DNA - Chemistry Courses
... down the chain in another exon, with an intron between that is removed from the mRNA ...
... down the chain in another exon, with an intron between that is removed from the mRNA ...
Gene expressions analysis by massively parallel signature
... • Enzymes that cut double stranded DNA • The cleaved chemical bonds can be reformed by ligases • Restriction enzyme cuts only double-helical segments that contain a particular nucleotide sequence (i.e. recognition sequence) • Types of Restriction enzymes: I, II, III: I,III: recognize specific sequen ...
... • Enzymes that cut double stranded DNA • The cleaved chemical bonds can be reformed by ligases • Restriction enzyme cuts only double-helical segments that contain a particular nucleotide sequence (i.e. recognition sequence) • Types of Restriction enzymes: I, II, III: I,III: recognize specific sequen ...
Recombinant Human PKA 2 beta (regulatory subunit) protein
... Regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinases involved in cAMP signaling in cells. Type II regulatory chains mediate membrane association by binding to anchoring proteins, including the MAP2 kinase. ...
... Regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinases involved in cAMP signaling in cells. Type II regulatory chains mediate membrane association by binding to anchoring proteins, including the MAP2 kinase. ...
3.4 C: Transcription Quiz PROCTOR VERSION
... The resulting RNA transcript is due to a single substitution in the DNA sequence. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that a substitution in the DNA sequence will result in a change in the resulting RNA sequence, but does not understand that the given RNA transcript ...
... The resulting RNA transcript is due to a single substitution in the DNA sequence. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that a substitution in the DNA sequence will result in a change in the resulting RNA sequence, but does not understand that the given RNA transcript ...
(3.1.1.5a) Nucleic Acids
... To understand the importance of nucleic acids, you must first understand the importance of proteins. Proteins have to have a special shape in order to do their job. For example, proteins that serve as enzymes have to have their active site, the groove that the substrate fits in. That shape is determ ...
... To understand the importance of nucleic acids, you must first understand the importance of proteins. Proteins have to have a special shape in order to do their job. For example, proteins that serve as enzymes have to have their active site, the groove that the substrate fits in. That shape is determ ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
DNA- The Molecule of Life
... mRNA attaches to the ribosome (rRNA). (The rRNA slides along the mRNA like a bead on a string.) rRNA “reads” the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called a codon. ·Translation always begins with a special codon (AUG) called the initiator or start codon. ...
... mRNA attaches to the ribosome (rRNA). (The rRNA slides along the mRNA like a bead on a string.) rRNA “reads” the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called a codon. ·Translation always begins with a special codon (AUG) called the initiator or start codon. ...
to Unit 10 Notes
... antianti-codon (3 bases) An tRNA antianti-codon "mates" with codon on the mRNA molecule There are 61 different tRNA molecules, yet only about 20 amino acids (hint: 3 stop codons) codons) ...
... antianti-codon (3 bases) An tRNA antianti-codon "mates" with codon on the mRNA molecule There are 61 different tRNA molecules, yet only about 20 amino acids (hint: 3 stop codons) codons) ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... 4 blue tubes (cytosine) 4 yellow tubes (guanine) 5 green tubes (thymine) 5 orange tubes (adenine) 20 white tubes (phosphates) 9 white rods (hydrogen bonds) 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide ...
... 4 blue tubes (cytosine) 4 yellow tubes (guanine) 5 green tubes (thymine) 5 orange tubes (adenine) 20 white tubes (phosphates) 9 white rods (hydrogen bonds) 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide ...
Genome Sequence Acquisition
... For most researchers, the final goal of genomic research is not the genomic data itself but an understanding of the proteins encoded for by a genome. Steps to determining protein structure and function: Find ORFs, or coding sequences (CDSs) Translate ORFs Is this a known protein? If not, find ...
... For most researchers, the final goal of genomic research is not the genomic data itself but an understanding of the proteins encoded for by a genome. Steps to determining protein structure and function: Find ORFs, or coding sequences (CDSs) Translate ORFs Is this a known protein? If not, find ...
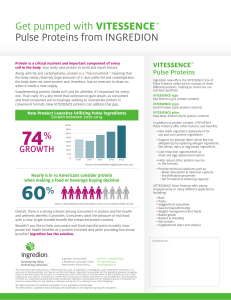
60% 74% - Ingredion
... Get pumped with VITESSENCE™ Pulse Proteins from INGREDION Protein is a critical nutrient and important component of every cell in the body. Your body uses protein to build and repair tissues. Along with fat and carbohydrates, protein is a “macronutrient,” meaning that the body needs relatively large ...
... Get pumped with VITESSENCE™ Pulse Proteins from INGREDION Protein is a critical nutrient and important component of every cell in the body. Your body uses protein to build and repair tissues. Along with fat and carbohydrates, protein is a “macronutrient,” meaning that the body needs relatively large ...
Connect the dots…DNA to Disease, Oltmann
... 4. If you were a scientist working with mice and discovered a gene that had something to do with obesity in mice, describe how you might find out if there is a similar gene that is known to exist in humans? 5. If you had more nucleotides in your sequence to enter into BLAST (say 1000 instead of 100) ...
... 4. If you were a scientist working with mice and discovered a gene that had something to do with obesity in mice, describe how you might find out if there is a similar gene that is known to exist in humans? 5. If you had more nucleotides in your sequence to enter into BLAST (say 1000 instead of 100) ...
BP 32: Posters - DNA/RNA - DPG
... transcription inhibition. The microstructure originated from individual transcription sites, which locally displaced DNA by an RNA-rich region upon transcription activation. Our experimental results can be recapitulated in a simulated microemulsion. Here, the accumulation of nuclear RNA induces a gl ...
... transcription inhibition. The microstructure originated from individual transcription sites, which locally displaced DNA by an RNA-rich region upon transcription activation. Our experimental results can be recapitulated in a simulated microemulsion. Here, the accumulation of nuclear RNA induces a gl ...
Protein synthesis
... Each mRNA transcript is read simultaneously by more than one ribosome. A second, third, fourth, etc. ribosome starts to read the mRNA transcript before the first ribosome has completed the synthesis of one ...
... Each mRNA transcript is read simultaneously by more than one ribosome. A second, third, fourth, etc. ribosome starts to read the mRNA transcript before the first ribosome has completed the synthesis of one ...
Genetisches Seminar
... Understanding the mechanisms by which populations become reproductively isolated is a major goal of evolutionary biology. Postzygotic reproductive isolation in response to hybridizations of plants that differ in ploidy (interploidy hybridizations) is a major path for sympatric speciation in plants. ...
... Understanding the mechanisms by which populations become reproductively isolated is a major goal of evolutionary biology. Postzygotic reproductive isolation in response to hybridizations of plants that differ in ploidy (interploidy hybridizations) is a major path for sympatric speciation in plants. ...
Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein ab114419 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Protein concentration is above or equal to 0.05 mg/ml. Best used within three months from the date of receipt. ...
... Protein concentration is above or equal to 0.05 mg/ml. Best used within three months from the date of receipt. ...
Cellular Classification & Organelles: A Look at the Endomembrane
... composition of lipids and proteins suited to that membrane’s specific function Ex: enzymes embedded in the mitochondrial membrane function in cellular respiration…which creates the ATP energy our cells need to function! ...
... composition of lipids and proteins suited to that membrane’s specific function Ex: enzymes embedded in the mitochondrial membrane function in cellular respiration…which creates the ATP energy our cells need to function! ...
Biophysics : Aspects of Amino Acids Sequence in Proteins and
... Abstract: Protein is the polypeptide chain of amino-acid sequence. Proteins of all species, from bacteria to humans, are made up from the same set of 20 standard amino acids. In order to carry out their function they must take a particular shape which is known as fold. All the enzymes hormones and a ...
... Abstract: Protein is the polypeptide chain of amino-acid sequence. Proteins of all species, from bacteria to humans, are made up from the same set of 20 standard amino acids. In order to carry out their function they must take a particular shape which is known as fold. All the enzymes hormones and a ...
Oc - TUM
... Cells respond to intrinsic and extrinsic signals by modulating transcriptional control of certain genes Gene activity is the result of the function of cis- and trans-acting factors Trans-acting proteins react to environmental signals by using built-in sensors that continually monitor cellular condit ...
... Cells respond to intrinsic and extrinsic signals by modulating transcriptional control of certain genes Gene activity is the result of the function of cis- and trans-acting factors Trans-acting proteins react to environmental signals by using built-in sensors that continually monitor cellular condit ...
Ligand Binding - Stroud -Lecture 1
... at millisecond intervals by synchrotron hydroxyl radical footprinting. 1998 Science 279, ...
... at millisecond intervals by synchrotron hydroxyl radical footprinting. 1998 Science 279, ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.