Travel Brochure of the Body Systems
... 1. Describe the basic structure and function of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and explain how it operates. (Diagram) 3. List the parts and discuss the function of the Central Nervous System (CNS). Discuss the structure and control centers of the brain. 4. Describe the Per ...
... 1. Describe the basic structure and function of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and explain how it operates. (Diagram) 3. List the parts and discuss the function of the Central Nervous System (CNS). Discuss the structure and control centers of the brain. 4. Describe the Per ...
The Respiratory System. Presented by Toni Davis and Niamh
... Groups of neurons scattered through the pons and Medulla Oblongota make up the respiratory center of the brain. The Medullary Rhythmycity area have two neuron groups: Dorsal and Ventral that extend the length of the Medulla Oblongota ...
... Groups of neurons scattered through the pons and Medulla Oblongota make up the respiratory center of the brain. The Medullary Rhythmycity area have two neuron groups: Dorsal and Ventral that extend the length of the Medulla Oblongota ...
Total Cross Sectional Diameter and Pressures
... • MSFP represents the pressure equilibrated only in the systemic circulation. • Pulmonary circulation has little capacitance – Little resistance (~ 12% max) ...
... • MSFP represents the pressure equilibrated only in the systemic circulation. • Pulmonary circulation has little capacitance – Little resistance (~ 12% max) ...
Blood Clotting and Hemorrhage, cont.
... • These capillaries are slightly larger than blood capillaries. • Have a unique structure that allows interstitial fluid to flow into them but not out • Thin-walled vessels with one-way valves that prevent backflow of lymphatic fluid • Located both superficially (near the skin surface) and deeper in ...
... • These capillaries are slightly larger than blood capillaries. • Have a unique structure that allows interstitial fluid to flow into them but not out • Thin-walled vessels with one-way valves that prevent backflow of lymphatic fluid • Located both superficially (near the skin surface) and deeper in ...
D:\Fotos Website va 1-8-07\AdemhalingEN.cdr
... They do not breathe through their mouths unless they have an injury or abnormality to the soft palate (the structure that separates the mouth from the nasal passages). 2) At canter and gallop normal horses take one breath perfectly in time with one stride. This is referred to as respiratory-locomoto ...
... They do not breathe through their mouths unless they have an injury or abnormality to the soft palate (the structure that separates the mouth from the nasal passages). 2) At canter and gallop normal horses take one breath perfectly in time with one stride. This is referred to as respiratory-locomoto ...
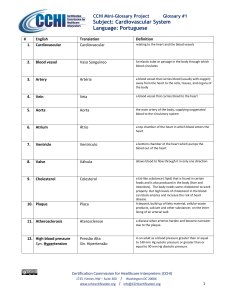
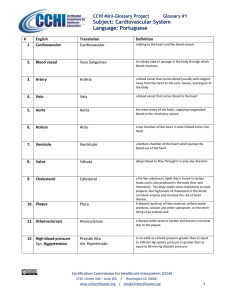
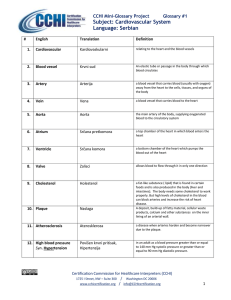
Subject: Cardiovascular System Language: Portuguese
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
MS Word file - Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
... supply to a restricted area of the brain, resulting in brief neurologic dysfunction that usually persists for less than 24 hours. It may be a warning sign of an imminent full-blown stroke. are most often caused by defective heart valves. A stenotic heart valve has a smaller-than-normal opening and c ...
frog dissection PP2
... Ectothermic (cold-blooded): body temperature varies with its environment’s temperature ...
... Ectothermic (cold-blooded): body temperature varies with its environment’s temperature ...
Respiratory System
... Smooth muscle increases Parasympathetic nerve stimulation constrict Sympathetic nerve stimulation relax Mucous secretion decreases ...
... Smooth muscle increases Parasympathetic nerve stimulation constrict Sympathetic nerve stimulation relax Mucous secretion decreases ...
Study Guide Respiratory system
... 48. Breathing rate is regulated by response to the level of _________ detected in the blood. 49. A disease in which the elasticity and surface area of the lung tissue is lost is commonly caused by __________________. 50. Breathing is controlled by contractions of the __________________muscle. 51. Wh ...
... 48. Breathing rate is regulated by response to the level of _________ detected in the blood. 49. A disease in which the elasticity and surface area of the lung tissue is lost is commonly caused by __________________. 50. Breathing is controlled by contractions of the __________________muscle. 51. Wh ...
ch_22 - WordPress.com
... Hypoglycemia- low blood glucose level. Hyper glycemia- high blood glucose level. Diabetes mellitus- loss of glucose through urine. Glycogenesis- conversion of glucose into glycogen. ...
... Hypoglycemia- low blood glucose level. Hyper glycemia- high blood glucose level. Diabetes mellitus- loss of glucose through urine. Glycogenesis- conversion of glucose into glycogen. ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary Systems Practice Test
... 32. (Skeletal / Smooth) muscle is found in the walls of blood vessels and many internal organs. 33. The (epidermis / dermis) makes up the outer most layer of skin. 34. The (integumentary / endocrine) system functions to protect the body against UV radiation. ...
... 32. (Skeletal / Smooth) muscle is found in the walls of blood vessels and many internal organs. 33. The (epidermis / dermis) makes up the outer most layer of skin. 34. The (integumentary / endocrine) system functions to protect the body against UV radiation. ...
Circulatory System— The Plasma Pipeline
... Association for the Advancement of Science. Used by permission of Oxford University Press, Inc. Please note: judgments about the alignment of content presented here with the learning goals in BENCHMARKS FOR SCIENCE LITERACY are those of the author and do not represent the opinion or endorsement of t ...
... Association for the Advancement of Science. Used by permission of Oxford University Press, Inc. Please note: judgments about the alignment of content presented here with the learning goals in BENCHMARKS FOR SCIENCE LITERACY are those of the author and do not represent the opinion or endorsement of t ...
Chapter 27 Introduction to Animals Chapter 27 Section 1
... o Respiratory – moves air into and out of the lungs and controls gas exchange between the blood and the lungs. o Skeletal – protects and supports the body and its organs, interacts with skeletal muscles to provide movement, and produces red and white blood cells and platelets. Body Cavit ies – hous ...
... o Respiratory – moves air into and out of the lungs and controls gas exchange between the blood and the lungs. o Skeletal – protects and supports the body and its organs, interacts with skeletal muscles to provide movement, and produces red and white blood cells and platelets. Body Cavit ies – hous ...
1314 - 1 - Page 1 Name: ____________________________________________ 1)
... Additional oxygen will diffuse into the blood as carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood in the lungs. Additional carbon dioxide will diffuse into the blood as oxygen diffuses out of the blood in the lungs. ...
... Additional oxygen will diffuse into the blood as carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood in the lungs. Additional carbon dioxide will diffuse into the blood as oxygen diffuses out of the blood in the lungs. ...
Training Effects of Aerobic exercise on the Cardiovascular
... oxygen would take from the air in the lungs to a muscle cell. 2. Describe the path and all related steps that a molecule of carbon dioxide could take from a muscle cell to the air in the lungs. 3. Define and provide the units for blood pressure, heart rate, cardiac output, stroke volume, ateriovenou ...
... oxygen would take from the air in the lungs to a muscle cell. 2. Describe the path and all related steps that a molecule of carbon dioxide could take from a muscle cell to the air in the lungs. 3. Define and provide the units for blood pressure, heart rate, cardiac output, stroke volume, ateriovenou ...
ch 34 reviewing this chapter
... Duodenum of small intestine receives bile from the liver and pancreatic juice from the pancreas. Bile emulsifies fat (breaks it into smaller droplets) to ready it for digestion by an enzyme from pancreas. Pancreas also produces enzymes that digest starch and protein (see chart that you were given in ...
... Duodenum of small intestine receives bile from the liver and pancreatic juice from the pancreas. Bile emulsifies fat (breaks it into smaller droplets) to ready it for digestion by an enzyme from pancreas. Pancreas also produces enzymes that digest starch and protein (see chart that you were given in ...
( 2 ) : circulatory system and urinary system Its structure
... 7-Each side of the heart consists of ……………….. chambers, the upper one is called ……………… and the lower one is called………………………. 8-The two sides of the heart are separtated by ………………………………. 9-In each side of the heart , there is a ……………………. To prevent the blood from returning back to the …………………. 11-The ...
... 7-Each side of the heart consists of ……………….. chambers, the upper one is called ……………… and the lower one is called………………………. 8-The two sides of the heart are separtated by ………………………………. 9-In each side of the heart , there is a ……………………. To prevent the blood from returning back to the …………………. 11-The ...
TEKS 8.6 B
... one that tries to keep the body constant. There are a number of negative feedback systems in the human body such as those involved in the control of blood glucose, blood calcium, blood pressure, reproduction, reaction, growth and metabolism. A very common example is how the body reacts to reverse th ...
... one that tries to keep the body constant. There are a number of negative feedback systems in the human body such as those involved in the control of blood glucose, blood calcium, blood pressure, reproduction, reaction, growth and metabolism. A very common example is how the body reacts to reverse th ...
Renal * Kidneys Excretion and Osmoregulation - TCC-YR11
... Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood to the alveoli of the lungs and through skin surfaces. Salts may be removed through the skin; for example, by sweat in mammals. Salts are also secreted into the large intestine. The kidneys have a significant role in the regulation of salt levels in the body, a ...
... Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood to the alveoli of the lungs and through skin surfaces. Salts may be removed through the skin; for example, by sweat in mammals. Salts are also secreted into the large intestine. The kidneys have a significant role in the regulation of salt levels in the body, a ...
MS Word file - Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters
... allows blood to flow through it in only one direction ...
... allows blood to flow through it in only one direction ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.