Genome and sex 10-29
... When coevolving with parasites, all selfing C. elegans populations became extinct within 20 generations; but not sexual one! ...
... When coevolving with parasites, all selfing C. elegans populations became extinct within 20 generations; but not sexual one! ...
Darwin
... Struggle for existence: members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities. ◦ Predators that are faster or have a particular way of ensnaring other organisms, will catch more prey. ◦ Those prey that are faster, better camouflaged, or better protected can av ...
... Struggle for existence: members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities. ◦ Predators that are faster or have a particular way of ensnaring other organisms, will catch more prey. ◦ Those prey that are faster, better camouflaged, or better protected can av ...
Evol Theory, Evidence
... common ancestor (True) 2. Acquired characteristics could be passed on to offspring (False) ...
... common ancestor (True) 2. Acquired characteristics could be passed on to offspring (False) ...
Evolution
... The process of humans selecting the variations that they find most attractive or useful, and breeding or reproducing those traits in the new offspring. ...
... The process of humans selecting the variations that they find most attractive or useful, and breeding or reproducing those traits in the new offspring. ...
Random Selection Kelly Pankowski My artwork is deeply influenced
... My artwork is deeply influenced by my early history as both a practicing catholic and from my time studying biology at the undergraduate level. To be more specific, the conflicting foundations of thought behind both the theory of evolution and prevalent religious dogmas fuel the conceptual framework ...
... My artwork is deeply influenced by my early history as both a practicing catholic and from my time studying biology at the undergraduate level. To be more specific, the conflicting foundations of thought behind both the theory of evolution and prevalent religious dogmas fuel the conceptual framework ...
Introduction to Sex Education
... Middle East. Some laws have been passed to try and ban the use of FGM. Used for cultural, religious, tradition and preserving virginity. ...
... Middle East. Some laws have been passed to try and ban the use of FGM. Used for cultural, religious, tradition and preserving virginity. ...
A very different form of selection
... for bright colors, beautiful songs, etc. Darwin came up with another form of selection: ...
... for bright colors, beautiful songs, etc. Darwin came up with another form of selection: ...
Sexual selection essay
... I think it is important to realise that there theories do not have to be looked at in isolation. For example, the male behaviour or ornament could have evolved due to sensory exploitation but then a positive feedback system could have been set up where Fisher’s theory might explain the upkeep of the ...
... I think it is important to realise that there theories do not have to be looked at in isolation. For example, the male behaviour or ornament could have evolved due to sensory exploitation but then a positive feedback system could have been set up where Fisher’s theory might explain the upkeep of the ...
ppt
... Natural Selection and Species Fitness Overtime, natural selection results in changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness (survival rate) ...
... Natural Selection and Species Fitness Overtime, natural selection results in changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness (survival rate) ...
Lecture slides
... ‐ bottleneck effect ‐ founder effect 4. Gene flow (migration) 5. Natural Selection ...
... ‐ bottleneck effect ‐ founder effect 4. Gene flow (migration) 5. Natural Selection ...
Lecture 2 - Organic Origins Debate
... Humans consume large amount of meat, compared to other primates Provisioning explains high male parental investment & sexual division of labour However, egalitarian food sharing “Showoffs” get sexual access & other benefits in exchange for meat ...
... Humans consume large amount of meat, compared to other primates Provisioning explains high male parental investment & sexual division of labour However, egalitarian food sharing “Showoffs” get sexual access & other benefits in exchange for meat ...
PDF file
... correlated with intelligence and health. (In addition, men who have more symmetric bodies are not only more attractive, they invest less effort in their relationships.) There may a reason for all this: during development many insults (infections, poisons) can affect how well the embryo develops and ...
... correlated with intelligence and health. (In addition, men who have more symmetric bodies are not only more attractive, they invest less effort in their relationships.) There may a reason for all this: during development many insults (infections, poisons) can affect how well the embryo develops and ...
QS039--Ch21--Mechanisms of Evolution
... a. ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
... a. ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
Evolution powerpoint
... For humans, it is not a change we will observe in our lifetime but studies are done on organisms with a short life span and done by farmers in something called selective breeding The mechanism of evolution is called NATURAL SELECTION – Charles Darwin and the Galapagos Islands In nature plants and ma ...
... For humans, it is not a change we will observe in our lifetime but studies are done on organisms with a short life span and done by farmers in something called selective breeding The mechanism of evolution is called NATURAL SELECTION – Charles Darwin and the Galapagos Islands In nature plants and ma ...
Slide 1
... resources are limited, offspring compete with each other to survive. Species that go after the same resources also compete to survive. ...
... resources are limited, offspring compete with each other to survive. Species that go after the same resources also compete to survive. ...
Evolution Powerpoint
... baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis. Those with the most advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
... baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis. Those with the most advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
Vocabulary Terms Natural Selection and Modern Genetics
... 3. gene pool: The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. 4. variation: Any difference among organisms of the same species. 5. mutations: Random changes in the genetic code; may be helpful or harmful. 6. adaptation: A genetic variation that provides an organism with ...
... 3. gene pool: The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. 4. variation: Any difference among organisms of the same species. 5. mutations: Random changes in the genetic code; may be helpful or harmful. 6. adaptation: A genetic variation that provides an organism with ...
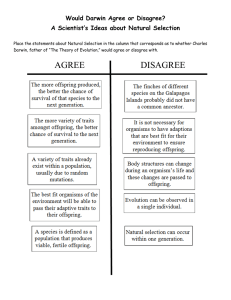
Would Darwin Agree or Disagree
... Place the statements about Natural Selection in the column that corresponds as to whether Charles Darwin, father of “The Theory of Evolution,” would agree or disagree with. ...
... Place the statements about Natural Selection in the column that corresponds as to whether Charles Darwin, father of “The Theory of Evolution,” would agree or disagree with. ...
Lecture 6
... rates of replication. -Natural (and sexual) selection builds adaptations that are: built of existing variation (mutations). ...
... rates of replication. -Natural (and sexual) selection builds adaptations that are: built of existing variation (mutations). ...
Chapter 6.1 Trashketball
... 6. Species produce more offspring than can possibly survive A. Natural selection B. Overproduction C. Evolution D. Variation ...
... 6. Species produce more offspring than can possibly survive A. Natural selection B. Overproduction C. Evolution D. Variation ...
Sexual selection

Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection where typically members of one gender choose mates of the other gender to mate with, called intersexual selection, and where females normally do the choosing, and competition between members of the same gender to sexually reproduce with members of the opposite sex, called intrasexual selection. These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have better reproductive success than others within a population either from being sexier or preferring sexier partners to produce offspring. For instance in the breeding season sexual selection in frogs occurs with the males first gathering at the water's edge and croaking. The females then arrive and choose the males with the deepest croaks and best territories. Generalizing, males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to a group of fertile females. Females have a limited number of offspring they can have and they maximize the return on the energy they invest in reproduction.First articulated by Charles Darwin who described it as driving speciation and that many organisms had evolved features whose function was deleterious to their individual survival, and then developed by Ronald Fisher in the early 20th century. Sexual selection can lead typically males to extreme efforts to demonstrate their fitness to be chosen by females, producing secondary sexual characteristics, such as ornate bird tails like the peacock plumage, or the antlers of deer, or the manes of lions, caused by a positive feedback mechanism known as a Fisherian runaway, where the passing on of the desire for a trait in one sex is as important as having the trait in the other sex in producing the runaway effect. Although the sexy son hypothesis indicates that females would prefer male sons, Fisher's principle explains why the sex ratio is 1:1 almost without exception. Sexual selection is also found in plants and fungi.The maintenance of sexual reproduction in a highly competitive world has long been one of the major mysteries of biology given that asexual reproduction can reproduce much more quickly as 50% of offspring are not males, unable to produce offspring themselves. However, research published in 2015 indicates that sexual selection can explain the persistence of sexual reproduction.