C. Organ Level
... are a type of high-energy radiation that passes readily through soft tissues. Computer tomography (CT) – the computer-assisted technique produces images of a series of thin cross sections through the body Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – takes advantage of the behavior of the hydrogen atoms in wat ...
... are a type of high-energy radiation that passes readily through soft tissues. Computer tomography (CT) – the computer-assisted technique produces images of a series of thin cross sections through the body Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – takes advantage of the behavior of the hydrogen atoms in wat ...
PowerPoint: Physiology Overview
... into the bloodstream 2. Regulates other structures (growth, reproduction, food use by cells, etc.) 3. Regulated by feedback controls that function to maintain homeostasis ...
... into the bloodstream 2. Regulates other structures (growth, reproduction, food use by cells, etc.) 3. Regulated by feedback controls that function to maintain homeostasis ...
I. Introduction to class - Cal State LA
... 1. Pulmonary circuit: Delivers blood to lungs. Oxygenation of blood. 2. Systemic circuit: Delivers oxygenated blood to tissues and organs of body (brain, liver, heart, ...
... 1. Pulmonary circuit: Delivers blood to lungs. Oxygenation of blood. 2. Systemic circuit: Delivers oxygenated blood to tissues and organs of body (brain, liver, heart, ...
2circulation
... blood cells are made inside your bones. You have more red blood cells than white blood cells. The red blood cells carry oxygen. The white blood cells help your body fight germs. You would be sick most of the time if you did not have white blood cells. Your blood pressure is the force of your blood a ...
... blood cells are made inside your bones. You have more red blood cells than white blood cells. The red blood cells carry oxygen. The white blood cells help your body fight germs. You would be sick most of the time if you did not have white blood cells. Your blood pressure is the force of your blood a ...
TRANSPORT
... Lymph is a fluid that bathes all the cells of the body. It is also called intracellular fluid. Lymph consists mainly of fluid that escapes from the blood through the walls of the capillaries. It is similar in composition to the blood plasma. The exchange of materials between the blood and the tissue ...
... Lymph is a fluid that bathes all the cells of the body. It is also called intracellular fluid. Lymph consists mainly of fluid that escapes from the blood through the walls of the capillaries. It is similar in composition to the blood plasma. The exchange of materials between the blood and the tissue ...
Overview
... Pulmonary circulation is the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart. Systemic circulation is the flow of blood to all the body tissues except the lungs. ...
... Pulmonary circulation is the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart. Systemic circulation is the flow of blood to all the body tissues except the lungs. ...
File
... “Man is the most insane species. He worships an invisible God and destroys a visible Nature. Unaware that this Nature he’s destroying is this God he’s worshipping.” ...
... “Man is the most insane species. He worships an invisible God and destroys a visible Nature. Unaware that this Nature he’s destroying is this God he’s worshipping.” ...
017_blood
... – Hemorrhage or increased RBC destruction reduces RBC numbers – Insufficient hemoglobin (e.g., iron deficiency) – Reduced availability of O2 (e.g., high altitudes) ...
... – Hemorrhage or increased RBC destruction reduces RBC numbers – Insufficient hemoglobin (e.g., iron deficiency) – Reduced availability of O2 (e.g., high altitudes) ...
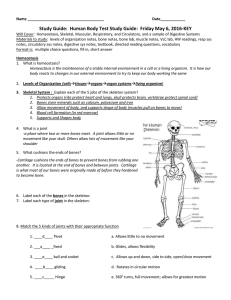
Homeostasis, Levels of Organization of Living Things, Skeletal
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment in a cell or a living organism. It is how our body reacts to changes in our external environment to try to keep our body working the same 2. Levels of Organization (cellstissuesorgansorgan systemsliving organism) 3. Skeletal System ...
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment in a cell or a living organism. It is how our body reacts to changes in our external environment to try to keep our body working the same 2. Levels of Organization (cellstissuesorgansorgan systemsliving organism) 3. Skeletal System ...
Type AB Blood
... volume. They are made from stem cells in bone marrow. • There are five types of leukocytes. Each is an important component of the immune system. If a germ or infection enters the body various forms of leucocytes go into action. • Neutrophils destroy foreign substances such as bacteria. The neutrophi ...
... volume. They are made from stem cells in bone marrow. • There are five types of leukocytes. Each is an important component of the immune system. If a germ or infection enters the body various forms of leucocytes go into action. • Neutrophils destroy foreign substances such as bacteria. The neutrophi ...
Homeostasis, Regulation, and Feedback Loops
... When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond: negative feedback or positive feedback In negative feedback, the body systems make adjustments to return the body back to normal after a disturbance. Because this tends to keep things constant, it allows us to ma ...
... When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond: negative feedback or positive feedback In negative feedback, the body systems make adjustments to return the body back to normal after a disturbance. Because this tends to keep things constant, it allows us to ma ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... higher than Everest pATM is _____________ Molecules are __________ closer together ...
... higher than Everest pATM is _____________ Molecules are __________ closer together ...
Human Body Systems
... show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
... show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
Human Body Systems - Hamilton Township High School
... show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
... show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
lect11-4cut
... rbc only 5-7 micrometers wide). Where most exchange of materials takes place – Every cell in body within 100 micrometers of a capillary! – 250,000 capillaries in area size of little fingernail ...
... rbc only 5-7 micrometers wide). Where most exchange of materials takes place – Every cell in body within 100 micrometers of a capillary! – 250,000 capillaries in area size of little fingernail ...
Final Exam Material Outline MS Word
... pressure. Cuff pressure is further reduced until no pulse is heard, indicating that blood is flowing continuously through the artery and that the pressure between the ventricular contractions is overcoming the cuff pressure. This is the lower reading: the diastolic pressure. The numbers are in milli ...
... pressure. Cuff pressure is further reduced until no pulse is heard, indicating that blood is flowing continuously through the artery and that the pressure between the ventricular contractions is overcoming the cuff pressure. This is the lower reading: the diastolic pressure. The numbers are in milli ...
Introduction to the Physiology Unit and Kingdom Protista
... C) Once the gas needed for cellular respiration enters the body, what system moves the gas throughout the organism so it can be distributed to all cells? ...
... C) Once the gas needed for cellular respiration enters the body, what system moves the gas throughout the organism so it can be distributed to all cells? ...
Body Systems - Phoenix Union High School District
... Respiratory System Facts… • Each of your lungs contains about 300 million balloon-like structures called alveoli, which replace the carbon-dioxide waste in your blood with oxygen. • Yawning is a result of your body not taking in enough oxygen from the air, which causes a shortage of oxygen in our b ...
... Respiratory System Facts… • Each of your lungs contains about 300 million balloon-like structures called alveoli, which replace the carbon-dioxide waste in your blood with oxygen. • Yawning is a result of your body not taking in enough oxygen from the air, which causes a shortage of oxygen in our b ...
Smoking - Noadswood Science
... blood, and remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood • Alveoli in the lungs are adapted to make gas exchange happen easily and efficiently: they cause the lungs to have a very large surface area; are moist with thin walls; and have many capillaries ...
... blood, and remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood • Alveoli in the lungs are adapted to make gas exchange happen easily and efficiently: they cause the lungs to have a very large surface area; are moist with thin walls; and have many capillaries ...
Jeopardy
... When you inhale your chest cavity expands, and an area of low blood pressure is created, when you exhale the chest cavity contracts and the pressure then increases. ...
... When you inhale your chest cavity expands, and an area of low blood pressure is created, when you exhale the chest cavity contracts and the pressure then increases. ...
Human Body Systems
... • Put your hands on your sides just slightly higher than your waist. • Take a few deep breaths • What physical changes do you feel during each breath? • What organs allow you to take deep breaths? ...
... • Put your hands on your sides just slightly higher than your waist. • Take a few deep breaths • What physical changes do you feel during each breath? • What organs allow you to take deep breaths? ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.