HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS / HOMEOSTASIS Pre
... independently of each other. Instead, their processes are integrated to the extent that if one system fails, the other systems could not continue to function. Each system depends on the others, either directly or indirectly, to keep the body functioning normally. Homeostasis is an organism's ability ...
... independently of each other. Instead, their processes are integrated to the extent that if one system fails, the other systems could not continue to function. Each system depends on the others, either directly or indirectly, to keep the body functioning normally. Homeostasis is an organism's ability ...
Lab 10 - Creighton Biology
... The kidneys play a vital role in homeostasis, or the maintenance of constant conditions within the body. They regulate the chemical content, the pH, and the osmotic pressure of the blood. The kidneys form urine by the combined processes of glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular sec ...
... The kidneys play a vital role in homeostasis, or the maintenance of constant conditions within the body. They regulate the chemical content, the pH, and the osmotic pressure of the blood. The kidneys form urine by the combined processes of glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular sec ...
Chapter 10 - Vascular Physiology
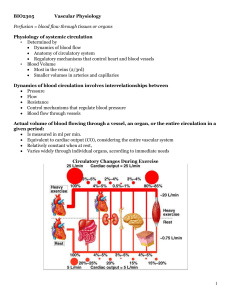
... • Arteriole resistance is greatest because they have the smallest diameter. • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total cross-sectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase in each of these will result in an increase in BP. • BP can be regulated by: • Kidney and symp ...
... • Arteriole resistance is greatest because they have the smallest diameter. • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total cross-sectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase in each of these will result in an increase in BP. • BP can be regulated by: • Kidney and symp ...
Biology - H Hungary is already a member of EU system so you can
... Steps from glycolysis to the electron transport chain. Why are mitochondria important? Lets break down each of the steps so you can see how food turns into ATP energy packets and water. The food we eat must first be converted to basic chemicals that the cell can use. Some of the best energy supplyin ...
... Steps from glycolysis to the electron transport chain. Why are mitochondria important? Lets break down each of the steps so you can see how food turns into ATP energy packets and water. The food we eat must first be converted to basic chemicals that the cell can use. Some of the best energy supplyin ...
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
... Use information given in part (b) to explain why only one red blood cell at a time can pass through a capillary. ...
... Use information given in part (b) to explain why only one red blood cell at a time can pass through a capillary. ...
Natural History of Vertebrates Lecture Notes Chapter 2
... The function is to allow the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. This occurs in different ways depending upon habitat and size of the organism. 1. gills - aquatic 2. skin - aquatic 3. lungs - aquatic to terrestrial Ancestral vertebrates were small and used cutaneous respiration, ...
... The function is to allow the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. This occurs in different ways depending upon habitat and size of the organism. 1. gills - aquatic 2. skin - aquatic 3. lungs - aquatic to terrestrial Ancestral vertebrates were small and used cutaneous respiration, ...
Cardiovascular System Part 2
... Venous hypertension: increased blood pressure in veins, incompetent valves; pooling of blood along length of vein until normal valve reached; arteries continue to pump blood into vein, increasing pressure; prolonged standing Hypotension: low blood pressure; usually systolic <90, diastolic <60; can c ...
... Venous hypertension: increased blood pressure in veins, incompetent valves; pooling of blood along length of vein until normal valve reached; arteries continue to pump blood into vein, increasing pressure; prolonged standing Hypotension: low blood pressure; usually systolic <90, diastolic <60; can c ...
Diabetes Form 100
... Student should not exercise if blood glucose is >300 and ketones is > small or until hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia is resolved A source of fast-acting glucose & glucagon should be available in case of hypoglycemia Special Instructions: Staff Trained: ...
... Student should not exercise if blood glucose is >300 and ketones is > small or until hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia is resolved A source of fast-acting glucose & glucagon should be available in case of hypoglycemia Special Instructions: Staff Trained: ...
B11Annelida - Science at NESS
... travel along the ground = lost setae over time Hirudin: A chemical released into the hosts blood to prevent the blood from clotting Anaesthetic : This chemical numbs the area where the leech feeds so the host doesn’t feel it. ...
... travel along the ground = lost setae over time Hirudin: A chemical released into the hosts blood to prevent the blood from clotting Anaesthetic : This chemical numbs the area where the leech feeds so the host doesn’t feel it. ...
Functional Anatomy of Respiratory System
... Blood reaching the tissues has approximately the same partial pressures of gases as the blood leaving the lungs. When this blood reaches the systemic capillaries, oxygen diffuses out of the blood into the tissues where the PO2 is low at 40 mmHg due to rapid use of O2 by cells for cellular respiratio ...
... Blood reaching the tissues has approximately the same partial pressures of gases as the blood leaving the lungs. When this blood reaches the systemic capillaries, oxygen diffuses out of the blood into the tissues where the PO2 is low at 40 mmHg due to rapid use of O2 by cells for cellular respiratio ...
nov 1999
... 16. Which of the following conditions would cause the change in the fluid levels as shown after 10 minutes? SOLUTION IN SIDE A distilled water 2% glucose 5% protein 2% salt ...
... 16. Which of the following conditions would cause the change in the fluid levels as shown after 10 minutes? SOLUTION IN SIDE A distilled water 2% glucose 5% protein 2% salt ...
unit 8 - blood / lymphatic / cardiovascular systems
... The largest artery in the body extends from the left ventricle and is called the _______________. The first branch feeds the myocardium with blood and are the ___________________________. The next branch ________________________________________takes blood into the right arm and the right side of the ...
... The largest artery in the body extends from the left ventricle and is called the _______________. The first branch feeds the myocardium with blood and are the ___________________________. The next branch ________________________________________takes blood into the right arm and the right side of the ...
ch2
... d- They explained that this activity needs more of ATP molecules which exist in the companion cell. e- And this is proved later by experiments which show that the transportation process is delayed with the decrease of temperature or oxygen in cells, thus delaying the movement of cytoplasm tubes (sie ...
... d- They explained that this activity needs more of ATP molecules which exist in the companion cell. e- And this is proved later by experiments which show that the transportation process is delayed with the decrease of temperature or oxygen in cells, thus delaying the movement of cytoplasm tubes (sie ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
... the stomach, function of liver enzymes, blood type). It is also important to note that environmental factors, factors that are non-genetic, can dramatically influence the characteristics of an organism. For example, if one identical twin is raised eating a healthy, nutritious diet and the other deve ...
... the stomach, function of liver enzymes, blood type). It is also important to note that environmental factors, factors that are non-genetic, can dramatically influence the characteristics of an organism. For example, if one identical twin is raised eating a healthy, nutritious diet and the other deve ...
Circulatory System Lesson
... use). The teacher will instruct the students to design an experiment to test their hypotheses about blood pressure using the models as the vessels and air to simulate blood flow. 4. STUDENTS, in groups of 2 to 4, will create a valid scientific investigation to investigate the relationship between bl ...
... use). The teacher will instruct the students to design an experiment to test their hypotheses about blood pressure using the models as the vessels and air to simulate blood flow. 4. STUDENTS, in groups of 2 to 4, will create a valid scientific investigation to investigate the relationship between bl ...
body fluids and circulation chapter 18
... pressure causing the closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves due to attempted backflow of blood into the atria. As the ventricular pressure increases further, the semilunar valves guarding the pulmonary artery (right side) and the aorta (left side) are forced open, allowing the blood in the ventric ...
... pressure causing the closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves due to attempted backflow of blood into the atria. As the ventricular pressure increases further, the semilunar valves guarding the pulmonary artery (right side) and the aorta (left side) are forced open, allowing the blood in the ventric ...
Ch. 28.1 - St John Brebeuf
... Aquatic arthropods may be internal or external fertilization (females will release eggs and males will shed sperm around the eggs) GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: Molting of ...
... Aquatic arthropods may be internal or external fertilization (females will release eggs and males will shed sperm around the eggs) GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: Molting of ...
Field Biology Vertebrate Dissection - Organ Functions
... 3. Thymus gland - important organ for immunity, involved in producing T cells for antigen recognition. 4. Right atrium - chamber which receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and passes it to the right ventricle. 5. Right lung - organ that exchanges gases between air and blood. 6. Diaphragm - ...
... 3. Thymus gland - important organ for immunity, involved in producing T cells for antigen recognition. 4. Right atrium - chamber which receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and passes it to the right ventricle. 5. Right lung - organ that exchanges gases between air and blood. 6. Diaphragm - ...
HBSGlossary - Kenwood Academy High School
... Adduction: Movement toward the midline off the body. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): An adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed. This energy is used to drive endergonic reactions in the cell. Adipose Tissue: Connective tissue in whic ...
... Adduction: Movement toward the midline off the body. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): An adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed. This energy is used to drive endergonic reactions in the cell. Adipose Tissue: Connective tissue in whic ...
The Body Systems
... passageways and fills up our lungs. Within each lung, the tiny alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels and oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of the vessels. ...
... passageways and fills up our lungs. Within each lung, the tiny alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels and oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of the vessels. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.