Glossary of Terms used in the Pediatric Surgical Heart Unit
... Pulse oximeter………………..a machine that uses a light to measure the amount of oxygen the blood is carrying in the body (AKA pulse ox) Regurgitation………………….a condition in which blood leaks backwards into the heart through the valves that do not close completely (also called leakage or insufficiency) Ref ...
... Pulse oximeter………………..a machine that uses a light to measure the amount of oxygen the blood is carrying in the body (AKA pulse ox) Regurgitation………………….a condition in which blood leaks backwards into the heart through the valves that do not close completely (also called leakage or insufficiency) Ref ...
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
... to propel blood, breakdown food, excrete wastes, utilizing every internal organ in the body ...
... to propel blood, breakdown food, excrete wastes, utilizing every internal organ in the body ...
Vessels
... -When blood pressure rises in the right atrium, vasodilation occurs as usual, but CO is actually increased. Why is that? What else happens when the right atrium is stretched? ii. Chemoreceptors involved in blood flow regulation are located in the carotid bodies (near carotid sinuses) and aortic bodi ...
... -When blood pressure rises in the right atrium, vasodilation occurs as usual, but CO is actually increased. Why is that? What else happens when the right atrium is stretched? ii. Chemoreceptors involved in blood flow regulation are located in the carotid bodies (near carotid sinuses) and aortic bodi ...
Mindy
... communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment c. Students know how feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting ...
... communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment c. Students know how feedback loops in the nervous and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body d. Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting ...
INTRODUCTION • Minerals are inorganic nutrients. That is, they are
... Maintains fluid level within the cell. Necessary for transmitting nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Potassium: Sources ...
... Maintains fluid level within the cell. Necessary for transmitting nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Potassium: Sources ...
What is the peripheral circulation?
... • Veins: thinner walls, less elastic and smooth muscle tissue, increase in diameter and thickness as they approach the heart. ...
... • Veins: thinner walls, less elastic and smooth muscle tissue, increase in diameter and thickness as they approach the heart. ...
LE - 5 - Circulatory System
... Red blood cells Small round cells produced in bone marrow 5 liters of blood in body 5-6 million RBC in drop of human blood last 3-4 months (120 days) ...
... Red blood cells Small round cells produced in bone marrow 5 liters of blood in body 5-6 million RBC in drop of human blood last 3-4 months (120 days) ...
Circulatory system power point
... Red blood cells Small round cells produced in bone marrow 5 liters of blood in body 5-6 million RBC in drop of human blood last 3-4 months (120 days) ...
... Red blood cells Small round cells produced in bone marrow 5 liters of blood in body 5-6 million RBC in drop of human blood last 3-4 months (120 days) ...
The Circulatory System
... afflicted area is deprived of oxygen and nutrients which results in a variety of symptoms, like speech problems, or the inability to move an arm ...
... afflicted area is deprived of oxygen and nutrients which results in a variety of symptoms, like speech problems, or the inability to move an arm ...
Compiled Organ System Notes
... As blood begins to circulate, it leaves the heart from the left ventricle and goes into the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery in the body. The blood leaving the aorta is full of oxygen. This is important for the cells in the brain and the body to do their work. The oxygen rich blood travels th ...
... As blood begins to circulate, it leaves the heart from the left ventricle and goes into the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery in the body. The blood leaving the aorta is full of oxygen. This is important for the cells in the brain and the body to do their work. The oxygen rich blood travels th ...
Circulation and Gas Exchange Chapter 42 (all)
... • Every organism must exchange materials with its environment (whether it be nutrients or gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) – And this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level ...
... • Every organism must exchange materials with its environment (whether it be nutrients or gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) – And this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level ...
Organ system - Bibb County Schools
... environments and responds to changes (stimuli) – Control center – determines the set point at which the variable is maintained – Effector – provides the means to respond to the stimulus ...
... environments and responds to changes (stimuli) – Control center – determines the set point at which the variable is maintained – Effector – provides the means to respond to the stimulus ...
Homeostasis
... • protect itself against pathogens • regulate respiratory gases • maintain fluid and salt balance • regulate energy and nutrient supply • maintain a constant body temperature ...
... • protect itself against pathogens • regulate respiratory gases • maintain fluid and salt balance • regulate energy and nutrient supply • maintain a constant body temperature ...
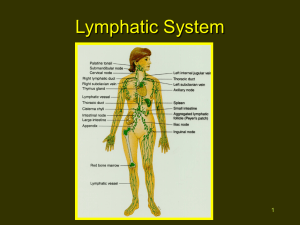
Lymphatic System
... – Thoracic duct into left subclavian vein – Right lymphatic duct into right subclavian vein ...
... – Thoracic duct into left subclavian vein – Right lymphatic duct into right subclavian vein ...
Powerpoint notes
... 1. Usually ________, along bones 2. This ___________ them from injury and temperature loss. Notes: 1. Walls can ___________ 2. Arteries have very __________________ 3. Expansion is the “___________” we feel ...
... 1. Usually ________, along bones 2. This ___________ them from injury and temperature loss. Notes: 1. Walls can ___________ 2. Arteries have very __________________ 3. Expansion is the “___________” we feel ...
RT Terminology - Respiratory Therapy Files
... • Lung volume Amount of gas in the lungs. The total volume of gas in the lungs is subdivided into compartments (volumes) and capacities (combinations of two or more volumes). Tidal volume (TV or VT) is the volume of air that enters the lungs during inspiration and leaves during expiration. Functiona ...
... • Lung volume Amount of gas in the lungs. The total volume of gas in the lungs is subdivided into compartments (volumes) and capacities (combinations of two or more volumes). Tidal volume (TV or VT) is the volume of air that enters the lungs during inspiration and leaves during expiration. Functiona ...
lab_110
... don’t worry about all of the arteries and veins that are in your manual – just those on the exit activity ...
... don’t worry about all of the arteries and veins that are in your manual – just those on the exit activity ...
Diffusion
... Breathing involves the exchange of gases in the lungs – a process that occurs by diffusion. What happens when you breathe in? Oxygen in inhaled air diffuses through the lungs and into the bloodstream. The oxygen is then transported throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by res ...
... Breathing involves the exchange of gases in the lungs – a process that occurs by diffusion. What happens when you breathe in? Oxygen in inhaled air diffuses through the lungs and into the bloodstream. The oxygen is then transported throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by res ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.