RNA
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
RNA-protein interaction
... 二. Outlook and further perspectives RNA-protein interactions are a central component of posttranscriptional regulation at multiple levels including RNA processing, transport and translation. The sequenced Human genome reveals hundreds of potential RNA binding proteins . A critical step towards unde ...
... 二. Outlook and further perspectives RNA-protein interactions are a central component of posttranscriptional regulation at multiple levels including RNA processing, transport and translation. The sequenced Human genome reveals hundreds of potential RNA binding proteins . A critical step towards unde ...
Slide 1
... Scanning of an Affymetrix GeneChip yields one intensity value for each probe (cell). A high intensity value for a probe (cell) implies that many sequences from the biological sample were able to bind to the sequences in the probe (cell). There is concern that some of the mRNA that binds to a particu ...
... Scanning of an Affymetrix GeneChip yields one intensity value for each probe (cell). A high intensity value for a probe (cell) implies that many sequences from the biological sample were able to bind to the sequences in the probe (cell). There is concern that some of the mRNA that binds to a particu ...
The Secret Code of Life:
... The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. There are 34 total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. (Would a doublet code work just as well?? i.e. on ...
... The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. There are 34 total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. (Would a doublet code work just as well?? i.e. on ...
RNA PP
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the nucleus. ...
What is RNA? - Biology for Life
... • Unlike DNA, most RNA molecules are singlestranded and can adopt very complex threedimensional structures. ...
... • Unlike DNA, most RNA molecules are singlestranded and can adopt very complex threedimensional structures. ...
DNA RNA Proteins - Aurora City Schools
... Promoter serves as a specific binding site for RNA polymerase and determines which of the two strands of the DNA double helix is used as the template. Specific nucleotide sequence at promoter is TATAAA Called the “TATA box”; located 25-35 base pairs before the transcription start site of a gen ...
... Promoter serves as a specific binding site for RNA polymerase and determines which of the two strands of the DNA double helix is used as the template. Specific nucleotide sequence at promoter is TATAAA Called the “TATA box”; located 25-35 base pairs before the transcription start site of a gen ...
m5zn_a4ac3a22336dedd
... A transcriptional activator is a protein that increases gene transcription of a gene or set of genes. Most activators are DNA-binding proteins. Most activators function by binding sequence-specifically to a DNA site located in or near a promoter and making protein-protein interactions with the gener ...
... A transcriptional activator is a protein that increases gene transcription of a gene or set of genes. Most activators are DNA-binding proteins. Most activators function by binding sequence-specifically to a DNA site located in or near a promoter and making protein-protein interactions with the gener ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
VIZSGAKÉRDÉSEK A FELKÉSZÜLÉSHEZ*
... Types and functions of RNA-s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, LncRNA). RNA polymerases and their functions, the comparison of properties of RNA and DNA polymerases. The initiation, elongation and termination of RNA synthesis (prokaryotes, eukaryotes, the nucleotide coupling, σ-depnedent and σindependent te ...
... Types and functions of RNA-s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, LncRNA). RNA polymerases and their functions, the comparison of properties of RNA and DNA polymerases. The initiation, elongation and termination of RNA synthesis (prokaryotes, eukaryotes, the nucleotide coupling, σ-depnedent and σindependent te ...
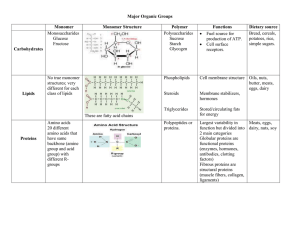
Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
Secretory Protein mRNA Finds Another Way Out
... It turns out that mRNAs that encode many secretory proteins do indeed have additional functions, as Alexander Palazzo, Tom Rapoport, and their colleagues report in a new study. While many proteins are created and destroyed within the same cell, others are secreted. One property that differentiates s ...
... It turns out that mRNAs that encode many secretory proteins do indeed have additional functions, as Alexander Palazzo, Tom Rapoport, and their colleagues report in a new study. While many proteins are created and destroyed within the same cell, others are secreted. One property that differentiates s ...
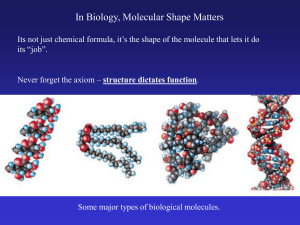
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
promoters
... The addition of s to the polymerase core gives the RNA polymerase holoenzyme recognizing a site at -10 to form the closed complex. In the holoenzyme form, an additional DNA binding domain of s, the region 4.2, become unmasked, and this recognizes a second site at -35, approximately 2 helical turns o ...
... The addition of s to the polymerase core gives the RNA polymerase holoenzyme recognizing a site at -10 to form the closed complex. In the holoenzyme form, an additional DNA binding domain of s, the region 4.2, become unmasked, and this recognizes a second site at -35, approximately 2 helical turns o ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... • DNA provides workers with the instructions for making the proteins and the workers build the proteins • Other workers bring parts, the amino acids, over to the assembly line • The workers for protein synthesis are RNA molecules, which take the instructions from DNA and assemble the protein amino ...
... • DNA provides workers with the instructions for making the proteins and the workers build the proteins • Other workers bring parts, the amino acids, over to the assembly line • The workers for protein synthesis are RNA molecules, which take the instructions from DNA and assemble the protein amino ...
here
... The function of RNA polymerase is to produced RNA by reading a section of DNA. DNA is directional and consequently, RNA polymerase can read DNA in only one direction, namely from 3’ to 5’ (otherwise, the product would not uniquely defined). ...
... The function of RNA polymerase is to produced RNA by reading a section of DNA. DNA is directional and consequently, RNA polymerase can read DNA in only one direction, namely from 3’ to 5’ (otherwise, the product would not uniquely defined). ...
Proteins & Nucleic Acids - St. Mary Catholic Secondary School
... Ladder shape – Rails - A series of alternating phosphates and sugars linked by covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds. Rungs of the ladder are made of the nitrogenous bases and their hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases involved with DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. The adenine ...
... Ladder shape – Rails - A series of alternating phosphates and sugars linked by covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds. Rungs of the ladder are made of the nitrogenous bases and their hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases involved with DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. The adenine ...
16-17 Biology Fall Final Study Guide
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.