E U F T DG Unfolded state, ensemble Native fold, one
... chains may or may not contribute. For the latter, mutations have little effect. ...
... chains may or may not contribute. For the latter, mutations have little effect. ...
MBG305_LS_01
... body (an exception is, for example, red blood cells which have no nucleus and therefore no DNA) – a total of ~1022 nucleotides! • Many DNA regions code for proteins, and are called genes (1 gene codes for 1 protein as a base rule, but the reality is a lot more complicated) – Name examples ...
... body (an exception is, for example, red blood cells which have no nucleus and therefore no DNA) – a total of ~1022 nucleotides! • Many DNA regions code for proteins, and are called genes (1 gene codes for 1 protein as a base rule, but the reality is a lot more complicated) – Name examples ...
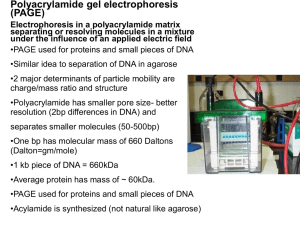
Polyacrylamide gels
... Pore size is determined by % acrylamide and the amount of cross linker The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
... Pore size is determined by % acrylamide and the amount of cross linker The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... Link together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain Only 20 amino acids ...
... Link together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain Only 20 amino acids ...
Manual: Universal Human miRNA Reference RNA
... Stratagene Universal Human miRNA Reference RNA is an ideal reference control for miRNA microarray or miRNA-targeted QRTPCR experiments. The Universal Human miRNA Reference RNA may also be used as an optimization or standardization reagent for these or other applications aimed at human miRNA analysis ...
... Stratagene Universal Human miRNA Reference RNA is an ideal reference control for miRNA microarray or miRNA-targeted QRTPCR experiments. The Universal Human miRNA Reference RNA may also be used as an optimization or standardization reagent for these or other applications aimed at human miRNA analysis ...
Exam #2 Bio310 Microbiology F`06 11/15/06
... b.) After inoculation and a week in the incubator you put your gelatin tube in an ice bath for ten minutes and it hardened (does not flow when turned upside down). Bacterium produces gelatinase, which enables it to break down gelatin for food. Breakdown of gelatin results in the tube staying liquid ...
... b.) After inoculation and a week in the incubator you put your gelatin tube in an ice bath for ten minutes and it hardened (does not flow when turned upside down). Bacterium produces gelatinase, which enables it to break down gelatin for food. Breakdown of gelatin results in the tube staying liquid ...
biochemistry, cell and molecular biology test
... and binds to unfolded proteins, thereby preventing them from aggregating. c. It binds to unfolded proteins in the lumen of the ER and adds glucose molecules, which then bind to calnexin. d. It is the enzyme that adds a large preformed oligosaccharide onto asparagine residues in proteins. e. It glyco ...
... and binds to unfolded proteins, thereby preventing them from aggregating. c. It binds to unfolded proteins in the lumen of the ER and adds glucose molecules, which then bind to calnexin. d. It is the enzyme that adds a large preformed oligosaccharide onto asparagine residues in proteins. e. It glyco ...
The control of gene expression
... Polycistronic mRNA = a large mRNA molecule that is a transcript of several genes. Is translated into separate polypeptides Contains stop and start codons for the translation of each polypeptide. Grouping structural genes into operons is advantageous because: Expression of these genes can be c ...
... Polycistronic mRNA = a large mRNA molecule that is a transcript of several genes. Is translated into separate polypeptides Contains stop and start codons for the translation of each polypeptide. Grouping structural genes into operons is advantageous because: Expression of these genes can be c ...
HRB/MRCG 2011/7 Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of
... temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). The background to this was the knowledge that TLE is associated large-scale, wide-ranging changes in gene expression. Identifying mechanisms controlling those gene changes could lead to deeper understanding of causes of the disease and also new approaches to treatment. ...
... temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). The background to this was the knowledge that TLE is associated large-scale, wide-ranging changes in gene expression. Identifying mechanisms controlling those gene changes could lead to deeper understanding of causes of the disease and also new approaches to treatment. ...
Facile Kinase Activation with Membrane Permeable Small
... screen protein activity in living cells or to study protein function, it is valuable to have the capacity to turn proteins “on” or “off”. This can be done via genetic manipulation. However, genetic manipulation is slow and can lead to compensatory mechanisms within the cell that alter protein functi ...
... screen protein activity in living cells or to study protein function, it is valuable to have the capacity to turn proteins “on” or “off”. This can be done via genetic manipulation. However, genetic manipulation is slow and can lead to compensatory mechanisms within the cell that alter protein functi ...
Statistical Analysis of Gene Expression Micro Arrays
... Even though entire DNA strands exist in chromatin form at times, they can be unpacked to allow access to certain strands for protein production and replication. Methylation occurs, meaning the process when the DNA is unpacked and methyl groups (CH3) groups are placed on the ends of the DNA strand fo ...
... Even though entire DNA strands exist in chromatin form at times, they can be unpacked to allow access to certain strands for protein production and replication. Methylation occurs, meaning the process when the DNA is unpacked and methyl groups (CH3) groups are placed on the ends of the DNA strand fo ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... • A lot of DNA consists of long stretches of repeated nucleotides . • These vary between individuals and can be separated using gel electrophoresis. • Dna profiling usually uses about 10 STR’s ...
... • A lot of DNA consists of long stretches of repeated nucleotides . • These vary between individuals and can be separated using gel electrophoresis. • Dna profiling usually uses about 10 STR’s ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
handout nucleic acids and DNA replication
... The code for primary structure cannot be carried in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA since this structure is identical in all DNA molecules. The only part of DNA that varies between different molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of am ...
... The code for primary structure cannot be carried in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA since this structure is identical in all DNA molecules. The only part of DNA that varies between different molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of am ...
DNA Oncovirus
... • Promotes cancer in ways other than direct DNA damage/ do not change the primary sequence of DNA • Alter the expression or repression of certain genes and cellular events related to proliferation and differentiation • Promoters, hormone modifying agents, peroxisome proliferators, cytotoxic agents, ...
... • Promotes cancer in ways other than direct DNA damage/ do not change the primary sequence of DNA • Alter the expression or repression of certain genes and cellular events related to proliferation and differentiation • Promoters, hormone modifying agents, peroxisome proliferators, cytotoxic agents, ...
bioknowledgy note pkt - Peoria Public Schools
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
Griffith`s Experiment
... 1. Store Information – Information is stored in the order and amount of nucleotides that make up the DNA. The sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait is called a … Gene 2. Copy Information – During S of Interphase your cells replicate the DNA. 3. Transmitting Information – Copies of all of ...
... 1. Store Information – Information is stored in the order and amount of nucleotides that make up the DNA. The sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait is called a … Gene 2. Copy Information – During S of Interphase your cells replicate the DNA. 3. Transmitting Information – Copies of all of ...
2. Molecular Biology (Core) – 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA Name
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
0101BWhat characterizes a prokaryotic cell
... b) cells c) isomers d) monomers e) isotopes __38) Which of the following is not a macromolecule? a) protein b) starch c) nucleotide d) lipid e) DNA __39) A(n) ____________ is a basic unit of a carbohydrate. a) monosaccharide b) starch c) nucleotide d) glycerol e) amino acids __40) Which of the follo ...
... b) cells c) isomers d) monomers e) isotopes __38) Which of the following is not a macromolecule? a) protein b) starch c) nucleotide d) lipid e) DNA __39) A(n) ____________ is a basic unit of a carbohydrate. a) monosaccharide b) starch c) nucleotide d) glycerol e) amino acids __40) Which of the follo ...
RNAzol RT (R4533) - Technical Bulletin - Sigma
... total and small RNA and can be completed at room temperature in less than 1 hour starting with fresh tissue or cells. The protocol for isolation of mRNA and micro RNA yields two fractions – an mRNA-containing fraction consisting of RNA of >200 bases and a micro RNA-containing fraction consisting of ...
... total and small RNA and can be completed at room temperature in less than 1 hour starting with fresh tissue or cells. The protocol for isolation of mRNA and micro RNA yields two fractions – an mRNA-containing fraction consisting of RNA of >200 bases and a micro RNA-containing fraction consisting of ...
ppt - Department of Plant Sciences
... Figure 8.17 Excision of selectable marker gene following T-DNA insertion into the plant genome. XVE is a chimeric transcription factor. It contains three functional domains, a LexA DNA binding domain (X), the VP16 activation domain (V), and the estrogen receptor binding domain (E). The G10-90 promot ...
... Figure 8.17 Excision of selectable marker gene following T-DNA insertion into the plant genome. XVE is a chimeric transcription factor. It contains three functional domains, a LexA DNA binding domain (X), the VP16 activation domain (V), and the estrogen receptor binding domain (E). The G10-90 promot ...
in Power-Point Format
... • Quantifying (how much transcript at a set time) • Transcripts often not uniform terminator -: continuum of species smeared on gel • Techniques specific for sequence of interest • Nuclease S1 mapping locates 5’ and 3’ ends (later) ...
... • Quantifying (how much transcript at a set time) • Transcripts often not uniform terminator -: continuum of species smeared on gel • Techniques specific for sequence of interest • Nuclease S1 mapping locates 5’ and 3’ ends (later) ...
Investigating regulation of aging by transcription factors DAF 16 and
... Aging in eukaryotic organisms is a deleterious process that can result in changes in metabolism, reproduction and physiology. Mutations and accretion of damaged proteins that lead to different diseases eventually lead to a decreased lifespan (Eleftherianos and Castillo 2012). Observing the dispropor ...
... Aging in eukaryotic organisms is a deleterious process that can result in changes in metabolism, reproduction and physiology. Mutations and accretion of damaged proteins that lead to different diseases eventually lead to a decreased lifespan (Eleftherianos and Castillo 2012). Observing the dispropor ...
5`ccugaugcaugccuagaugccauaacgggcuuaaauagauga3`
... 15. Three types of RNA polymerases are used in eukaryotic transcription. Which statement concerning eukaryotic RNA polymerases is CORRECT? a) All RNA polymerases have a carboxy-terminal domain that becomes phosphorylated. b) RNA polymerase I transcribes genes coding for pre-rRNA. c) RNA polymerase I ...
... 15. Three types of RNA polymerases are used in eukaryotic transcription. Which statement concerning eukaryotic RNA polymerases is CORRECT? a) All RNA polymerases have a carboxy-terminal domain that becomes phosphorylated. b) RNA polymerase I transcribes genes coding for pre-rRNA. c) RNA polymerase I ...
PDCD8 Antibody
... mitochondrial intermembrane space in healthy cells. Induction of apoptosis results in the translocation of this protein to the nucleus where it effects chromosome condensation and fragmentation. In addition, AIFM1 induces mitochondria to release the apoptogenic proteins cytochrome c and caspase-9.Th ...
... mitochondrial intermembrane space in healthy cells. Induction of apoptosis results in the translocation of this protein to the nucleus where it effects chromosome condensation and fragmentation. In addition, AIFM1 induces mitochondria to release the apoptogenic proteins cytochrome c and caspase-9.Th ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.