CIT - Cork Institute of Technology
... b) In relation to point mutations within a coding region of a gene, differentiate between the following mutations and indicate their effect at an amino acid level. ...
... b) In relation to point mutations within a coding region of a gene, differentiate between the following mutations and indicate their effect at an amino acid level. ...
Reverse_Transcription_PCR
... basic enzymatic properties enzyme’s level of RNase H activity the length of the target RNA presence of complex RNA secondary structure downstream application ...
... basic enzymatic properties enzyme’s level of RNase H activity the length of the target RNA presence of complex RNA secondary structure downstream application ...
Naming Conventions The NCBI RefSeq human mRNA
... The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) finds regions of local similarity between sequences. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches. BLAST can be used to infer functional and evolutionary relationships b ...
... The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) finds regions of local similarity between sequences. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches. BLAST can be used to infer functional and evolutionary relationships b ...
Structure/Function studies on urokinase plasminogen activator
... Lys220 and uPAR-Arg220 proteins to 1.25-Å resolution. This will be achieved by recombinant expression and crystallography essentially as described (6). We will also determine the structure for novel coding region variants identified in our sequencing analyses that show functional effects in 1. 3. Is ...
... Lys220 and uPAR-Arg220 proteins to 1.25-Å resolution. This will be achieved by recombinant expression and crystallography essentially as described (6). We will also determine the structure for novel coding region variants identified in our sequencing analyses that show functional effects in 1. 3. Is ...
Introduction to
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
A1980JQ46200001
... ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to carboxylate sidechains in the protein. 1 My results appeared to rule out all but very weak associations. “When I moved on to work in John Edsall’s laboratory at Harvard it was inevitable that, in addition to my primary work on myosin, I became involved in ...
... ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to carboxylate sidechains in the protein. 1 My results appeared to rule out all but very weak associations. “When I moved on to work in John Edsall’s laboratory at Harvard it was inevitable that, in addition to my primary work on myosin, I became involved in ...
DNA and protein synthesis
... cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), because each of our 46 chromosomes contains one DNA molecule. The DNA molecule ...
... cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), because each of our 46 chromosomes contains one DNA molecule. The DNA molecule ...
1 - contentextra
... and proteins. It is an amide link. Phospholipid A lipid consisting of two fatty acids condensed with a glycerol molecule and a phosphate group. These molecules have distinct hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts and are important in membrane structures. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) A technique used t ...
... and proteins. It is an amide link. Phospholipid A lipid consisting of two fatty acids condensed with a glycerol molecule and a phosphate group. These molecules have distinct hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts and are important in membrane structures. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) A technique used t ...
Macromolecules 2: Proteins and Nucleic Acids Amino Acids differ
... • Sometimes a single functional PROTEIN is made of several POLYPEPTIDES that work together as a unit ...
... • Sometimes a single functional PROTEIN is made of several POLYPEPTIDES that work together as a unit ...
Revised Higher Human Biology Unit 1 Revision Summary STEM
... into messenger RNA (mRNA), which will leave the nucleus. This process is called transcription. A region of DNA, called a promoter, initiates transcription. RNA polymerase is the enzyme used to add RNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the DNA strand. Due to base pairing, a complementary copy of DNA is ta ...
... into messenger RNA (mRNA), which will leave the nucleus. This process is called transcription. A region of DNA, called a promoter, initiates transcription. RNA polymerase is the enzyme used to add RNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the DNA strand. Due to base pairing, a complementary copy of DNA is ta ...
The Process Whereby Your Genes Make Your Proteins
... The Process Whereby Your Genes Make Your Proteins You don’t have to have a science degree to understand the means by which your genes influence your health. You do, however, need to know a little bit about the process by which your genes make your proteins. Once you understand the process whereby yo ...
... The Process Whereby Your Genes Make Your Proteins You don’t have to have a science degree to understand the means by which your genes influence your health. You do, however, need to know a little bit about the process by which your genes make your proteins. Once you understand the process whereby yo ...
Unit 13 Biotechnology
... Transcription • Process of producing a messenger RNA copy using the DNA template. • mRNA takes the message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm • In RNA, there is no thymine (T) • In RNA, sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose • Base-pairing in RNA – A-U – C-G ...
... Transcription • Process of producing a messenger RNA copy using the DNA template. • mRNA takes the message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm • In RNA, there is no thymine (T) • In RNA, sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose • Base-pairing in RNA – A-U – C-G ...
Lecture2_Chap1 File
... encodes the protein hexokinase is first transcribed into a ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule with the complementary ribonucleotide sequence. The RNA sequence (messenger RNA) is then translated into the linear protein chain of hexokinase, which folds into its native three-dimensional shape, most likely ...
... encodes the protein hexokinase is first transcribed into a ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule with the complementary ribonucleotide sequence. The RNA sequence (messenger RNA) is then translated into the linear protein chain of hexokinase, which folds into its native three-dimensional shape, most likely ...
Sequencing and Phylogeny - World Health Organization
... Sequencing Process to determine the exact order of nucleotides in DNA ...
... Sequencing Process to determine the exact order of nucleotides in DNA ...
Day 2 Western blotting
... dithiothreitol /DTT). Proteins solubilised in SDS bind the detergent uniformly along their length to a level of 1.4g SDS/g protein. This creates a charge/mass ratio which is consistent between proteins. For this reason, separation on a polyacrylamide gel in the presence of SDS occurs by mass alone, ...
... dithiothreitol /DTT). Proteins solubilised in SDS bind the detergent uniformly along their length to a level of 1.4g SDS/g protein. This creates a charge/mass ratio which is consistent between proteins. For this reason, separation on a polyacrylamide gel in the presence of SDS occurs by mass alone, ...
Chapter 3
... Lack of the –OH group on each #2 carbon of the deoxyribose sugar decreases its reactivity. The double-strand nature of the molecule increases its stability. The hydrophobic interior of DNA is difficult to disrupt due to "hydrophobic bonding" between the nonpolar nitrogenous bases that orient toward ...
... Lack of the –OH group on each #2 carbon of the deoxyribose sugar decreases its reactivity. The double-strand nature of the molecule increases its stability. The hydrophobic interior of DNA is difficult to disrupt due to "hydrophobic bonding" between the nonpolar nitrogenous bases that orient toward ...
Recombinant DNA key
... a. Assuming you are reading the non-coding strand and that there are no introns, find an open reading frame (ORF) in this region. Circle the point where translation will start, and put a box around the point where translation will stop. Then give the number of amino acids in the protein this gene wo ...
... a. Assuming you are reading the non-coding strand and that there are no introns, find an open reading frame (ORF) in this region. Circle the point where translation will start, and put a box around the point where translation will stop. Then give the number of amino acids in the protein this gene wo ...
PowerPoint - Biological Sciences
... • The leader peptide retards the folding of the protein so that molecular chaperone proteins can interact with it and direct its folding • The leader peptide also provides recognition signals for the translocation machinery • A leader peptidase removes the leader sequence when folding and targeting ...
... • The leader peptide retards the folding of the protein so that molecular chaperone proteins can interact with it and direct its folding • The leader peptide also provides recognition signals for the translocation machinery • A leader peptidase removes the leader sequence when folding and targeting ...
Is the process of manipulating genes and genomes Biotechnology
... -Is the process of manipulating organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products ...
... -Is the process of manipulating organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products ...
Press Release
... led by Lars Steinmetz has turned this on its head. The researchers have shown that one end of the mRNA begins to decay while the other is still serving as a template for protein production. Thus, studying the decaying mRNA also provides a snapshot of how proteins are produced. The discovery was made ...
... led by Lars Steinmetz has turned this on its head. The researchers have shown that one end of the mRNA begins to decay while the other is still serving as a template for protein production. Thus, studying the decaying mRNA also provides a snapshot of how proteins are produced. The discovery was made ...
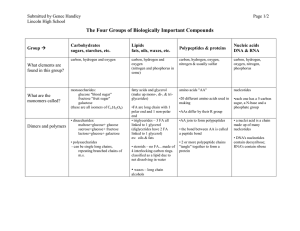
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
没有幻灯片标题
... 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protei ...
... 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protei ...
proteins and protein structure
... protein that it needs to carry out its life activities. Having certain amino acids in certain positions is crucial to the protein’s overall shape and consequently to its function. For example, the change of just one amino acid alters the shape of hemoglobin enough to create the condition of sickle c ...
... protein that it needs to carry out its life activities. Having certain amino acids in certain positions is crucial to the protein’s overall shape and consequently to its function. For example, the change of just one amino acid alters the shape of hemoglobin enough to create the condition of sickle c ...
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) enables researchers to
... 3) Genes commonly used to alter plants Genes are never transferred alone. They are parts of constructs, known as ‘expression cassettes’. Each gene is sandwiched between a promoter, which signals the cell to turn the foreign gene on and a ...
... 3) Genes commonly used to alter plants Genes are never transferred alone. They are parts of constructs, known as ‘expression cassettes’. Each gene is sandwiched between a promoter, which signals the cell to turn the foreign gene on and a ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.