Worms and Mollusks
... • Siphon: tube-like structure through which water enters and leaves the body, capturing plankton in the process ...
... • Siphon: tube-like structure through which water enters and leaves the body, capturing plankton in the process ...
Chapter 20 – Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of aldosterone (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of aldosterone (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
Anatomy And Physiology Unit Exam
... Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Exam NAME: ______________________ ...
... Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Exam NAME: ______________________ ...
109 Maintenance 4-5
... • 2 mechanisms regulate the distribution of blood in capillary beds. 1) contraction of smooth muscle layer in the wall of an arteriole constricts the vessel, decreasing blood flow to a capillary bed. 2) rings of smooth muscles, precapillary sphincters, control the flow of blood between arterioles a ...
... • 2 mechanisms regulate the distribution of blood in capillary beds. 1) contraction of smooth muscle layer in the wall of an arteriole constricts the vessel, decreasing blood flow to a capillary bed. 2) rings of smooth muscles, precapillary sphincters, control the flow of blood between arterioles a ...
revised 10.2 notes - Trimble County Schools
... List and describe the functions of the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory system. Through the walls of which organ is most alcohol absorbed into the bloodstream? In what other organ does the remainder of the absorption occur? When the blood enters the lung region from the heart, what ar ...
... List and describe the functions of the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory system. Through the walls of which organ is most alcohol absorbed into the bloodstream? In what other organ does the remainder of the absorption occur? When the blood enters the lung region from the heart, what ar ...
Growth and Development Body Systems (19)
... Walt Disney: Walt was fired from the Kansas City newspaper for not being creative enough and was considered “slow” as a child. He is now considered one of the best known motion picture producers in the world, and holds the record for the most awards and most nominations. ...
... Walt Disney: Walt was fired from the Kansas City newspaper for not being creative enough and was considered “slow” as a child. He is now considered one of the best known motion picture producers in the world, and holds the record for the most awards and most nominations. ...
Frog Dissection Post Lab
... 4. What is the organ that is the first major site of chemical digestion? _________________________________ 5. What is the structure that eggs, sperm, urine and wastes all empty into? ____________________________ 6. The small intestine leads to the: __________________________________________________ ...
... 4. What is the organ that is the first major site of chemical digestion? _________________________________ 5. What is the structure that eggs, sperm, urine and wastes all empty into? ____________________________ 6. The small intestine leads to the: __________________________________________________ ...
The Respiratory System
... saturation of Hb. (this means that more oxygen is being carried by the blood.) ...
... saturation of Hb. (this means that more oxygen is being carried by the blood.) ...
Urinary System
... of the renal medulla, water flows freely out of the descending limb by osmosis until the tonicity of the filtrate and interstitium equilibrate. Longer descending limbs allow more time for water to flow out of the filtrate, so longer limbs make the filtrate more hypertonic than shorter limbs. Ascendi ...
... of the renal medulla, water flows freely out of the descending limb by osmosis until the tonicity of the filtrate and interstitium equilibrate. Longer descending limbs allow more time for water to flow out of the filtrate, so longer limbs make the filtrate more hypertonic than shorter limbs. Ascendi ...
Diaphragm (sheet of muscle)
... The intercostal muscles contract and cause the rib cage to move up and out. At the same time the diaphragm flattens downwards. The volume of the chest (thorax) increases, so air pressure drops. External air pressure is now higher than the pressure of air in the chest as a result more air is forc ...
... The intercostal muscles contract and cause the rib cage to move up and out. At the same time the diaphragm flattens downwards. The volume of the chest (thorax) increases, so air pressure drops. External air pressure is now higher than the pressure of air in the chest as a result more air is forc ...
Yr 9 Science Test Revision
... Test tube 3 had its pH increased to 8. rennin does not function at a high pH. It prefers an optimum pH of around 2, similar to the pH of the stomach. Q32. Give three features of the small intestine that makes it efficient in its role. A: it is 6-7m long; it has folds and villi, which serve to increa ...
... Test tube 3 had its pH increased to 8. rennin does not function at a high pH. It prefers an optimum pH of around 2, similar to the pH of the stomach. Q32. Give three features of the small intestine that makes it efficient in its role. A: it is 6-7m long; it has folds and villi, which serve to increa ...
Fast Facts - Social Circle City Schools
... Muscle tissue: - composed of long cells called muscle fibers that are capable of contracting when stimulated by nerve impulses - skeletal (striated) muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle ...
... Muscle tissue: - composed of long cells called muscle fibers that are capable of contracting when stimulated by nerve impulses - skeletal (striated) muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle ...
The Red Cell Volume Procedure - PPT
... Blood Volume • Blood volume is kept constant by cardiac output and atrial pressure decreasing if the blood volume is decreased. • This causes kidneys to retain fluid, this accumulation of fluid brings the blood volume back to normal. • The opposite happens if there is a blood increase causing it to ...
... Blood Volume • Blood volume is kept constant by cardiac output and atrial pressure decreasing if the blood volume is decreased. • This causes kidneys to retain fluid, this accumulation of fluid brings the blood volume back to normal. • The opposite happens if there is a blood increase causing it to ...
ex - Cloudfront.net
... • Contains a thermostat that responds to body temperature (high and low) • Activates mechanisms that promote heat gain or loss • Heat saving: vasoconstriction, raising fur, shivering • Body cooling: vasodilation, sweating, panting ...
... • Contains a thermostat that responds to body temperature (high and low) • Activates mechanisms that promote heat gain or loss • Heat saving: vasoconstriction, raising fur, shivering • Body cooling: vasodilation, sweating, panting ...
Some animals, such as insects, have an open circulatory system
... respiration need glucose and oxygen. Carbon dioxide and water are the waste products of respiration and need to be transported to the lungs so that they can be excreted. Blood is made from four components: Plasma - the liquid part of blood. It transports nutrients (e.g. glucose), amino acids, anti ...
... respiration need glucose and oxygen. Carbon dioxide and water are the waste products of respiration and need to be transported to the lungs so that they can be excreted. Blood is made from four components: Plasma - the liquid part of blood. It transports nutrients (e.g. glucose), amino acids, anti ...
PowerPoint Presentation - WKC Anatomy and Physiology
... Factors affecting blood pressure and flow Control of blood pressure and flow Circulatory routes ...
... Factors affecting blood pressure and flow Control of blood pressure and flow Circulatory routes ...
Heart workbook ANSWERS_Nyboer
... 13. Explain the differences in the strength of the pulse between the carotid artery (neck) and the brachial artery (wrist). Carotid: higher pressure, closer to the heart Brachial: lower pressure, farther from the heart 14. Explain the change in pulse after exercise. Blood is flowing faster and your ...
... 13. Explain the differences in the strength of the pulse between the carotid artery (neck) and the brachial artery (wrist). Carotid: higher pressure, closer to the heart Brachial: lower pressure, farther from the heart 14. Explain the change in pulse after exercise. Blood is flowing faster and your ...
marking scheme
... Geotropism enables roots to extend deeply in the soil for anchorage; (any one 1mk) 2 a) i) Optimum temperature for maximum enzyme activity; Temperature below optimum level inactivate the enzymes/ temperature above optimum level denatures enzymes; ii) Optimum PH for maximum enzyme activity; enzymes a ...
... Geotropism enables roots to extend deeply in the soil for anchorage; (any one 1mk) 2 a) i) Optimum temperature for maximum enzyme activity; Temperature below optimum level inactivate the enzymes/ temperature above optimum level denatures enzymes; ii) Optimum PH for maximum enzyme activity; enzymes a ...
Biology Chapter 27 (Worms and Mollusks)
... Also known as the segmented worms. The body is divided into separate body segments. Marine,fresh water,and on land. Parasitic and free-living. ex. ...
... Also known as the segmented worms. The body is divided into separate body segments. Marine,fresh water,and on land. Parasitic and free-living. ex. ...
Do turtles have teeth
... THE GALL BLADDER, a greenish colored sac found in the liver, stores BILE made by the LIVER. The PANCREAS is an elongated organ located in the first loop of intestine between the beginning of the small intestine and stomach. It secretes TRYPSIN that is used in the small intestine to break down protei ...
... THE GALL BLADDER, a greenish colored sac found in the liver, stores BILE made by the LIVER. The PANCREAS is an elongated organ located in the first loop of intestine between the beginning of the small intestine and stomach. It secretes TRYPSIN that is used in the small intestine to break down protei ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... • There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: • Nerve tissue—carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body • Muscle tissue (cardiac, smooth, skeletal)—contracts and shortens, making body parts move • Epithelial tissue—covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining and/or ...
... • There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: • Nerve tissue—carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body • Muscle tissue (cardiac, smooth, skeletal)—contracts and shortens, making body parts move • Epithelial tissue—covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining and/or ...
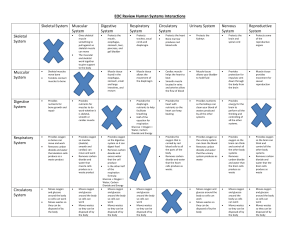
Practice Questions
... the anus, the respiratory releases carbon dioxide and the urinary system expels nitrogenous waste as urine. Remember the urinary system is also known as the excretory system. ...
... the anus, the respiratory releases carbon dioxide and the urinary system expels nitrogenous waste as urine. Remember the urinary system is also known as the excretory system. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.