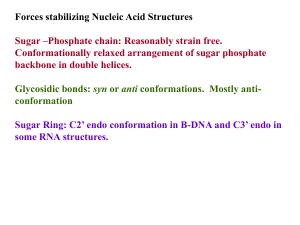
Pharmacogenetics Glossary
... base pairs - the pairs of complementary bases that form the rungs of DNA: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). base sequence - the order of bases in DNA. cell - the basic unit of life; the smallest basic part of every living thing that can function by itself. It i ...
... base pairs - the pairs of complementary bases that form the rungs of DNA: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). base sequence - the order of bases in DNA. cell - the basic unit of life; the smallest basic part of every living thing that can function by itself. It i ...
Mutations: Altering the Code
... and then tRNA. You will use a codon wheel to determine which amino acids bond to the mRNA codons (not DNA or tRNA anticodons) in the code. Encoding Activity (On a separate page) In this activity you will be able to create a sentence in English using DNA code. Just as our cells are able to “read” DNA ...
... and then tRNA. You will use a codon wheel to determine which amino acids bond to the mRNA codons (not DNA or tRNA anticodons) in the code. Encoding Activity (On a separate page) In this activity you will be able to create a sentence in English using DNA code. Just as our cells are able to “read” DNA ...
180-183
... factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-carrying form). Because the ability to cause disease w ...
... factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-carrying form). Because the ability to cause disease w ...
Unit 4
... - Each three bases of mRNA are called a codon, these codons line up with the amino acids picked up by the tRNA. 12. Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. - Initiation: polymerase attaches to promoter regions on the DNA and be ...
... - Each three bases of mRNA are called a codon, these codons line up with the amino acids picked up by the tRNA. 12. Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. - Initiation: polymerase attaches to promoter regions on the DNA and be ...
swgdam 3.9 - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... • The Huaxia Platinum MM is robust to raw material change ...
... • The Huaxia Platinum MM is robust to raw material change ...
Comparing DNA and RNA
... Like DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid— a molecule made of nucleotides linked together, RNA differs from DNA in three ways, First, RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA. Second, RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose rather t ...
... Like DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid— a molecule made of nucleotides linked together, RNA differs from DNA in three ways, First, RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA. Second, RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose rather t ...
Lecture 4. - Government Degree College Pulwama
... the molecular repositories of genetic information. The structure of every protein, and ultimately of every biomolecule and cellular component, is a product of information programmed into the nucleotide sequence of a cell’s nucleic acids. The ability to store and transmit genetic information from one ...
... the molecular repositories of genetic information. The structure of every protein, and ultimately of every biomolecule and cellular component, is a product of information programmed into the nucleotide sequence of a cell’s nucleic acids. The ability to store and transmit genetic information from one ...
Genetic Engineering
... The scientists can join natural pieces of DNA to synthesized one using enzymes that splice DNA back together They can also combine DNA from two completely different organisms together This is called recombinant DNA because it combines the DNA from two different sources together ...
... The scientists can join natural pieces of DNA to synthesized one using enzymes that splice DNA back together They can also combine DNA from two completely different organisms together This is called recombinant DNA because it combines the DNA from two different sources together ...
Unit 8 Molecular Genetics Chp 16 DNA PPT
... • A human cell can copy its 6 billion base pairs and divide into daughter cells in only a few hours. • This process is remarkably accurate, with only one error per billion nucleotides. • More than a dozen enzymes and other proteins participate in DNA replication. ...
... • A human cell can copy its 6 billion base pairs and divide into daughter cells in only a few hours. • This process is remarkably accurate, with only one error per billion nucleotides. • More than a dozen enzymes and other proteins participate in DNA replication. ...
Examination IV Key
... c. [2 points] Nucleosomes have two primary functions. For one of these functions, describe the function and then describe how the nucleosomes carry out that function. They compact DNA by making the DNA have less length than if the DNA was not in a supercoil. d. [2 points] For the other function of n ...
... c. [2 points] Nucleosomes have two primary functions. For one of these functions, describe the function and then describe how the nucleosomes carry out that function. They compact DNA by making the DNA have less length than if the DNA was not in a supercoil. d. [2 points] For the other function of n ...
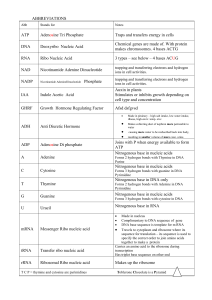
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
Dominant trait - Integrated Science 3
... The external trait or result of the genotype Stronger trait, only need to have one copy The information storage of a cell Version of a type of gene The twisted stairway shape of DNA Permanent change in the DNA, through alteration of sequences Enzyme used to cut DNA Long pieces of DNA which contains ...
... The external trait or result of the genotype Stronger trait, only need to have one copy The information storage of a cell Version of a type of gene The twisted stairway shape of DNA Permanent change in the DNA, through alteration of sequences Enzyme used to cut DNA Long pieces of DNA which contains ...
DNA—The Double Helix
... Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction and heredity. Chromosomes are microscopic, threadlike strands composed of the chemical DNA (short for deoxyribonu ...
... Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction and heredity. Chromosomes are microscopic, threadlike strands composed of the chemical DNA (short for deoxyribonu ...
transcription and rna
... mRNAs are processed RNA Polymerase catalyzes RNA synthesis Recognizes and binds to promoter Unwinds DNA helix in prokaryotes (other proteins required in eukaryotes) Initiates transcription (no primer needed); no proofreading Links RNA nucleotides in 5’3’ direction Requirements for RNA polymerase: D ...
... mRNAs are processed RNA Polymerase catalyzes RNA synthesis Recognizes and binds to promoter Unwinds DNA helix in prokaryotes (other proteins required in eukaryotes) Initiates transcription (no primer needed); no proofreading Links RNA nucleotides in 5’3’ direction Requirements for RNA polymerase: D ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... III. DNA Replication – Occurs during interphase of a cell’s life cycle, DNA replication is making identical copies of chromosomes. Step 1: Many DNA Helicase enzymes attach themselves to, and cut hydrogen bonds between bases. Why are so many DNA Helicase enzymes needed? Step 2: With H-bonds cut, the ...
... III. DNA Replication – Occurs during interphase of a cell’s life cycle, DNA replication is making identical copies of chromosomes. Step 1: Many DNA Helicase enzymes attach themselves to, and cut hydrogen bonds between bases. Why are so many DNA Helicase enzymes needed? Step 2: With H-bonds cut, the ...
DM1100 - smobio
... electrophoresis, and allows for real time monitoring. Buffering 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 10 mM Na-EDTA, 0.025% Orange G and 10% Glycerol. Quality Control 1. 17 defined bands are observed during electrophoresis in agarose gel. 2. No nuclease activity is detected by a direct nuclease activity assay. ...
... electrophoresis, and allows for real time monitoring. Buffering 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 10 mM Na-EDTA, 0.025% Orange G and 10% Glycerol. Quality Control 1. 17 defined bands are observed during electrophoresis in agarose gel. 2. No nuclease activity is detected by a direct nuclease activity assay. ...
Welcome to Amgen Manufacturing Limited Juncos, Puerto Rico
... DNA techniques, it started to be used to refer to laboratory-based techniques to satisfy food and health demands Modern biotechnology was initiated in mid 1980 when the United States Supreme Court ruled that a genetically-modified microorganism could be patented in the case of Diamond vs. Chakrabart ...
... DNA techniques, it started to be used to refer to laboratory-based techniques to satisfy food and health demands Modern biotechnology was initiated in mid 1980 when the United States Supreme Court ruled that a genetically-modified microorganism could be patented in the case of Diamond vs. Chakrabart ...
lesson 3 domains and binomial
... • It is made from a sequence of amino acids. which varies slightly from species to species. • If the sequence is very similar between two species, we can infer that they are quite closely related. • We could also compare DNA or RNA sequences between organisms as opposed to amino acid sequences. ...
... • It is made from a sequence of amino acids. which varies slightly from species to species. • If the sequence is very similar between two species, we can infer that they are quite closely related. • We could also compare DNA or RNA sequences between organisms as opposed to amino acid sequences. ...
Recombinant DNA and gene cloning To use an unique feature(s) of
... partial sequence of the gene (based on protein sequence) activity (enzyme activity) genetic defect (temperature/chemical sensitivity) Strategy: 1) break up the DNA; 2) separated each fragement into a unique locations (library); 3) screen your gene out from the library. Tools 1) restriction endonucle ...
... partial sequence of the gene (based on protein sequence) activity (enzyme activity) genetic defect (temperature/chemical sensitivity) Strategy: 1) break up the DNA; 2) separated each fragement into a unique locations (library); 3) screen your gene out from the library. Tools 1) restriction endonucle ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.