Genetic Technology
... is now recombinant DNA molecule) Put back into bacteria Many reproductive cycles later = amplification of gene & protein it makes ...
... is now recombinant DNA molecule) Put back into bacteria Many reproductive cycles later = amplification of gene & protein it makes ...
Bio 210 Cell Chemistry Lecture 5 “Proteins and Nucleic Acids”
... acetyl choline receptor: nerve cell ...
... acetyl choline receptor: nerve cell ...
Fifth Lecture
... during mitosis and transcription of genetic information. • In addition, radiation can cause structural aberrations with pieces of the chromosomes break and form aberrant shapes. • Unequal division of nuclear chromatin material between daughter cells may result in production of nonviable, abnormal nu ...
... during mitosis and transcription of genetic information. • In addition, radiation can cause structural aberrations with pieces of the chromosomes break and form aberrant shapes. • Unequal division of nuclear chromatin material between daughter cells may result in production of nonviable, abnormal nu ...
Y13 Biology Y2 PLCs Student Teacher 1
... Glycolysis is the first stage of anaerobic and aerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm and is an anaerobic process. Glycolysis involves the following stages: phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate, using ATP production of triose phosphate oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruv ...
... Glycolysis is the first stage of anaerobic and aerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm and is an anaerobic process. Glycolysis involves the following stages: phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate, using ATP production of triose phosphate oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruv ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... Primary sequence reveals important clues about a protein • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly conserved regions that are important for function. • Clus ...
... Primary sequence reveals important clues about a protein • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly conserved regions that are important for function. • Clus ...
Gene Expression and DNA Replication
... Gene Expression and DNA Replication • Transcription, the first stage in gene expression, involves transfer of information found in a double-stranded DNA molecule to the base sequence of a single-stranded RNA molecule. If the RNA molecule is a messenger RNA, then the process known as translation con ...
... Gene Expression and DNA Replication • Transcription, the first stage in gene expression, involves transfer of information found in a double-stranded DNA molecule to the base sequence of a single-stranded RNA molecule. If the RNA molecule is a messenger RNA, then the process known as translation con ...
Protein and Amino Acid
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
DNA and Gene Expression - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... tRNAs are charged by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Each enzyme is specific for one amino acid and its corresponding tRNA. Translation occurs at a ribosome. It holds mRNA and charged tRNAs in the correct position to allow assembly of the polypeptide. Ribosomes can make any type of protein, they can be ...
... tRNAs are charged by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Each enzyme is specific for one amino acid and its corresponding tRNA. Translation occurs at a ribosome. It holds mRNA and charged tRNAs in the correct position to allow assembly of the polypeptide. Ribosomes can make any type of protein, they can be ...
SynCAM2a ΔPDZ Δ4.1B ΔPDZ - University of Oregon (SPUR)
... A capillary needle is used to inject 3-4 nL of the DNA constructs into one cell embryos. ...
... A capillary needle is used to inject 3-4 nL of the DNA constructs into one cell embryos. ...
RNA and DNA aptamers. Ribozymes and DNAzymes Daniel
... Aptamers: molecules that bind other molecules with good affinity and specificity Usually these are proteins . . . . But they can also be RNA or DNA. That is, single stranded RNA or DNA molecules can and will fold up into secondary and tertiary structures depending on their sequence. DNA can be synth ...
... Aptamers: molecules that bind other molecules with good affinity and specificity Usually these are proteins . . . . But they can also be RNA or DNA. That is, single stranded RNA or DNA molecules can and will fold up into secondary and tertiary structures depending on their sequence. DNA can be synth ...
ppt - Duke Computer Science
... Aptamers: molecules that bind other molecules with good affinity and specificity Usually these are proteins . . . . But they can also be RNA or DNA. That is, single stranded RNA or DNA molecules can and will fold up into secondary and tertiary structures depending on their sequence. DNA can be synth ...
... Aptamers: molecules that bind other molecules with good affinity and specificity Usually these are proteins . . . . But they can also be RNA or DNA. That is, single stranded RNA or DNA molecules can and will fold up into secondary and tertiary structures depending on their sequence. DNA can be synth ...
Proteins = polymers of 20 amino acids, connected by peptide bonds
... This course is aimed at first and second year graduate students and advanced undergraduates interested in understanding the structures and mechanisms of macromolecular structures in biology. You will learn about the physical basis for these structures, their folding, stability, and interactions with ...
... This course is aimed at first and second year graduate students and advanced undergraduates interested in understanding the structures and mechanisms of macromolecular structures in biology. You will learn about the physical basis for these structures, their folding, stability, and interactions with ...
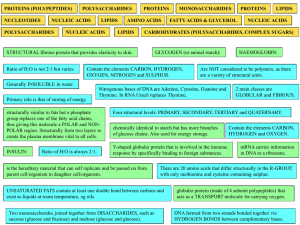
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
... thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
... thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
Document
... Antisense RNAs are small, highly structured single-stranded molecules that act through sequence complementarity to inhibit target RNA (sense RNA) function. Mechanisms of regulation :(1) translation blockage by antisense hybridization to target mRNAs; (2) translation initiation inhibition by occlusio ...
... Antisense RNAs are small, highly structured single-stranded molecules that act through sequence complementarity to inhibit target RNA (sense RNA) function. Mechanisms of regulation :(1) translation blockage by antisense hybridization to target mRNAs; (2) translation initiation inhibition by occlusio ...
Comprehenexam- - HCC Learning Web
... A. In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around _____________________ B. What kind of chemical bond is found between paired bases of the DNA double helix? ____ C. Which of the following separates the DNA strands during replication? __________ D. Which of the following covalently connects segments of D ...
... A. In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around _____________________ B. What kind of chemical bond is found between paired bases of the DNA double helix? ____ C. Which of the following separates the DNA strands during replication? __________ D. Which of the following covalently connects segments of D ...
Gene expression Most genes are not expressed at a particular time
... expression patterns of the lambda genes UV light activates a bacterial protein called recA. recA is primarily a DNA repair enzyme, but it also has the effect of cleaving the repressor molecule ...
... expression patterns of the lambda genes UV light activates a bacterial protein called recA. recA is primarily a DNA repair enzyme, but it also has the effect of cleaving the repressor molecule ...
ranjan rajeev
... 1. National Institute of Plant Genome Research, New Delhi, India 2. Department of Plant Molecular Biology, University of Delhi South Campus, New Delhi, India ...
... 1. National Institute of Plant Genome Research, New Delhi, India 2. Department of Plant Molecular Biology, University of Delhi South Campus, New Delhi, India ...
Quantitative RT-PCR
... Any degraded RNA samples should not be used for the quantitative analysis. 2. Primer Design for RT-PCR a. Design both 5' sense primer and 3' antisense primer for PCR following the classical parameters for primer design. The 3' primer will also be used for reverse transcription. The length of the amp ...
... Any degraded RNA samples should not be used for the quantitative analysis. 2. Primer Design for RT-PCR a. Design both 5' sense primer and 3' antisense primer for PCR following the classical parameters for primer design. The 3' primer will also be used for reverse transcription. The length of the amp ...
Document
... RNA processing mRNA transport mRNA degradation and storage 5. Translation 6. Posttranslational modulation of protein activity ...
... RNA processing mRNA transport mRNA degradation and storage 5. Translation 6. Posttranslational modulation of protein activity ...
Slide 1
... • Why make oligo analogues? – Structure/activity relationships (i.e., catalytic versatility) – Antisense technology – Insight into evolutionary process? ...
... • Why make oligo analogues? – Structure/activity relationships (i.e., catalytic versatility) – Antisense technology – Insight into evolutionary process? ...
Boolean models of gene regulatory networks
... Some genes code for proteins. Others (e.g., rRNA, tRNA) code for functional RNA. ...
... Some genes code for proteins. Others (e.g., rRNA, tRNA) code for functional RNA. ...
Gene Section RARRES1 (retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1)
... involved in the malignant progression of prostate cancer. Restoration of RARRES1 expression in malignant prostate cell lines led to a decrease of invasiveness and tumorigenicity in nude mice. It is speculated that RARRES1 may function as a cell adhesion molecule. Since the protein shows sequence sim ...
... involved in the malignant progression of prostate cancer. Restoration of RARRES1 expression in malignant prostate cell lines led to a decrease of invasiveness and tumorigenicity in nude mice. It is speculated that RARRES1 may function as a cell adhesion molecule. Since the protein shows sequence sim ...
FREE Sample Here
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
The amino acids, peptide bonds, and the primary structure of proteins
... After translation, some proteins undergo further covalent modification • Proteolytic processing • Phosphorylation: addition of a phosphate group (PO43-) to a Ser or Tyr residue. • Glycosylation: addition of sugar groups to Asn (Nglycosylation) or Ser (O-glycosylation). • Alteration of chain termini ...
... After translation, some proteins undergo further covalent modification • Proteolytic processing • Phosphorylation: addition of a phosphate group (PO43-) to a Ser or Tyr residue. • Glycosylation: addition of sugar groups to Asn (Nglycosylation) or Ser (O-glycosylation). • Alteration of chain termini ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.