Biology and you - properties of life and the scientific method
... 2. Adult Stem Cells- (aka-Somatic Stem Cells)cells associated with a certain organ or organ system and can only be activated to become a part of that specific system. ...
... 2. Adult Stem Cells- (aka-Somatic Stem Cells)cells associated with a certain organ or organ system and can only be activated to become a part of that specific system. ...
5`-cgaucggauccagcuggacgcuagcguaaaaaaaa-3`
... The bacteria replicates the vector contains one or more copies of the vector and gene. The initial fragment is now said to be cloned. The plasmid and the insert can be then isolated in bulk for ...
... The bacteria replicates the vector contains one or more copies of the vector and gene. The initial fragment is now said to be cloned. The plasmid and the insert can be then isolated in bulk for ...
Exploratorium Presentation
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
CHEM 331 Problem Set #7
... cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. The spores of B. subtilis, a soil organism, are at constant risk of being lofted to the top of the soil or into the air, where they are subject to UV exposure, possibly for prolonged periods. Protection from UVinduced mutation is critical to spore DNA integrity. 12. Si ...
... cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. The spores of B. subtilis, a soil organism, are at constant risk of being lofted to the top of the soil or into the air, where they are subject to UV exposure, possibly for prolonged periods. Protection from UVinduced mutation is critical to spore DNA integrity. 12. Si ...
K`NEX Activity
... 1. Use pp. 18-19 in the glossy manual 2. Unzip your DNA molecule making sure to leave all of the connecting pieces on the side you intend to transcribe. 3. Have Mr. Curry inspect your molecule to make sure it is correctly assembled and initial here: Extension/Discussion: 1. Name three major differen ...
... 1. Use pp. 18-19 in the glossy manual 2. Unzip your DNA molecule making sure to leave all of the connecting pieces on the side you intend to transcribe. 3. Have Mr. Curry inspect your molecule to make sure it is correctly assembled and initial here: Extension/Discussion: 1. Name three major differen ...
PCR reading answers
... 12. Briefly explain the role of each enzyme for in vivo replication....... topoisomerase - stabilizes the DNA helix ahead of the replication fork ; it does allow for some unwinding of the double helix in a controlled manner during replication or transcription.... .....literal translation = "enzyme ...
... 12. Briefly explain the role of each enzyme for in vivo replication....... topoisomerase - stabilizes the DNA helix ahead of the replication fork ; it does allow for some unwinding of the double helix in a controlled manner during replication or transcription.... .....literal translation = "enzyme ...
high order thinking skills (hots ).
... 25. While carrying out a PCR ,denaturation step was missed . What will be its effect on the process ? =Two bstrands of DNA will not be separated and primer will not be able to anneal to the template. 26. A scientist found a rare plant species without seeds and flowers and want to increase their numb ...
... 25. While carrying out a PCR ,denaturation step was missed . What will be its effect on the process ? =Two bstrands of DNA will not be separated and primer will not be able to anneal to the template. 26. A scientist found a rare plant species without seeds and flowers and want to increase their numb ...
Review - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... Use Promoters – tell the RNA polymerase where to stop and where to end KEY DIFFERENCE: Only uses one strand from parental DNA NOT BOTH! ...
... Use Promoters – tell the RNA polymerase where to stop and where to end KEY DIFFERENCE: Only uses one strand from parental DNA NOT BOTH! ...
Experimental Evidence for DNA
... A rabbit was injected with a sample of human blood. The rabbit’s serum was later mixed with samples of serum from a human, a chimpanzee, a gorilla, an orangutan, a gibbon and a rhesus monkey. Draw a graph to predict the relationship between each of these species and the degree of precipitation. Expr ...
... A rabbit was injected with a sample of human blood. The rabbit’s serum was later mixed with samples of serum from a human, a chimpanzee, a gorilla, an orangutan, a gibbon and a rhesus monkey. Draw a graph to predict the relationship between each of these species and the degree of precipitation. Expr ...
Name Date Block__ Biology • So far in the course we have
... (A) always pairs with (T) A-T. Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C) G-C. This base pairing is called complementary. ...
... (A) always pairs with (T) A-T. Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C) G-C. This base pairing is called complementary. ...
Chapter Review
... _____ 4. James Watson and Francis Crick a. took X-ray pictures of DNA. b. discovered that genes are in chromosomes. c. bred pea plants to study heredity. d. made models to figure out DNA’s shape. _____ 5. In a DNA molecule, which of the following bases pair together? a. adenine and cytosine b. thymi ...
... _____ 4. James Watson and Francis Crick a. took X-ray pictures of DNA. b. discovered that genes are in chromosomes. c. bred pea plants to study heredity. d. made models to figure out DNA’s shape. _____ 5. In a DNA molecule, which of the following bases pair together? a. adenine and cytosine b. thymi ...
DNA , Mitosis and Meiosis PowerPoint
... • DNA replicates before division • Before division organelles in cell must be copied • After telophase cytokinesis Lesson Launcher Questions 1. Give 3 examples of somatic cells. 2. What are gametes? 3. What process creates gametes? 4. What process creates somatic cells? 5. What is the difference in ...
... • DNA replicates before division • Before division organelles in cell must be copied • After telophase cytokinesis Lesson Launcher Questions 1. Give 3 examples of somatic cells. 2. What are gametes? 3. What process creates gametes? 4. What process creates somatic cells? 5. What is the difference in ...
Different types of PCR
... DNA is cut with two restriction enzymes to generate specific sequences, which are then amplified suitably. The mere addition or deletion of bases at the 3′ end determines the selectivity and complexity of the amplification. //----GAATTC---//----TTAA---// //----CTTAAG--//-----AATT---// EcoRI MseI ...
... DNA is cut with two restriction enzymes to generate specific sequences, which are then amplified suitably. The mere addition or deletion of bases at the 3′ end determines the selectivity and complexity of the amplification. //----GAATTC---//----TTAA---// //----CTTAAG--//-----AATT---// EcoRI MseI ...
Biology: DNA Review Packet
... 1. Label EVERY sugar (S), phosphate (P), and nitrogen base (A, T, C, G) in the diagram below. ...
... 1. Label EVERY sugar (S), phosphate (P), and nitrogen base (A, T, C, G) in the diagram below. ...
Document
... Describe the structure of DNA by doing the following: 1. List the three parts of a nucleotide 2. Describe the base pairing rules (how do the bases match up with each other) 3. Describe the role and location of hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule 1. Phosphate, deoxyribose (sugar), nitrogenous bases (A,T ...
... Describe the structure of DNA by doing the following: 1. List the three parts of a nucleotide 2. Describe the base pairing rules (how do the bases match up with each other) 3. Describe the role and location of hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule 1. Phosphate, deoxyribose (sugar), nitrogenous bases (A,T ...
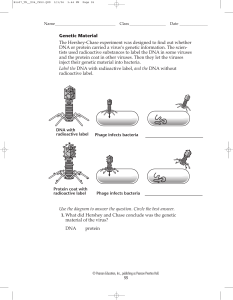
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
Why don’t antibodies get rid of HIV?
... replication fork. Lagging strand: DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously (Okazaki fragments), then stitched together. ...
... replication fork. Lagging strand: DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously (Okazaki fragments), then stitched together. ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.