27.3 Circulation - BarkersBioChemSciences
... • A ventricle pumpso blood out of the heart to the rest of the body. Amphibian hearts usually have three chambers: two atria and one ventricle. • The left atrium receoives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. • The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body. • Both atria empty into the ventr ...
... • A ventricle pumpso blood out of the heart to the rest of the body. Amphibian hearts usually have three chambers: two atria and one ventricle. • The left atrium receoives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. • The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body. • Both atria empty into the ventr ...
File - The Official Website of Eliel Arrey
... e. None of the above, more information is needed. 43. A sphygmomanometers measure the gauge pressure in the systemic circulation, which is the pressure above atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg at sea level). At what component of the circulatory circuit would one expect to detect the largest drop in bloo ...
... e. None of the above, more information is needed. 43. A sphygmomanometers measure the gauge pressure in the systemic circulation, which is the pressure above atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg at sea level). At what component of the circulatory circuit would one expect to detect the largest drop in bloo ...
File
... body to the heart, where it enters the _____________________________. 2. The blood is pumped out of the right atrium into the __________________________. 3. Travels through the ___________________________ to the ___________________, where it picks up oxygen. 4. From the lungs, blood travels through ...
... body to the heart, where it enters the _____________________________. 2. The blood is pumped out of the right atrium into the __________________________. 3. Travels through the ___________________________ to the ___________________, where it picks up oxygen. 4. From the lungs, blood travels through ...
Class Notes
... – Short distance between air and blood – Complete involvement of air and blood – Walls of alveoli are elastic ...
... – Short distance between air and blood – Complete involvement of air and blood – Walls of alveoli are elastic ...
3.4.4 Lungs Breathing - Spanish Point Biology
... – Short distance between air and blood – Complete involvement of air and blood – Walls of alveoli are elastic ...
... – Short distance between air and blood – Complete involvement of air and blood – Walls of alveoli are elastic ...
Lecture 9
... Gas Exchange • All the complex multicellular critters use oxygen to produce ATP in mitochondria – So all cells need gas exchange for this ...
... Gas Exchange • All the complex multicellular critters use oxygen to produce ATP in mitochondria – So all cells need gas exchange for this ...
LC Biology Sample Paper 6 HL Solutions
... (i) Tissue Fluid is the fluid surrounding cells in a tissue. It is formed from fluid that leaks out of the capillaries at the arteriole and in the tissue. / It is also referred to as ECF, extra cellular fluid and helps to maintain / the osmotic balance of the cells of the tissue. (3) (3) Build up is ...
... (i) Tissue Fluid is the fluid surrounding cells in a tissue. It is formed from fluid that leaks out of the capillaries at the arteriole and in the tissue. / It is also referred to as ECF, extra cellular fluid and helps to maintain / the osmotic balance of the cells of the tissue. (3) (3) Build up is ...
Circulatory System
... Arteries (red) bring the blood towards the organ and veins (blue) carry blood out of the digestive system. o Blood flowing through the lungs picks up oxygen which is transported to the cells. Blood vessels (capillaries) surround the alveoli. o Carries wastes (ex. excess water) from body tissues ...
... Arteries (red) bring the blood towards the organ and veins (blue) carry blood out of the digestive system. o Blood flowing through the lungs picks up oxygen which is transported to the cells. Blood vessels (capillaries) surround the alveoli. o Carries wastes (ex. excess water) from body tissues ...
Homeostasis and feedback The Human Body
... levels in the blood, and system), brain (nervous (EPO) release of carbon dioxide system), kidneys (urinary into exhaled air from lungs, system) secretion of erythropoietin by kidneys to stimulate formation of red blood cells Homeostatic Processes ...
... levels in the blood, and system), brain (nervous (EPO) release of carbon dioxide system), kidneys (urinary into exhaled air from lungs, system) secretion of erythropoietin by kidneys to stimulate formation of red blood cells Homeostatic Processes ...
Chapter 18
... out of the body through a tube, the urethra. A chemical analysis of urine can be useful in detecting medical problems such as diabetes (urine will have glucose) or malfunctioning of kidney (urine will have protein). Kidneys also maintain homeostasis by regulating the amount of water in body. As urin ...
... out of the body through a tube, the urethra. A chemical analysis of urine can be useful in detecting medical problems such as diabetes (urine will have glucose) or malfunctioning of kidney (urine will have protein). Kidneys also maintain homeostasis by regulating the amount of water in body. As urin ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... – Moves from alveoli into blood. – Blood is almost completely saturated with oxygen when it leaves the capillary – P02 in blood decreases because of mixing with deoxygenated blood – Oxygen moves from tissue capillaries into the tissues ...
... – Moves from alveoli into blood. – Blood is almost completely saturated with oxygen when it leaves the capillary – P02 in blood decreases because of mixing with deoxygenated blood – Oxygen moves from tissue capillaries into the tissues ...
Notes - Academic Computer Center
... Several other factors enhance venous return to the right atrium. Gravity returns blood from the head and neck when upright but opposes return from the legs. Skeletal muscle pump = squeezing of veins by leg muscles that forces blood upwards. Respiratory pump = the effect on venous blood flow cr ...
... Several other factors enhance venous return to the right atrium. Gravity returns blood from the head and neck when upright but opposes return from the legs. Skeletal muscle pump = squeezing of veins by leg muscles that forces blood upwards. Respiratory pump = the effect on venous blood flow cr ...
Describe the function of red blood cells.
... drawn through a needle placed in a vein in one arm. Then a special machine separates the plasma (and often the platelets) from your blood sample. This process is called plasmapheresis. The remaining red blood cells and other blood components are then returned to your body, along with a little saline ...
... drawn through a needle placed in a vein in one arm. Then a special machine separates the plasma (and often the platelets) from your blood sample. This process is called plasmapheresis. The remaining red blood cells and other blood components are then returned to your body, along with a little saline ...
Nervous System - FreeConferenceCall.com
... Respiratory System The respiratory system brings air into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, trachea, and lungs. When you breathe in, air enters your nose or mouth and goes down a long tube called the trachea. The trachea branches into two bronchial tubes, or primary bronchi, ...
... Respiratory System The respiratory system brings air into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, trachea, and lungs. When you breathe in, air enters your nose or mouth and goes down a long tube called the trachea. The trachea branches into two bronchial tubes, or primary bronchi, ...
Body Systems
... Oxygen molecules loaded onto hemoglobin molecules in bloodstream Hemoglobin- protein molecules responsible for carrying oxygen in bloodstream Ambient air 21% oxygen This is inhaled during ventilation 5% oxygen is removed from air Respiration makes this oxygen replace CO2 in blood 16% of oxygen gas, ...
... Oxygen molecules loaded onto hemoglobin molecules in bloodstream Hemoglobin- protein molecules responsible for carrying oxygen in bloodstream Ambient air 21% oxygen This is inhaled during ventilation 5% oxygen is removed from air Respiration makes this oxygen replace CO2 in blood 16% of oxygen gas, ...
The Drug Recognition Expert (DRE)
... measuring the quantity of alcohol present in the blood system measuring the alcohol content in the breath ...
... measuring the quantity of alcohol present in the blood system measuring the alcohol content in the breath ...
- Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 2.Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells 3.White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) 4.Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) BrainPop Video - Blood ...
... 2.Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells 3.White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) 4.Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) BrainPop Video - Blood ...
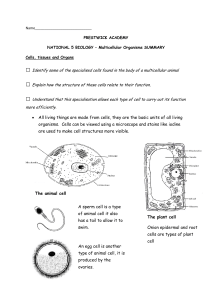
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... □ Name some of the diseases which could be cured by the use of stem cells □ Discuss some of the ethical issues associated with the use of stem cells in medical ...
... □ Name some of the diseases which could be cured by the use of stem cells □ Discuss some of the ethical issues associated with the use of stem cells in medical ...
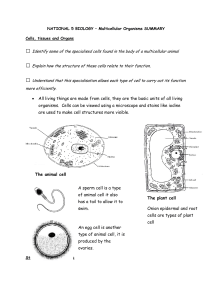
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... □ Name some of the diseases which could be cured by the use of stem cells □ Discuss some of the ethical issues associated with the use of stem cells in medical ...
... □ Name some of the diseases which could be cured by the use of stem cells □ Discuss some of the ethical issues associated with the use of stem cells in medical ...
Unit IV- Nervous System
... c. Bile - emulsify fats d. Pancreatic Juice - starches and proteins and fats ...
... c. Bile - emulsify fats d. Pancreatic Juice - starches and proteins and fats ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.