12 – key role in normal functioning of the brain and nervous system and formation of blood. B12 increases the energy at the root Biotin – necessary for cell growth. Helpful in maintaining a steady blood ...
... produce healthy red blood cells and prevent anemia. Folic acid helps prevent hair loss. Vitamin B12 – key role in normal functioning of the brain and nervous system and formation of blood. B12 increases the energy at the root Biotin – necessary for cell growth. Helpful in maintaining a steady blood ...
Organization and Systems: Quiz Name: Organs
... 2. A group of similar cells working together forms _______________. 3. An organ system is formed by a group of similar _______________ working together. 4. A structure that allows for easy management of similar items refers to _______________. 5. The groups of organ systems working together to maint ...
... 2. A group of similar cells working together forms _______________. 3. An organ system is formed by a group of similar _______________ working together. 4. A structure that allows for easy management of similar items refers to _______________. 5. The groups of organ systems working together to maint ...
physiology - Western Springs College
... breakdown of ATP to make energy. These systems are dependent on the type of activity being performed. The 3 pathways are: - ATP-CP - Lactic Acid - Aerobic ...
... breakdown of ATP to make energy. These systems are dependent on the type of activity being performed. The 3 pathways are: - ATP-CP - Lactic Acid - Aerobic ...
respiration - Mrs. Towers` Website
... 30. The rate of breathing is chiefly dependent on chemical factors in the blood. Which of the following is not an important factor? a) O2 concentration b) Hemoglobin concentration c) CO2 concentration d) all of these 31. The rate of release of oxygen from oxyhemoglobin (HbO2 ----> Hb + O2) will incr ...
... 30. The rate of breathing is chiefly dependent on chemical factors in the blood. Which of the following is not an important factor? a) O2 concentration b) Hemoglobin concentration c) CO2 concentration d) all of these 31. The rate of release of oxygen from oxyhemoglobin (HbO2 ----> Hb + O2) will incr ...
What is the Circulatory System and What Does It Do? The circulatory
... cells floating in a fluid called plasma. Red blood cells possess a chemical called hemoglobin, which is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the individual cells of the body. Why do cells need oxygen? In return, the hemoglobin trades its oxygen for carbon dioxide, a waste product of the ...
... cells floating in a fluid called plasma. Red blood cells possess a chemical called hemoglobin, which is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the individual cells of the body. Why do cells need oxygen? In return, the hemoglobin trades its oxygen for carbon dioxide, a waste product of the ...
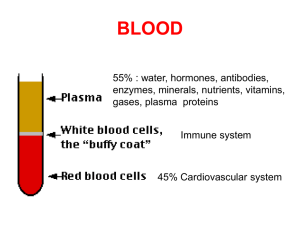
Chapter 17- Blood - El Camino College
... most numerous component of formed elements. These cells contain no nucleus or organelles, instead they are packed with hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a combination of proteins and iron molecules. Erythrocytes collect oxygen at the lungs and deliver it to the tissues then carry carbon dioxide back to the ...
... most numerous component of formed elements. These cells contain no nucleus or organelles, instead they are packed with hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a combination of proteins and iron molecules. Erythrocytes collect oxygen at the lungs and deliver it to the tissues then carry carbon dioxide back to the ...
Fellmann et al/Human Geography, 8/e
... tubes called blood vessels and is transported by a pump called the heart. All of the nutrients and oxygen that tissues need must be delivered directly to them by the blood vessels. Due to its efficiency, a closed circulatory system allows organisms to become larger. Annelids and all vertebrates are ...
... tubes called blood vessels and is transported by a pump called the heart. All of the nutrients and oxygen that tissues need must be delivered directly to them by the blood vessels. Due to its efficiency, a closed circulatory system allows organisms to become larger. Annelids and all vertebrates are ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.























