NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
simulating protein synthesis
... In this activity you will gain some basic knowledge of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. While doing these processes, you will simulate the role of DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, and a ribosome. Procedure Overview On page 2 you will see a strand of DNA called the coding strand. It will have the base ...
... In this activity you will gain some basic knowledge of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. While doing these processes, you will simulate the role of DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, and a ribosome. Procedure Overview On page 2 you will see a strand of DNA called the coding strand. It will have the base ...
DNA Structure and Function Miescher Discovered DNA
... • DNA consists of two nucleotide strands • Strands run in opposite directions • Strands are held together by hydrogen ...
... • DNA consists of two nucleotide strands • Strands run in opposite directions • Strands are held together by hydrogen ...
You Light Up My Life
... DNA Repair • Mistakes can occur during replication • DNA polymerase can read correct sequence from complementary strand and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
... DNA Repair • Mistakes can occur during replication • DNA polymerase can read correct sequence from complementary strand and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
T4 DNA Polymerase
... One unit is defined as the amount of T4 DNA Polymerase that catalyzes the incorporation of 10 nmol of dNTP into acid insoluble material in 30 minutes at 37°C using poly(dA-dT):poly(dA-dT) as a template:primer. Storage Conditions Store all components at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles of all ...
... One unit is defined as the amount of T4 DNA Polymerase that catalyzes the incorporation of 10 nmol of dNTP into acid insoluble material in 30 minutes at 37°C using poly(dA-dT):poly(dA-dT) as a template:primer. Storage Conditions Store all components at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles of all ...
DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
... ______ Ligase binds okazaki fragments together 15. Why is DNA replication called “semi-conservative”? __________________________________________ 16. What enzyme unwinds or unzips the parent strand? ________________ 17. The junction between separated strands is called the ____________________________ ...
... ______ Ligase binds okazaki fragments together 15. Why is DNA replication called “semi-conservative”? __________________________________________ 16. What enzyme unwinds or unzips the parent strand? ________________ 17. The junction between separated strands is called the ____________________________ ...
16.3 DNA and Protein Synthesis
... mRNA to make a new DNA strand. C. Amino acids will begin to attach to the correct codons on the mRNA strand. D. The correct anticodon anticodon on onaatRNA tRNAmolecule moleculewill will match up with with the the first firstmRNA mRNAcodon. codon. ...
... mRNA to make a new DNA strand. C. Amino acids will begin to attach to the correct codons on the mRNA strand. D. The correct anticodon anticodon on onaatRNA tRNAmolecule moleculewill will match up with with the the first firstmRNA mRNAcodon. codon. ...
DNA Structure
... -The DNA molecule splits into 2 at the replication points, unzipping due to the enzymes breaking the hydrogen bonds. The DNA polymerase then produces 2 new complementary strands following the rules of base paring by joining individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. Each strand serves as a te ...
... -The DNA molecule splits into 2 at the replication points, unzipping due to the enzymes breaking the hydrogen bonds. The DNA polymerase then produces 2 new complementary strands following the rules of base paring by joining individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. Each strand serves as a te ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
... Describe the basic structure (double helix, sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA, and describe its function in genetic inheritance. What is DNA: http://www.statedclearly.com/what-is-dna/ ...
... Describe the basic structure (double helix, sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA, and describe its function in genetic inheritance. What is DNA: http://www.statedclearly.com/what-is-dna/ ...
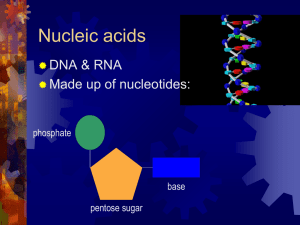
Nucleic Acids Test Topics
... - Point mutations are the change of one single nucleotide in the DNA - Frameshift mutations are the addition/insertion or deletion of one side nucleotide pair in the DNA strand. This causes the entire reading of the codons to be read incorrectly or messed up. - DNA polymerase will proofread the DNA ...
... - Point mutations are the change of one single nucleotide in the DNA - Frameshift mutations are the addition/insertion or deletion of one side nucleotide pair in the DNA strand. This causes the entire reading of the codons to be read incorrectly or messed up. - DNA polymerase will proofread the DNA ...
AP BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET MRS TERHUNE
... Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (overall process, where each occurs) Major purpose of glycolysis Purpose of Krebs Cycle Production of ATP in the ETC (oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis) Process of light reactions Process of light independent reactions Difference between C3 and C4 pla ...
... Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (overall process, where each occurs) Major purpose of glycolysis Purpose of Krebs Cycle Production of ATP in the ETC (oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis) Process of light reactions Process of light independent reactions Difference between C3 and C4 pla ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... identical—(semi-conservative part old/part new) Know the structure of a chromosome supercoiling…DNA coils around histone proteins and forms a nucleosome…see figure 12-10. Be able to show that you know how base pairing works Know the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA replication. DNA ...
... identical—(semi-conservative part old/part new) Know the structure of a chromosome supercoiling…DNA coils around histone proteins and forms a nucleosome…see figure 12-10. Be able to show that you know how base pairing works Know the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA replication. DNA ...
DNA
... • RNA is transcribed off DNA and functions as a mediator in gene expression protein synthesis • Some viruses have RNA as their genetic material but during infection the RNA has to revert back to its complementary DNA (cDNA) to cause successful infection. ...
... • RNA is transcribed off DNA and functions as a mediator in gene expression protein synthesis • Some viruses have RNA as their genetic material but during infection the RNA has to revert back to its complementary DNA (cDNA) to cause successful infection. ...
Genetic Code exercise
... (Not to be used in step 5!)_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 5. Write the amino acid sequence of the protein, using the genetic code, and the CODONS of the mRNA: _______________________________________________ Notes: * Start = AUG. * Amino-acids: Use the first 3 letters. (Methion ...
... (Not to be used in step 5!)_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 5. Write the amino acid sequence of the protein, using the genetic code, and the CODONS of the mRNA: _______________________________________________ Notes: * Start = AUG. * Amino-acids: Use the first 3 letters. (Methion ...
Lesson 3 | DNA and Genetics
... Describe the typical set of human chromosomes in each cell in terms of the number of chromosomes and explain what each parent contributes to each set. ...
... Describe the typical set of human chromosomes in each cell in terms of the number of chromosomes and explain what each parent contributes to each set. ...
DNA Replication Worksheet
... Helicase begins to break the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases. Cell starts into the mitosis phase of the cell cycle. Free floating nucleotides pair up with exposed nitrogen bases. Complete the statement , guanine, cytosine, and thymine are the four nitrogen bases. In DNA, always forms hydrogen ...
... Helicase begins to break the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases. Cell starts into the mitosis phase of the cell cycle. Free floating nucleotides pair up with exposed nitrogen bases. Complete the statement , guanine, cytosine, and thymine are the four nitrogen bases. In DNA, always forms hydrogen ...
Joining of Adjacent Nucleotides 2. Describe the purpose of DNA
... ribosomes in the process of transcription and translation including: Initiation Elongation Termination ...
... ribosomes in the process of transcription and translation including: Initiation Elongation Termination ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... Cytosine always pairs with Guanine Guanine always pairs with Cytosine Thymine always pairs with Adenine Adenine always pairs with Thymine ...
... Cytosine always pairs with Guanine Guanine always pairs with Cytosine Thymine always pairs with Adenine Adenine always pairs with Thymine ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.