Document
... living things have the same 4 base pairs in their DNA Amino acid similarities between organisms ...
... living things have the same 4 base pairs in their DNA Amino acid similarities between organisms ...
Change over Time (2)
... selection. After two groups have separated, natural selection may act on each group in different ways. Division Over many generations, two separated groups of a population may become very different until the point when they can no longer mate with one another. At this point, the two groups are no lo ...
... selection. After two groups have separated, natural selection may act on each group in different ways. Division Over many generations, two separated groups of a population may become very different until the point when they can no longer mate with one another. At this point, the two groups are no lo ...
Evolution, 9-3
... combination of characters and that share a common ancestor. Reproductive compatibility is not a criterion for deciding whether individuals belong to the same species or not. ...
... combination of characters and that share a common ancestor. Reproductive compatibility is not a criterion for deciding whether individuals belong to the same species or not. ...
Chapter 15 Evolution outline
... *new life forms that appear in fossil record are modified descendents from older species *he also inferred that all species descended from one or a few original types of organisms. 2) Modification by Natural Selection *Environment limits the growth of populations by increasing the rate of death or d ...
... *new life forms that appear in fossil record are modified descendents from older species *he also inferred that all species descended from one or a few original types of organisms. 2) Modification by Natural Selection *Environment limits the growth of populations by increasing the rate of death or d ...
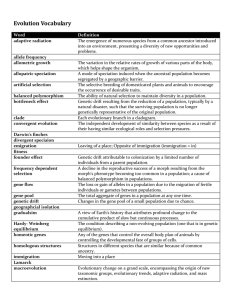
Evolution Vocabulary
... A view of Earth's history that attributes profound change to the cumulative product of slow but continuous processes. The condition describing a non-evolving population (one that is in genetic equilibrium). Any of the genes that control the overall body plan of animals by controlling the development ...
... A view of Earth's history that attributes profound change to the cumulative product of slow but continuous processes. The condition describing a non-evolving population (one that is in genetic equilibrium). Any of the genes that control the overall body plan of animals by controlling the development ...
evolution - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... The leaves of an oak (left) and the leaves of a gingko (right) are homologous — they were both inherited from a common ancestor with leaves. ...
... The leaves of an oak (left) and the leaves of a gingko (right) are homologous — they were both inherited from a common ancestor with leaves. ...
- mrsolson.com
... C. normal-sized muslces that would become larger only when the children lifted weights D. larger-than-average muscles 31. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection A. individuals are modified by adverse environmental conditions B. the environment affects all organisms in a population in the ...
... C. normal-sized muslces that would become larger only when the children lifted weights D. larger-than-average muscles 31. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection A. individuals are modified by adverse environmental conditions B. the environment affects all organisms in a population in the ...
Evolution Power Point
... Natural selection is based on 4 facts: 1.Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2.There is variation among offspring. 3.There are limited resources (not enough food, water, space, etc. for everyone). 4.The organisms best fit to their environment will survive and the others will not. ...
... Natural selection is based on 4 facts: 1.Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2.There is variation among offspring. 3.There are limited resources (not enough food, water, space, etc. for everyone). 4.The organisms best fit to their environment will survive and the others will not. ...
Evolution Notes
... All great apes apart from man have 24 pairs of chromosomes. There is therefore a hypothesis that the common ancestor of all great apes had 24 pairs of chromosomes and that the fusion of two of the ancestor's chromosomes created chromosome 2 in humans. The evidence for this hypothesis is very strong. ...
... All great apes apart from man have 24 pairs of chromosomes. There is therefore a hypothesis that the common ancestor of all great apes had 24 pairs of chromosomes and that the fusion of two of the ancestor's chromosomes created chromosome 2 in humans. The evidence for this hypothesis is very strong. ...
Brain Squeeze
... relationship between two species is extremely close, the evolution of one species affects the evolution of the other species. ...
... relationship between two species is extremely close, the evolution of one species affects the evolution of the other species. ...
Struggle for Existence
... disadvantages in the struggle for existence • Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce, passing the characteristic to their offspring. Individuals without the characteristic die • Species change over time due to natural selection… new species arise and others disappear • Sp ...
... disadvantages in the struggle for existence • Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce, passing the characteristic to their offspring. Individuals without the characteristic die • Species change over time due to natural selection… new species arise and others disappear • Sp ...
study guide for evolution test – friday june 3rd
... 1) The answers to the frequently asked questions (FAQs) in the first lecture about evolution such as: a. Can creationism legally be taught in the public schools of the United States? b. Are humans descendents of apes? c. Are there any religions which accept the teaching of modern evolutionary theory ...
... 1) The answers to the frequently asked questions (FAQs) in the first lecture about evolution such as: a. Can creationism legally be taught in the public schools of the United States? b. Are humans descendents of apes? c. Are there any religions which accept the teaching of modern evolutionary theory ...
Big Idea 1 - Amundsen High School
... 1) the age of rocks where a fossil is found, the rate of decay of isotopes including carbon-14 2) the relationships within phylogenetic trees 3) the mathematical calculations that take into account information from chemical properties and/or geographical data ...
... 1) the age of rocks where a fossil is found, the rate of decay of isotopes including carbon-14 2) the relationships within phylogenetic trees 3) the mathematical calculations that take into account information from chemical properties and/or geographical data ...
Lines of Evidence Internet Lesson
... 7. Similar characteristics between species due to relatedness are known as homologies. How are homologies between species discovered (revealed)? ...
... 7. Similar characteristics between species due to relatedness are known as homologies. How are homologies between species discovered (revealed)? ...
Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.
... NOTE: Such a sequence, whereby links are seen between extinct organisms and species alive today, is predicted by evolutionary theory. One of the best documented series is the evolution of modern horses. ...
... NOTE: Such a sequence, whereby links are seen between extinct organisms and species alive today, is predicted by evolutionary theory. One of the best documented series is the evolution of modern horses. ...
Evidence of Evolution
... complex forms. NOTE: Such a sequence, whereby links are seen between extinct organisms and species alive today, is predicted by evolutionary theory. One of the best documented series is the evolution of modern horses. ...
... complex forms. NOTE: Such a sequence, whereby links are seen between extinct organisms and species alive today, is predicted by evolutionary theory. One of the best documented series is the evolution of modern horses. ...
File
... 1. The potential for a species to increase in number 2. The genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction 3. Competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to survive and reproduce 4. The resulting proliferation ...
... 1. The potential for a species to increase in number 2. The genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction 3. Competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to survive and reproduce 4. The resulting proliferation ...
Natural Selection - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone. • (1830) Charles Lyell: Argued for uniformitarianism, which holds that the geological processes we see today must be the same ones that occurred long ago. ...
... • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone. • (1830) Charles Lyell: Argued for uniformitarianism, which holds that the geological processes we see today must be the same ones that occurred long ago. ...
Ch 22 Notes
... “evolution.” Finished major points in 1844… but didn’t publish it (afraid of the consequences for his family – thought they’d be shunned). Until 1858… when he received a letter from Alfred Wallace… then he decided to publish his essay. He was shunned, but over time his ideas were accepted. Now they ...
... “evolution.” Finished major points in 1844… but didn’t publish it (afraid of the consequences for his family – thought they’d be shunned). Until 1858… when he received a letter from Alfred Wallace… then he decided to publish his essay. He was shunned, but over time his ideas were accepted. Now they ...
Powerpoint - Helena High School
... Vestigial Structures • inherited from ancestors but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendent ...
... Vestigial Structures • inherited from ancestors but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendent ...
Bio K Study Guide – Early earth and evolution
... 8. Identify how the following plays a role Darwin’s ideas on Natural Selection a. Overproduction of offspring ...
... 8. Identify how the following plays a role Darwin’s ideas on Natural Selection a. Overproduction of offspring ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities of life ...
... members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities of life ...
Evidence of common descent

Evidence of common descent of living organisms has been discovered by scientists researching in a variety of disciplines over many decades and has demonstrated common descent of all life on Earth developing from a last universal ancestor. This evidence explicates that evolution does occur, and is able to show the natural processes by which the biodiversity of life on Earth developed. Additionally, this evidence supports the modern evolutionary synthesis—the current scientific theory that explains how and why life changes over time. Evolutionary biologists document evidence of common descent by making testable predictions, testing hypotheses, and developing theories that illustrate and describe its causes.Comparison of the DNA genetic sequences of organisms has revealed that organisms that are phylogenetically close have a higher degree of DNA sequence similarity than organisms that are phylogenetically distant. Further evidence for common descent comes from genetic detritus such as pseudogenes, regions of DNA that are orthologous to a gene in a related organism, but are no longer active and appear to be undergoing a steady process of degeneration from cumulative mutations.Fossils are important for estimating when various lineages developed in geologic time. As fossilization is an uncommon occurrence, usually requiring hard body parts and death near a site where sediments are being deposited, the fossil record only provides sparse and intermittent information about the evolution of life. Scientific evidence of organisms prior to the development of hard body parts such as shells, bones and teeth is especially scarce, but exists in the form of ancient microfossils, as well as impressions of various soft-bodied organisms. The comparative study of the anatomy of groups of animals shows structural features that are fundamentally similar or homologous, demonstrating phylogenetic and ancestral relationships with other organisms, most especially when compared with fossils of ancient extinct organisms. Vestigial structures and comparisons in embryonic development are largely a contributing factor in anatomical resemblance in concordance with common descent. Since metabolic processes do not leave fossils, research into the evolution of the basic cellular processes is done largely by comparison of existing organisms' physiology and biochemistry. Many lineages diverged at different stages of development, so it is possible to determine when certain metabolic processes appeared by comparing the traits of the descendants of a common ancestor. Universal biochemical organization and molecular variance patterns in all organisms also show a direct correlation with common descent.Further evidence comes from the field of biogeography because evolution with common descent provides the best and most thorough explanation for a variety of facts concerning the geographical distribution of plants and animals across the world. This is especially obvious in the field of insular biogeography. Combined with the theory of plate tectonics common descent provides a way to combine facts about the current distribution of species with evidence from the fossil record to provide a logically consistent explanation of how the distribution of living organisms has changed over time.The development and spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria, like the spread of pesticide resistant forms of plants and insects provides evidence that evolution due to natural selection is an ongoing process in the natural world. Alongside this, are observed instances of the separation of populations of species into sets of new species (speciation). Speciation has been observed directly and indirectly in the lab and in nature. Multiple forms of such have been described and documented as examples for individual modes of speciation. Furthermore, evidence of common descent extends from direct laboratory experimentation with the selective breeding of organisms—historically and currently—and other controlled experiments involving many of the topics in the article. This article explains the different types of evidence for evolution with common descent along with many specialized examples of each.