What is the circulatory system?
... under high pressure, or your blood pressure. • A capillary is a tiny blood vessel that allows exchanges between body cells and blood. • A vein carries blood back to the heart. Valves in veins keep blood from flowing backward. ...
... under high pressure, or your blood pressure. • A capillary is a tiny blood vessel that allows exchanges between body cells and blood. • A vein carries blood back to the heart. Valves in veins keep blood from flowing backward. ...
Kingdom Animalia II
... returning from the lungs, it is pumped under high pressure to the body. • (b) The high rate of oxygen-rich blood flow through the body enables birds and mammals to maintain high activity levels. Also, the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is prevented. • (c) The increased efficiency of the ...
... returning from the lungs, it is pumped under high pressure to the body. • (b) The high rate of oxygen-rich blood flow through the body enables birds and mammals to maintain high activity levels. Also, the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is prevented. • (c) The increased efficiency of the ...
Systems of the Human Body Study Guide
... 2. Air enters your body through your ________________ and your ______________. 3. Another name for the trachea is the _________________. 4. The trachea divides into two branches called the ________________ ______________. 5. Our bodies use oxygen, and gives off ___________________ __________________ ...
... 2. Air enters your body through your ________________ and your ______________. 3. Another name for the trachea is the _________________. 4. The trachea divides into two branches called the ________________ ______________. 5. Our bodies use oxygen, and gives off ___________________ __________________ ...
HAZARDS OF IMMOBILITY MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
... *** if 8 stress is placed on bone as in athletic activity, more bone is deposited *** if 9 stress or no stress as in prolonged bedrest, bone is reabsorbed *** Encourage clients to stand and walk as the body functions best in the vertical position *** Physical activity forces muscles to move and incr ...
... *** if 8 stress is placed on bone as in athletic activity, more bone is deposited *** if 9 stress or no stress as in prolonged bedrest, bone is reabsorbed *** Encourage clients to stand and walk as the body functions best in the vertical position *** Physical activity forces muscles to move and incr ...
Chapter 2: Multiple Choice -- This activity contains 15
... What kind of control system will detect a change in a controlled variable and reverse the change to restore the variable to its desired value (set point)? negative feedback control system cyclic feedback control system positive feedback control system monitored feedback control system What is the ab ...
... What kind of control system will detect a change in a controlled variable and reverse the change to restore the variable to its desired value (set point)? negative feedback control system cyclic feedback control system positive feedback control system monitored feedback control system What is the ab ...
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes
... homeostasis- the body’s ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the external env. is continuously changing A. Homeostatic Control Mechanisms (p. 10-11) 1. Receptor- stimulus response via afferent pathway 2. Control Center- determines set point and analyzes incoming info ...
... homeostasis- the body’s ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the external env. is continuously changing A. Homeostatic Control Mechanisms (p. 10-11) 1. Receptor- stimulus response via afferent pathway 2. Control Center- determines set point and analyzes incoming info ...
File
... The control of body temperature is important for maintaining homeostasis in vertebrates, particularly in habitats where the temperature varies with time of day and season. All methods of controlling body temperature incorporate three important features: 1) A source of heat 2) A way to conserve heat ...
... The control of body temperature is important for maintaining homeostasis in vertebrates, particularly in habitats where the temperature varies with time of day and season. All methods of controlling body temperature incorporate three important features: 1) A source of heat 2) A way to conserve heat ...
Nutrition Fact Sheet - God`s Love We Deliver
... Healthy kidneys maintain fluid balance and prevent swelling of the feet, ankles, hands, or face. As kidney function decreases it is harder to get rid of the extra fluid that can cause high blood pressure, make it hard to breath, and cause strain on the heart. Most dialysis patients urinate very litt ...
... Healthy kidneys maintain fluid balance and prevent swelling of the feet, ankles, hands, or face. As kidney function decreases it is harder to get rid of the extra fluid that can cause high blood pressure, make it hard to breath, and cause strain on the heart. Most dialysis patients urinate very litt ...
State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system
... 6.5.6 Explain the principles of synaptic transmission. Include the release, diffusion and binding of the neurotransmitter, initiation of an action potential in the post-synaptic membrane, and subsequent removal of the neurotransmitter. 6.5.7 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that re ...
... 6.5.6 Explain the principles of synaptic transmission. Include the release, diffusion and binding of the neurotransmitter, initiation of an action potential in the post-synaptic membrane, and subsequent removal of the neurotransmitter. 6.5.7 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that re ...
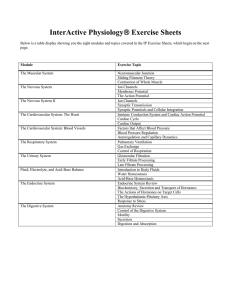
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. The binding of ACh opens ion channels in the dendrites or cell body that permits both _______ and ____________ to move through them. b. Which ion would move into the cell? ______________ out of the cell? ______________ c. Which ion has the greatest electrochemical gradient? ______________ d. The ...
... a. The binding of ACh opens ion channels in the dendrites or cell body that permits both _______ and ____________ to move through them. b. Which ion would move into the cell? ______________ out of the cell? ______________ c. Which ion has the greatest electrochemical gradient? ______________ d. The ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Water – 60-80% of body weight, provides fluid base for secretions and excretions Body temperature – 37°C (98°F), too low and chemical reactions slow down, too high and they speed up, death at either extreme Atmospheric pressure – pressure exerted on the body by the weight of air, breathing process i ...
... Water – 60-80% of body weight, provides fluid base for secretions and excretions Body temperature – 37°C (98°F), too low and chemical reactions slow down, too high and they speed up, death at either extreme Atmospheric pressure – pressure exerted on the body by the weight of air, breathing process i ...
The Circulatory System
... atrium to a ventricle, then from a ventricle into a blood vessel • A wall (interventricular septum) prevents blood from flowing between the two atriums or the two ventricles • This wall keeps blood rich in oxygen separate from blood low in oxygen • If oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-poor blood were to ...
... atrium to a ventricle, then from a ventricle into a blood vessel • A wall (interventricular septum) prevents blood from flowing between the two atriums or the two ventricles • This wall keeps blood rich in oxygen separate from blood low in oxygen • If oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-poor blood were to ...
6th Grade Science Scales * Unit 1: The Human Body
... In addition to score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond what was taught. Students demonstrate they have developed an understanding of: How how blood circulates through the body and what happens in each vessel along the way the difference ...
... In addition to score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond what was taught. Students demonstrate they have developed an understanding of: How how blood circulates through the body and what happens in each vessel along the way the difference ...
AP Biology Exam Review 6: Organism Form and Function
... Brain evolved from nerve nets to large, cephilized brains (cephilization); humans have large forebrain, where most complex functions occur o Peripheral – nerves branching off of spine 2. The Endocrine System Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (va ...
... Brain evolved from nerve nets to large, cephilized brains (cephilization); humans have large forebrain, where most complex functions occur o Peripheral – nerves branching off of spine 2. The Endocrine System Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (va ...
Biology - Essay.org
... tissue that lie along the sides of the glottis wall. These muscles can stretch the cords, change their shape or bring them close together. When the cords are close together, air rushing between them produce sound. The shape and stretch in the cords determines the pitch (highness or lowness) of the ...
... tissue that lie along the sides of the glottis wall. These muscles can stretch the cords, change their shape or bring them close together. When the cords are close together, air rushing between them produce sound. The shape and stretch in the cords determines the pitch (highness or lowness) of the ...
What is the respiratory system
... diaphragm expands reducing the amount of space for the lungs and forcing air out. The diaphragm is the main muscle used in breathing. ...
... diaphragm expands reducing the amount of space for the lungs and forcing air out. The diaphragm is the main muscle used in breathing. ...
The Respiratory System
... 22.13 If the volume of the cylinder in Figure 22.12 decreased from 1 liter to ¼ liter, how would the pressure change? 22.15 Would contraction of the external intercostals increase or decrease alveolar pressure? Would it cause air to enter or leave the lungs? Would contraction of the internal interco ...
... 22.13 If the volume of the cylinder in Figure 22.12 decreased from 1 liter to ¼ liter, how would the pressure change? 22.15 Would contraction of the external intercostals increase or decrease alveolar pressure? Would it cause air to enter or leave the lungs? Would contraction of the internal interco ...
VJJ Class - 6 Mark Question File
... c right atrium and ventricle to pump deoxygenated blood d valves to prevent backflow e why the left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle f the direction of blood flow through the heart Structure and function of arteries, veins, capillaries. a arteries transport blood away fro ...
... c right atrium and ventricle to pump deoxygenated blood d valves to prevent backflow e why the left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle f the direction of blood flow through the heart Structure and function of arteries, veins, capillaries. a arteries transport blood away fro ...
FISH BIOLOGY RESPIRATON
... How to cause free O2 to accumulate in distal end of rete? • Another counter-current exchange system: – long capillaries that fold back on self – afferent (incoming) part of capillary experiences drop in pH, Hb loses O2 – efferent (outgoing part of capillary has higher partial pressure (concentratio ...
... How to cause free O2 to accumulate in distal end of rete? • Another counter-current exchange system: – long capillaries that fold back on self – afferent (incoming) part of capillary experiences drop in pH, Hb loses O2 – efferent (outgoing part of capillary has higher partial pressure (concentratio ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... The skin removes some water and urea through perspiration. The liver produces urea and breaks down some wastes into forms that ...
... The skin removes some water and urea through perspiration. The liver produces urea and breaks down some wastes into forms that ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... formed in the plasma through a chain reaction. The chain is triggered by a substance, renin, released form kidneys. Renin is released from kidneys in response to renal ischemia, which may be due to a fall in blood pressure. ...
... formed in the plasma through a chain reaction. The chain is triggered by a substance, renin, released form kidneys. Renin is released from kidneys in response to renal ischemia, which may be due to a fall in blood pressure. ...
A1. All of the following are characteristics of ventilation EXCEPT: A
... pO2 of expired air is greater than alveolar air pO2 of interstitial fluids is less than pO2 in blood leaving the lungs pO2 in the blood is greater than alveolar air pCO2 of blood returning from the lungs equals that found in the alveoli C&D ...
... pO2 of expired air is greater than alveolar air pO2 of interstitial fluids is less than pO2 in blood leaving the lungs pO2 in the blood is greater than alveolar air pCO2 of blood returning from the lungs equals that found in the alveoli C&D ...
MASTERY TEST
... The respiratory membrane consists of a single layer of epithelial cells and basement membrane from a(n) and a(n) The rate at which a gas diffuses fi-om one area to another is determined by differences in areas. ...
... The respiratory membrane consists of a single layer of epithelial cells and basement membrane from a(n) and a(n) The rate at which a gas diffuses fi-om one area to another is determined by differences in areas. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.