Locard Exchange Principle
... Third, the results of the ___________ ___________ of the physical evidence are compared to __________ statements. Finally, both witness statements and laboratory results are used to ___________ the investigator's ____________ until one remains Anthropometrics literally meaning "__________ __ _______ ...
... Third, the results of the ___________ ___________ of the physical evidence are compared to __________ statements. Finally, both witness statements and laboratory results are used to ___________ the investigator's ____________ until one remains Anthropometrics literally meaning "__________ __ _______ ...
Homework 3.1 CHEM151: Biochemistry I Prof. Tsai Page 1 of 4 1
... 4. If you are given the writhing number (W) to be 10 and the linking number (L) to be 2, what is the twisting number (T)? 5. What is the difference between Type I and Type II topoisomerases? (2 points) 6. Will a supercoiled DNA molecule migrate faster or slower in gel electrophoresis when compared t ...
... 4. If you are given the writhing number (W) to be 10 and the linking number (L) to be 2, what is the twisting number (T)? 5. What is the difference between Type I and Type II topoisomerases? (2 points) 6. Will a supercoiled DNA molecule migrate faster or slower in gel electrophoresis when compared t ...
Viral particles
... and dsDNA, with either linear or circular molecules packaged into viral particles (see Table 10.1) • Phage genomes vary in size from 3000 bases to 650kb in size • Phage morphology varies from simple icosahedra or helical filaments to complex tailed structures ...
... and dsDNA, with either linear or circular molecules packaged into viral particles (see Table 10.1) • Phage genomes vary in size from 3000 bases to 650kb in size • Phage morphology varies from simple icosahedra or helical filaments to complex tailed structures ...
106 DNA- Proteins
... – guanine (G), – cytosine (C), – thymine (T found in DNA only), and – uracil (U found in RNA only). • Nucleic acids are formed by condensing two nucleotides (the phosphoric acid condenses with the O-H group of the sugar). ...
... – guanine (G), – cytosine (C), – thymine (T found in DNA only), and – uracil (U found in RNA only). • Nucleic acids are formed by condensing two nucleotides (the phosphoric acid condenses with the O-H group of the sugar). ...
presentation source
... • Therefore, blocking of regulatory proteins at some distance down a DNA sequence may effect a gene’s expression - may involve ‘enhancers’ • Binding of transcription factor begins at, but is not limited to, the TATA box • Transcription inhibited by – Anything that reduces availability of any factor ...
... • Therefore, blocking of regulatory proteins at some distance down a DNA sequence may effect a gene’s expression - may involve ‘enhancers’ • Binding of transcription factor begins at, but is not limited to, the TATA box • Transcription inhibited by – Anything that reduces availability of any factor ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... As new amino acids are brought to the ribosome, the growing peptide chain is attached to the new amino acid by a peptide bond. Elongation of the chain continues until a stop codon is encountered. At that point the peptide chain is released from the tRNA. A single mRNA can be read repeatedly to make ...
... As new amino acids are brought to the ribosome, the growing peptide chain is attached to the new amino acid by a peptide bond. Elongation of the chain continues until a stop codon is encountered. At that point the peptide chain is released from the tRNA. A single mRNA can be read repeatedly to make ...
Bell Work: 1/25/10
... To make Dolly, researchers isolated a somatic cell from an adult female sheep. Next, they transferred the nucleus from that cell to an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. After a couple of chemical tweaks, the egg cell, with its new nucleus, was behaving just like a freshly fertilized ...
... To make Dolly, researchers isolated a somatic cell from an adult female sheep. Next, they transferred the nucleus from that cell to an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. After a couple of chemical tweaks, the egg cell, with its new nucleus, was behaving just like a freshly fertilized ...
Genetic Technology
... • Genetic engineering – a faster and more reliable method for increasing the frequency of a specific allele in a population. ...
... • Genetic engineering – a faster and more reliable method for increasing the frequency of a specific allele in a population. ...
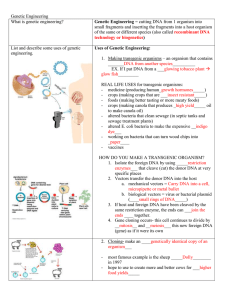
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
DNA Article
... which looks like a twisted ladder or spiral staircase. The two sides of the DNA ladder are made of alternating molecules of sugar and phosphate. The rungs of the DNA ladder are made up of a p ...
... which looks like a twisted ladder or spiral staircase. The two sides of the DNA ladder are made of alternating molecules of sugar and phosphate. The rungs of the DNA ladder are made up of a p ...
Student Name: Teacher
... 19. Often used to produce variegated plants, a genetic disorder that creates an organism with two or more genetically distinct types of cells is a/an: A. ...
... 19. Often used to produce variegated plants, a genetic disorder that creates an organism with two or more genetically distinct types of cells is a/an: A. ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... few tens of bases. The significance of minisatellites is that the patterns in different people or other organisms vary considerably. These can be electrophoresed to identify or fingerprint individuals ...
... few tens of bases. The significance of minisatellites is that the patterns in different people or other organisms vary considerably. These can be electrophoresed to identify or fingerprint individuals ...
Nucleic Acids - U of L Class Index
... complementary base pairing is emphasized for an understanding of the process by which DNA is replicated and its synthesis of mRNA for protein synthesis in the ribosomes. The control of protein synthesis through induction and repression is discussed. The concept of recombinant DNA is introduced as a ...
... complementary base pairing is emphasized for an understanding of the process by which DNA is replicated and its synthesis of mRNA for protein synthesis in the ribosomes. The control of protein synthesis through induction and repression is discussed. The concept of recombinant DNA is introduced as a ...
File - Mrs. Beeker the Science Teacher
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a _________________ base. 2. In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the __________________ of the next group. 3. In DNA, thymine is complementary to (or pairs with) ___________ ...
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a _________________ base. 2. In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the __________________ of the next group. 3. In DNA, thymine is complementary to (or pairs with) ___________ ...
TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
... 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions to make a particular ____________ from the DNA in the _____________ to the ribosomes. 2. The process of producing mRNA from the instructions in the DNA is called _______________. 3. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds and separates, exposin ...
... 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions to make a particular ____________ from the DNA in the _____________ to the ribosomes. 2. The process of producing mRNA from the instructions in the DNA is called _______________. 3. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds and separates, exposin ...
practice exam 3_answer key
... c. DNA ligase-translation d. Helicase-linking fragmented DNA e. Primase-synthesize (make) new strands of DNA 35. Which of the following enzymes provides a free 3 prime (OH) end by laying down a short RNA sequence for DNA polymerase to add nucleotides to? a. helicase b. primase c. ligase d. RNA polym ...
... c. DNA ligase-translation d. Helicase-linking fragmented DNA e. Primase-synthesize (make) new strands of DNA 35. Which of the following enzymes provides a free 3 prime (OH) end by laying down a short RNA sequence for DNA polymerase to add nucleotides to? a. helicase b. primase c. ligase d. RNA polym ...
Chapter 4 - Version B
... b. occurs in every living cell in a multicellular organism c. occurs before cytokinesis d. is only semi-conservative in eukaryotes, not prokaryotes e. may be conservative or semi-conservative at different points in an organism's life-cycle ...
... b. occurs in every living cell in a multicellular organism c. occurs before cytokinesis d. is only semi-conservative in eukaryotes, not prokaryotes e. may be conservative or semi-conservative at different points in an organism's life-cycle ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.