Notes - Central Dogma
... STOP 4. Where does DNA live? In the nucleus 5. In the story, what does a cookbook (recipe) represent? DNA instructions 6. In the story, what does a copy of the recipe represent? mRNA 7. In the story, what does a French toast represent? Product = protein STOP 8. DNA makes ________RNA____ makes __ ...
... STOP 4. Where does DNA live? In the nucleus 5. In the story, what does a cookbook (recipe) represent? DNA instructions 6. In the story, what does a copy of the recipe represent? mRNA 7. In the story, what does a French toast represent? Product = protein STOP 8. DNA makes ________RNA____ makes __ ...
Human Genetics
... Once it has a few amino acids lined up, it chains them together, forming a protein. That protein then goes out to do it’s job, building your body from the ground up! Remember – proteins come in many different forms, think of them like tools – many shapes and sizes, all with very different jobs. ...
... Once it has a few amino acids lined up, it chains them together, forming a protein. That protein then goes out to do it’s job, building your body from the ground up! Remember – proteins come in many different forms, think of them like tools – many shapes and sizes, all with very different jobs. ...
Chapter 10: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... 4. Nucleotides are joined to new chain by covalent bonds b/t phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar and are joined to original DNA strand by H-bonds Ex: Original DNA sequence: ATTCCG DNA polymerase builds new strand that is complementary or TAAGGC ...
... 4. Nucleotides are joined to new chain by covalent bonds b/t phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar and are joined to original DNA strand by H-bonds Ex: Original DNA sequence: ATTCCG DNA polymerase builds new strand that is complementary or TAAGGC ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 8 Notes
... Very highly conserved DNA is wrapped around the outside of the histone octamer 166 bp of DNA wraps around the histones Linker DNA connects nucleosomes 7 fold compaction Histone H1 ...
... Very highly conserved DNA is wrapped around the outside of the histone octamer 166 bp of DNA wraps around the histones Linker DNA connects nucleosomes 7 fold compaction Histone H1 ...
1 Basic Biology 1. Draw the structure of an eukaryotic cell and label
... To check and replace the faulty codons To provide a site for mRNA and tRNA to work together ...
... To check and replace the faulty codons To provide a site for mRNA and tRNA to work together ...
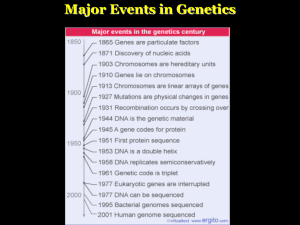
Major Events in Genetics
... – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
... – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
MBP 1022, LECTURE 3 DAN-ct30
... It is the chemical basicity of the nucleotides that has given them the common term "bases" as they are associated with nucleotides present in DNA and RNA. There are five major bases found in cells. The derivatives of purine are called adenine and guanine, and the derivatives of pyrimidine are called ...
... It is the chemical basicity of the nucleotides that has given them the common term "bases" as they are associated with nucleotides present in DNA and RNA. There are five major bases found in cells. The derivatives of purine are called adenine and guanine, and the derivatives of pyrimidine are called ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and a base containing nitrogen. These bases are called ...
... middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and a base containing nitrogen. These bases are called ...
Unit 4 Test Review
... 3. Adenine base present 4. Cytosine base present 5. Guanine base present 6. Thymine base present 7. Uracil base present 8. Shape is double helix 9. Shape is single stranded 10. Locate in nucleus 11. Located in cytoplasm 12. Stores genetic info 13. Functions in protein synthesis 16. More than one typ ...
... 3. Adenine base present 4. Cytosine base present 5. Guanine base present 6. Thymine base present 7. Uracil base present 8. Shape is double helix 9. Shape is single stranded 10. Locate in nucleus 11. Located in cytoplasm 12. Stores genetic info 13. Functions in protein synthesis 16. More than one typ ...
Ch 8-11 Review
... 1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. 4. Describe the process of asexual reproduction i ...
... 1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. 4. Describe the process of asexual reproduction i ...
Word Bank Adenine Codon Cytosine deletions
... a2) The DNA Structure is made up of different nucleotide attached together by the phosphate ...
... a2) The DNA Structure is made up of different nucleotide attached together by the phosphate ...
DNA Sequencing and Gene Analysis
... vectors that contain the origin of replication from a single stranded bacteriophage such as M13 or fd. Infecting bacteria containing this vector with a “helper phage” causes single stranded phage to be produced. The phage DNA contains the cloned insert The primer is complementary to the region in th ...
... vectors that contain the origin of replication from a single stranded bacteriophage such as M13 or fd. Infecting bacteria containing this vector with a “helper phage” causes single stranded phage to be produced. The phage DNA contains the cloned insert The primer is complementary to the region in th ...
NAME
... OPERON – a group of genes operating together INTRON – sequence of DNA that is NOT involved in coding for a protein which is cut out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes EXON – Expressed sequence of DNA that codes for a protein REPRESSOR – molecule that binds to the operator regio ...
... OPERON – a group of genes operating together INTRON – sequence of DNA that is NOT involved in coding for a protein which is cut out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes EXON – Expressed sequence of DNA that codes for a protein REPRESSOR – molecule that binds to the operator regio ...
BIO105 Learning objectives for test 3 Topic: The Cell cycle and
... - Describe the structure of DNA, and explain what kind of chemical bond connects the nucleotides of each strand and what type of bond holds the two strands together. - Explain semiconservative replication-Describe the process of DNA replication, and explain the role of helicase, single strand bindin ...
... - Describe the structure of DNA, and explain what kind of chemical bond connects the nucleotides of each strand and what type of bond holds the two strands together. - Explain semiconservative replication-Describe the process of DNA replication, and explain the role of helicase, single strand bindin ...
Intro to Nucleic Acids-Structure, Central Dogma
... • two helical polynucleotides coiled around an axis • chains run in opposite directions • sugar-phosphate backbone on the outside, bases on the inside • bases nearly perpendicular to the axis ...
... • two helical polynucleotides coiled around an axis • chains run in opposite directions • sugar-phosphate backbone on the outside, bases on the inside • bases nearly perpendicular to the axis ...
Review 2 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... How did Messelson and Stahl prove that DNA replication is semi conservative? How many replicons does E. coli have? Is the chromosomal DNA replication bidirectional in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Both DNA replication and transcription proceed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Mention one important dif ...
... How did Messelson and Stahl prove that DNA replication is semi conservative? How many replicons does E. coli have? Is the chromosomal DNA replication bidirectional in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Both DNA replication and transcription proceed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Mention one important dif ...
dna - bmcclain
... -Before cell division, chromatin forms chromosomes. -GENES are short segments of DNA that contain specific information for traits ...
... -Before cell division, chromatin forms chromosomes. -GENES are short segments of DNA that contain specific information for traits ...
dna replication
... Stabilization of the replication machine • DNA Pol delta and epsilon are attached to the DNA and held in place by other proteins – Sliding-clamp proteins (proliferating cell nuclear antigen - PCNA), allow the stable binding of DNA Pol and strand synthesis – Clamp-loading proteins (replication facto ...
... Stabilization of the replication machine • DNA Pol delta and epsilon are attached to the DNA and held in place by other proteins – Sliding-clamp proteins (proliferating cell nuclear antigen - PCNA), allow the stable binding of DNA Pol and strand synthesis – Clamp-loading proteins (replication facto ...
Genetic Engineering
... GENETIC ENGINEERING A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of i ...
... GENETIC ENGINEERING A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of i ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.