PDCD8 Antibody
... mitochondrial intermembrane space in healthy cells. Induction of apoptosis results in the translocation of this protein to the nucleus where it effects chromosome condensation and fragmentation. In addition, AIFM1 induces mitochondria to release the apoptogenic proteins cytochrome c and caspase-9.Th ...
... mitochondrial intermembrane space in healthy cells. Induction of apoptosis results in the translocation of this protein to the nucleus where it effects chromosome condensation and fragmentation. In addition, AIFM1 induces mitochondria to release the apoptogenic proteins cytochrome c and caspase-9.Th ...
Proteins
... • Lipoproteins--contain fatty acids – Good emulsifiers – Provide mechanism for lipid transport – Occur in membranes ...
... • Lipoproteins--contain fatty acids – Good emulsifiers – Provide mechanism for lipid transport – Occur in membranes ...
THE CENTRAL DOGMA THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... The Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary – the covalent bonded amino acid sequence ...
... The Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary – the covalent bonded amino acid sequence ...
04Johnson
... 4.2 Proteins • Proteins fold specifically the folding process is helped by special proteins called chaperone proteins • these proteins somehow correct a misfolded protein • defective chaperon proteins may play a role in certain genetic disorders that involve defective proteins ...
... 4.2 Proteins • Proteins fold specifically the folding process is helped by special proteins called chaperone proteins • these proteins somehow correct a misfolded protein • defective chaperon proteins may play a role in certain genetic disorders that involve defective proteins ...
BIOL562_Lecture_12
... polymerase in most mRNAs; signals in pre-mRNA are recognized by cleavage & polyA specificity factor (CPSF) & stimulation factor (CstF), polyA binding protein (PADP) helps to recruit As. Significance: mRNA stability & translation. ...
... polymerase in most mRNAs; signals in pre-mRNA are recognized by cleavage & polyA specificity factor (CPSF) & stimulation factor (CstF), polyA binding protein (PADP) helps to recruit As. Significance: mRNA stability & translation. ...
Editable PPT - Science Prof Online
... Rarely leads to a protein having a novel property that improves ability of organism and its descendants to ...
... Rarely leads to a protein having a novel property that improves ability of organism and its descendants to ...
Gene Section RAD51L3 (RAD51 like 3 (S. cerevisiae)) -
... insertion of proline at the 36th protein position rather than a serine. A third mutation observed is noted to occur at mRNA positions 810 (SNP ID: rs4796033). A mutation at this location results in a sequence of CAG (from the natural CGG). The effect of this substitution is the insertion of a glutam ...
... insertion of proline at the 36th protein position rather than a serine. A third mutation observed is noted to occur at mRNA positions 810 (SNP ID: rs4796033). A mutation at this location results in a sequence of CAG (from the natural CGG). The effect of this substitution is the insertion of a glutam ...
Objectives – Translation Part I
... Objectives – Translation Part II 1. Describe the entire process of translation in prokaryotes. Be sure to include all necessary components, including the specific roles of IF’s, EF’s and RF’s. 2. How does the initiator tRNA differ from all other tRNA’s in translation? 3. What is the total energy exp ...
... Objectives – Translation Part II 1. Describe the entire process of translation in prokaryotes. Be sure to include all necessary components, including the specific roles of IF’s, EF’s and RF’s. 2. How does the initiator tRNA differ from all other tRNA’s in translation? 3. What is the total energy exp ...
BIO PLACEMENT TEST REVIEW QUESTIONS Review 1: Answer
... 1) A primary source of scientific results is ___ A) The news media B) Anecdotes from others C) Articles in peer- reviewed journals D) The internet E) All of the above 2) A guess in a scientific process is called __; a unifying explanation for a range of observations is termed___? A) Theory: Hypothes ...
... 1) A primary source of scientific results is ___ A) The news media B) Anecdotes from others C) Articles in peer- reviewed journals D) The internet E) All of the above 2) A guess in a scientific process is called __; a unifying explanation for a range of observations is termed___? A) Theory: Hypothes ...
Lecture 16-LC710 Posted
... Nothing. It is the usage which differs. A primer is always used with a polymerase. An oligo is simply a chain of nucleotides ...
... Nothing. It is the usage which differs. A primer is always used with a polymerase. An oligo is simply a chain of nucleotides ...
Name
... Nothing. It is the usage which differs. A primer is always used with a polymerase. An oligo is simply a chain of nucleotides ...
... Nothing. It is the usage which differs. A primer is always used with a polymerase. An oligo is simply a chain of nucleotides ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Principles of Biochemistry. 4th Edition International Student Version Brochure
... 24 DNA Structure and Interactions with Proteins 821 25 DNA Synthesis and Repair 867 26 RNA Metabolism 919 27 The Genetic Code and Translation 962 28 Gene Expression in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1013 Solutions to Odd–Numbered Problems SP–1 Glossary G–1 Index I–1 ...
... 24 DNA Structure and Interactions with Proteins 821 25 DNA Synthesis and Repair 867 26 RNA Metabolism 919 27 The Genetic Code and Translation 962 28 Gene Expression in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1013 Solutions to Odd–Numbered Problems SP–1 Glossary G–1 Index I–1 ...
Review: proteins
... 3. There are _______________ kinds of amino acids, differing from each other only in their ______________ groups. 4. There are _______________ amino acids that humans can't manufacture, these must be obtained from food. They are called _______________ amino acids. 5. Use the following words to descr ...
... 3. There are _______________ kinds of amino acids, differing from each other only in their ______________ groups. 4. There are _______________ amino acids that humans can't manufacture, these must be obtained from food. They are called _______________ amino acids. 5. Use the following words to descr ...
Supplementary Figure 7 (ppt 226K)
... Supplementary Figure 7 Exogenous miR-34b/c over-expression does not completely counteract c-Myc stabilization induced by CDDP (2 µg/ml). Evaluation of the expression levels of (a) miR-34b and miR-34c, and (b) c-Myc, carried out by qRT-PCR (miRscript kit by Qiagen) and western blot analysis, respecti ...
... Supplementary Figure 7 Exogenous miR-34b/c over-expression does not completely counteract c-Myc stabilization induced by CDDP (2 µg/ml). Evaluation of the expression levels of (a) miR-34b and miR-34c, and (b) c-Myc, carried out by qRT-PCR (miRscript kit by Qiagen) and western blot analysis, respecti ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard
... information. • This information is put to work through the production of proteins. • Proteins fold into complex, threedimensional shapes to become key cell structures and regulators of cell functions. ...
... information. • This information is put to work through the production of proteins. • Proteins fold into complex, threedimensional shapes to become key cell structures and regulators of cell functions. ...
Central dogma of molecular biology
... RNA that is required for DNA synthesis from a naked DNA template. • There is no known DNA polymerase that can initiate synthesis of a DNA strand – they can only add nucleotides to a pre-existing strand. • Don’t confuse a template with a primer. ...
... RNA that is required for DNA synthesis from a naked DNA template. • There is no known DNA polymerase that can initiate synthesis of a DNA strand – they can only add nucleotides to a pre-existing strand. • Don’t confuse a template with a primer. ...
Methods S1.
... minutes until theNP‐40 became cloudy, then cooled down to room temperature. Samples were then centrifuged for 2 minutes to remove any insoluble material. Triglyceride determination with the VetAce autoanalyzer consisted in their initial breakdown into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol is then oxidi ...
... minutes until theNP‐40 became cloudy, then cooled down to room temperature. Samples were then centrifuged for 2 minutes to remove any insoluble material. Triglyceride determination with the VetAce autoanalyzer consisted in their initial breakdown into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol is then oxidi ...
CS5238: Combinatorial Methods in Computation
... The translation stop once ribosome read the stop codon (translation stop site) ...
... The translation stop once ribosome read the stop codon (translation stop site) ...
Lecture 33
... Unpunctuated – although some codons are signals Mutations - in coding region can cause various ill-effects, such as, change in desired amino acids, early or late stop, insertion, etc. ...
... Unpunctuated – although some codons are signals Mutations - in coding region can cause various ill-effects, such as, change in desired amino acids, early or late stop, insertion, etc. ...
pdf - NUS Computing
... The translation stop once ribosome read the stop codon (translation stop site) ...
... The translation stop once ribosome read the stop codon (translation stop site) ...
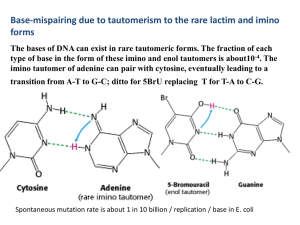
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent for informational base pairing. Note: additional OH at 2' equatorial results in a steric clash between this OH and the neighboring nucleobase. ...
... than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent for informational base pairing. Note: additional OH at 2' equatorial results in a steric clash between this OH and the neighboring nucleobase. ...
Topic 2 Review
... codon in the A site with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA with its amino acid. Peptide bond formation: component of large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid extending from the P site and the newly arrived amino acid in the A site. The poly ...
... codon in the A site with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA with its amino acid. Peptide bond formation: component of large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid extending from the P site and the newly arrived amino acid in the A site. The poly ...
6.5 - Institut für Philosophie (HU Berlin)
... 6.3 Molecular Genetics transcription & translation ...
... 6.3 Molecular Genetics transcription & translation ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.