Presentation
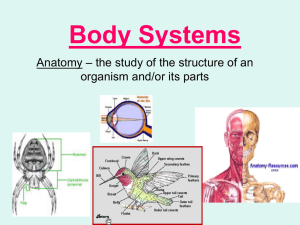
... Compare the structure and function of the four main kinds of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and ...
... Compare the structure and function of the four main kinds of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and ...
Ch21
... The relation between the oxygen carried in combination with hemoglobin and the PO2 of the blood can be described using the oxygen–hemoglobin __________ curve. ...
... The relation between the oxygen carried in combination with hemoglobin and the PO2 of the blood can be described using the oxygen–hemoglobin __________ curve. ...
CHORDATES & FISH
... nitrogen waste, and nutrients occurs __________________________________ Storage sac that holds urine waiting to be released __________________________________ Storage sac that holds gases obtained from the bloodstream that enables the fish to float or sink in the water ______________________________ ...
... nitrogen waste, and nutrients occurs __________________________________ Storage sac that holds urine waiting to be released __________________________________ Storage sac that holds gases obtained from the bloodstream that enables the fish to float or sink in the water ______________________________ ...
OSMOREGULATION
... in fish, several sex hormones also serve as pheromones - e.g. goldfish males respond to hormones released with ovulation ...
... in fish, several sex hormones also serve as pheromones - e.g. goldfish males respond to hormones released with ovulation ...
Regents Biology - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Diaphragm moves down & expands chest cavity pulls air into lungs ...
... Diaphragm moves down & expands chest cavity pulls air into lungs ...
Annexure `AAB-CD-01b` Course Title: ANATOMY AND
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
the nervous system
... collapsed veins, infection of the heart lining and valves, abscesses, cellulites, and liver disease. Pulmonary complications, including various types of pneumonia, may result from the poor health condition of the abuser, as well as from heroin's depressing effects on respiration. In addition to the ...
... collapsed veins, infection of the heart lining and valves, abscesses, cellulites, and liver disease. Pulmonary complications, including various types of pneumonia, may result from the poor health condition of the abuser, as well as from heroin's depressing effects on respiration. In addition to the ...
Nutrition- Powerpoint
... Small Intestine begins with the Duodenum Bile made by liver is stored in the gall bladder. Emulsify fats. Pancreas releases bicarbonate which neutralizes acidic chyme Pancreas adds many enzymes to the small intestine. ...
... Small Intestine begins with the Duodenum Bile made by liver is stored in the gall bladder. Emulsify fats. Pancreas releases bicarbonate which neutralizes acidic chyme Pancreas adds many enzymes to the small intestine. ...
How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation?
... • The circulatory system keeps blood pumping despite gravity’s pull – Muscle contractions help blood travel uphill in the veins of a giraffe’s long legs – The wriggling of the corn snake squeezes its veins and increases circulation ...
... • The circulatory system keeps blood pumping despite gravity’s pull – Muscle contractions help blood travel uphill in the veins of a giraffe’s long legs – The wriggling of the corn snake squeezes its veins and increases circulation ...
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... 2 A branch of biology that deals with the traits of all living things 4 A system of organs used in breathing 5 The passing on of genetic traits from parent to child 8 Structures in the lungs that pass oxygen into the blood 9 The tiny units that are the basic building blocks of living things 12 Organ ...
... 2 A branch of biology that deals with the traits of all living things 4 A system of organs used in breathing 5 The passing on of genetic traits from parent to child 8 Structures in the lungs that pass oxygen into the blood 9 The tiny units that are the basic building blocks of living things 12 Organ ...
The Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline Heart Anatomy
... blood divides into smaller ___________________ arteries that carry blood to all the organs throughout the body (except the air sacs in the lungs). - Exchange of nutrients and gases occurs across the thin capillary walls: Blood ________________ oxygen and picks up _______ ___________. Venules carry d ...
... blood divides into smaller ___________________ arteries that carry blood to all the organs throughout the body (except the air sacs in the lungs). - Exchange of nutrients and gases occurs across the thin capillary walls: Blood ________________ oxygen and picks up _______ ___________. Venules carry d ...
Respiratory System
... dioxide can pass through the membranes So that oxygen and carbon dioxide can dissolve in the water Diffusion can only happen when one area has a high concentration and the other area has a low concentration More surface to trade (exchange) gases Circulatory system can now move the gases to all cells ...
... dioxide can pass through the membranes So that oxygen and carbon dioxide can dissolve in the water Diffusion can only happen when one area has a high concentration and the other area has a low concentration More surface to trade (exchange) gases Circulatory system can now move the gases to all cells ...
Digestive, Respiratory, and Circulatory Systems
... AP Biology - Pig Dissection Exercise 30 – Digestive, Respiratory, and Circulatory Systems Name ...
... AP Biology - Pig Dissection Exercise 30 – Digestive, Respiratory, and Circulatory Systems Name ...
Amphibians
... Birds • Circulation: 4 chambered heart (one side pumps oxygen-poor blood to lungs the other side pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the ...
... Birds • Circulation: 4 chambered heart (one side pumps oxygen-poor blood to lungs the other side pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the ...
video slide
... • The mammalian excretory system centers on paired kidneys, which are also major site of water balance & salt regulation • Each kidney is supplied with blood by a renal artery & drained by a renal vein • Urine exits each kidney through a duct called the ureter ...
... • The mammalian excretory system centers on paired kidneys, which are also major site of water balance & salt regulation • Each kidney is supplied with blood by a renal artery & drained by a renal vein • Urine exits each kidney through a duct called the ureter ...
File
... . Side effects: loss of concentration, coordination and balance, and hallucinations - Stimulants = drugs that have an effect on the central nervous system, such as increased mental and/ or physical alertness . Stimulants overcome tiredness and offset lactic acid in muscles . Side effects: insomnia, ...
... . Side effects: loss of concentration, coordination and balance, and hallucinations - Stimulants = drugs that have an effect on the central nervous system, such as increased mental and/ or physical alertness . Stimulants overcome tiredness and offset lactic acid in muscles . Side effects: insomnia, ...
Acute Responses to Exercise
... contraction phase of the heart cycle. Will be the higher of the 2 values Diastolic blood pressure – is the blood pressure recorded during the relaxation phase of the heart cycle. Will always have a lower value. More blood is being pumped out per beat/minute and therefore it causes an increase in pre ...
... contraction phase of the heart cycle. Will be the higher of the 2 values Diastolic blood pressure – is the blood pressure recorded during the relaxation phase of the heart cycle. Will always have a lower value. More blood is being pumped out per beat/minute and therefore it causes an increase in pre ...
Chapter 44
... Urea which diffuses out of the collecting duct as it traverses the inner medulla forms along with NaCl the osmotic gradient that enables the kidney to produce urine that is hyperosmotic to the blood. The osmolarity of the urine is regulated by nervous system and hormonal control of water and salt re ...
... Urea which diffuses out of the collecting duct as it traverses the inner medulla forms along with NaCl the osmotic gradient that enables the kidney to produce urine that is hyperosmotic to the blood. The osmolarity of the urine is regulated by nervous system and hormonal control of water and salt re ...
B2 exam: Key words to understand
... Movement of molecules into the cell using energy from respiration. This occurs against a concentration gradient (from low to high concentration) and allows the cell to build up a high concentration of certain molecules. Eg the way plant root hair cells take in minerals. Tissue made of dead hollow ce ...
... Movement of molecules into the cell using energy from respiration. This occurs against a concentration gradient (from low to high concentration) and allows the cell to build up a high concentration of certain molecules. Eg the way plant root hair cells take in minerals. Tissue made of dead hollow ce ...
hearts - Evans Laboratory: Environmental Physiology @ CSUEB
... • closed circulatory systems provide two main advantages over open systems: 1. ability to generate high pressure and flow rates 2. ability to better control and direct blood flow to specific tissues • these features are important for oxygen delivery to metabolically active tissue and closed systems ...
... • closed circulatory systems provide two main advantages over open systems: 1. ability to generate high pressure and flow rates 2. ability to better control and direct blood flow to specific tissues • these features are important for oxygen delivery to metabolically active tissue and closed systems ...
HUMAN REPRODUCTION BIOLOGY 269
... urinary, reproductive, circulatory systems. Ectoderm will form skin and nervous system ...
... urinary, reproductive, circulatory systems. Ectoderm will form skin and nervous system ...
CV-4-2014
... • Afferent nerves (Buffer nerves) • Cardiovascular center: medulla • Efferent nerves: cardiac sympathetic nerve, sympathetic constrictor nerve, vagus nerve • Effector: heart & blood vessels ...
... • Afferent nerves (Buffer nerves) • Cardiovascular center: medulla • Efferent nerves: cardiac sympathetic nerve, sympathetic constrictor nerve, vagus nerve • Effector: heart & blood vessels ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.