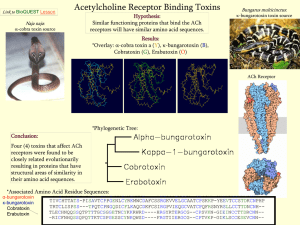
First Five 8/26/11
... Proteins • Large compounds made of amino acids in a chain • Structural components of animal cells • includes enzymes that catalyze (speed up) reactions • Needed for metabolism & building ...
... Proteins • Large compounds made of amino acids in a chain • Structural components of animal cells • includes enzymes that catalyze (speed up) reactions • Needed for metabolism & building ...
Organic compounds Carbon compounds are also called organic
... Steroids are also a type of lipid. There are many different types of steroids with different functions, but all can be recognized by their 4 fused carbon-ring structure. Proteins contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Proteins are large folded molecules made of amino acid sub-units ...
... Steroids are also a type of lipid. There are many different types of steroids with different functions, but all can be recognized by their 4 fused carbon-ring structure. Proteins contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Proteins are large folded molecules made of amino acid sub-units ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... variable R-group (makes a.a. chemically unique) peptide = short chain of amino acids; polypeptide = long chain of a.a. Humans must have 20 different a.a., but can produce only 10, others must come from food Structure is VERY important for function - pH and temperature can affect shape Food sources: ...
... variable R-group (makes a.a. chemically unique) peptide = short chain of amino acids; polypeptide = long chain of a.a. Humans must have 20 different a.a., but can produce only 10, others must come from food Structure is VERY important for function - pH and temperature can affect shape Food sources: ...
Student Guide
... The term carbohydrate was applied to the sugars and related organic compounds because many (but not all) fit the formula CH2O. Deoxyribose (a pentose (5) sugar) is a widely known example of a carbohydrate in which the hydrogen to oxygen ratio is not 2:1. Other sugars may contain nitrogen or phosphor ...
... The term carbohydrate was applied to the sugars and related organic compounds because many (but not all) fit the formula CH2O. Deoxyribose (a pentose (5) sugar) is a widely known example of a carbohydrate in which the hydrogen to oxygen ratio is not 2:1. Other sugars may contain nitrogen or phosphor ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... transcribing the information from the DNA in the nucleus. ...
... transcribing the information from the DNA in the nucleus. ...
METABOLISM FOUR CLASSES OF BIOMOLECULES (ALL
... amino acids are joined by a peptide bond…a type of covalent bond. ...
... amino acids are joined by a peptide bond…a type of covalent bond. ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... 93% of the human body is made up of Oxygen, Carbon, and Hydrogen. The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is tha ...
... 93% of the human body is made up of Oxygen, Carbon, and Hydrogen. The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is tha ...
Proteomics_Overview_BB_3_09_rev1
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
... DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
lab2 precipitation of casein at isoelectric point
... • Are substance of high molecular weight from 5000 to1000,000 daltons. • All protein Contain C, H, O, N, and most contain sulfur, some contain phosphorus and a few have mineral elements such as Fe, Mg and Cu. • Serve as structural components of animals ...
... • Are substance of high molecular weight from 5000 to1000,000 daltons. • All protein Contain C, H, O, N, and most contain sulfur, some contain phosphorus and a few have mineral elements such as Fe, Mg and Cu. • Serve as structural components of animals ...
Reading guide
... interactions. List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in H-bonding? 15. What is an ...
... interactions. List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in H-bonding? 15. What is an ...
Model Description Sheet
... According to the World Health Organization, 8.6 million people became ill and 1.3 million died in 2012 from tuberculosis (TB). Thioredoxin A (TrxA) is a binding protein in the bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent for TB. TB is prevalent in countries where infectious diseases ha ...
... According to the World Health Organization, 8.6 million people became ill and 1.3 million died in 2012 from tuberculosis (TB). Thioredoxin A (TrxA) is a binding protein in the bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent for TB. TB is prevalent in countries where infectious diseases ha ...
Bioinformatics Powerpoint - Heredity
... molecules in the process of transcription This information is then used at the ribosomes during the process of translation to dictate the order in which amino acids are assembled to form polypeptides. ...
... molecules in the process of transcription This information is then used at the ribosomes during the process of translation to dictate the order in which amino acids are assembled to form polypeptides. ...
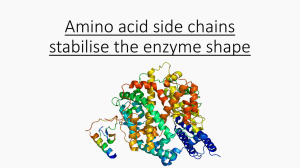
Amino acid side chains stabilise the enzyme shape Hydrogen bonds
... Many amino acids contain groups in the side chains that have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or nitrogen atom. Hydrogen bonding can occur between such groups. ...
... Many amino acids contain groups in the side chains that have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or nitrogen atom. Hydrogen bonding can occur between such groups. ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... acidic amino acid (such as glutamic acid). Show the charges on the side chains at pH 7. 4. Compare the chemical structure of a small non-polar amino acid (such as alanine) to one with a bulky hydrocarbon side chain (such as isoleucine). What kind of chemical interactions are non-polar side chains in ...
... acidic amino acid (such as glutamic acid). Show the charges on the side chains at pH 7. 4. Compare the chemical structure of a small non-polar amino acid (such as alanine) to one with a bulky hydrocarbon side chain (such as isoleucine). What kind of chemical interactions are non-polar side chains in ...
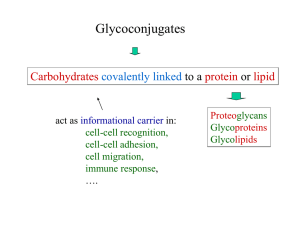
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
Las proteínas que `resisten` a la sal
... The main use of this scientific finding is the enzymatic engineering of enzymes, because, according to Oscar Millet, in bio-reactors there are "conditions of water shortages similar to those in saline environments”. In short, their use would be feasible in the field of biotechnology, namely the indu ...
... The main use of this scientific finding is the enzymatic engineering of enzymes, because, according to Oscar Millet, in bio-reactors there are "conditions of water shortages similar to those in saline environments”. In short, their use would be feasible in the field of biotechnology, namely the indu ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.