Gene mutations
... During DNA replication, mistakes can be made when DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides. If this mutation or mistake happens very early on in a baby’s development, the mutation can affect the entire baby. The rest of the cells will have that same mutation. Remember, we all start off as one c ...
... During DNA replication, mistakes can be made when DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides. If this mutation or mistake happens very early on in a baby’s development, the mutation can affect the entire baby. The rest of the cells will have that same mutation. Remember, we all start off as one c ...
Genetic Engineering - slater science
... a.) DNA extraction – simple chemical process to get DNA out of cell; cells are opened & DNA is separated from other cell parts b.) cutting DNA – restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences of nucleotides ...
... a.) DNA extraction – simple chemical process to get DNA out of cell; cells are opened & DNA is separated from other cell parts b.) cutting DNA – restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences of nucleotides ...
recombinant dna technology
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
... • FIRST, THE PLASMID IS TREATED WITH THE SAME RESTRICTION ENZYME AS WAS USED TO CREATE THE DNA FRAGMENT • THE RESTRICTION ENZYME WILL CUT THE PLASMID AT THE SAME RECOGNITION SEQUENCES, PRODUCING THE SAME STICKY ENDS CARRIED BY THE FRAGMENTS • MIXING THE FRAGMENTS WITH THE CUT PLASMIDS ALLOWS BASE-PA ...
Genetic Engineering
... a.) DNA extraction – simple chemical process to get DNA out of cell; cells are opened & DNA is separated from other cell parts b.) cutting DNA – restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences of nucleotides ...
... a.) DNA extraction – simple chemical process to get DNA out of cell; cells are opened & DNA is separated from other cell parts b.) cutting DNA – restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences of nucleotides ...
2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
... • Two polynucleotide chains of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs: Adenine pairs with thymine (A=T) via two hydrogen bonds Guanine pairs with cytosine (G=C) via three hydrogen bonds • In order for bases to be facing each other and thus able to pair, the two stra ...
... • Two polynucleotide chains of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs: Adenine pairs with thymine (A=T) via two hydrogen bonds Guanine pairs with cytosine (G=C) via three hydrogen bonds • In order for bases to be facing each other and thus able to pair, the two stra ...
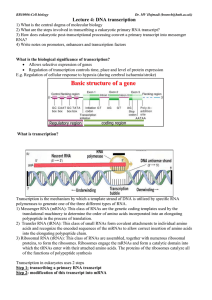
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA sequences called promoters that drive transcription (region where RNA polymerase binds ...
... A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA sequences called promoters that drive transcription (region where RNA polymerase binds ...
Nucleic Acids - saddleback.edu
... DNA is replicated (duplicated) so that each new cell receives a complete copy. • The number of chromosomes varies from organism to organism. For example, a horse has 64 chromosomes (32 pairs), a cat has 38 (19 pairs), a mosquito has 6 (3 pairs), and a human has 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs. ...
... DNA is replicated (duplicated) so that each new cell receives a complete copy. • The number of chromosomes varies from organism to organism. For example, a horse has 64 chromosomes (32 pairs), a cat has 38 (19 pairs), a mosquito has 6 (3 pairs), and a human has 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs. ...
forensic_biology
... nucleotide "letters" A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters—C, G, or T. Each person's genetic material contains a unique SNP pattern that is made up of many different gen ...
... nucleotide "letters" A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters—C, G, or T. Each person's genetic material contains a unique SNP pattern that is made up of many different gen ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... 1. the process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle 2. nucleus 3. S stage 4. so that every cell will have a complete set of DNA following cell division 5. something that serves as a pattern 6. ATCCATG 7. Proteins help unzip the DNA strand, hold the strands apart, and bond nucleotides togethe ...
... 1. the process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle 2. nucleus 3. S stage 4. so that every cell will have a complete set of DNA following cell division 5. something that serves as a pattern 6. ATCCATG 7. Proteins help unzip the DNA strand, hold the strands apart, and bond nucleotides togethe ...
Option B8 Nucleic Acids
... stranded DNA into single strands 6.Copy of the strands is transferred to a membrane and selected radioactively labeled DNA probes are added to the membrane to base pair with particular DNA sequences. Excess washed away. 7.Membrane is overlaid with X-ray film which becomes selectively ‘fogged’ by ...
... stranded DNA into single strands 6.Copy of the strands is transferred to a membrane and selected radioactively labeled DNA probes are added to the membrane to base pair with particular DNA sequences. Excess washed away. 7.Membrane is overlaid with X-ray film which becomes selectively ‘fogged’ by ...
File
... sequences or sequences as primers to cleaved DNA 3. Five steps in PCR process a. 1) Primer of synthetic nucleotides mixed with DNA fragment 2) Temperature of mixture increased to 980 C b. ...
... sequences or sequences as primers to cleaved DNA 3. Five steps in PCR process a. 1) Primer of synthetic nucleotides mixed with DNA fragment 2) Temperature of mixture increased to 980 C b. ...
DNA repair - Journal of Cell Science
... achieved by recognition of nicks, gaps or free 3′ ends that are present in the nascent strand during replication. In a downstream step, the newly synthesized strand is degraded, which removes the mismatch. MMR patches are ~100 to >1000 nucleotides in length. EXO1 is involved in 5′ to 3′ excision. It ...
... achieved by recognition of nicks, gaps or free 3′ ends that are present in the nascent strand during replication. In a downstream step, the newly synthesized strand is degraded, which removes the mismatch. MMR patches are ~100 to >1000 nucleotides in length. EXO1 is involved in 5′ to 3′ excision. It ...
Chapter 12 - WordPress.com
... DNA having a specific sequence of nucleotides. – The place where DNA replication begins. Replication fork- Y-shaped region where the parental strands of DNA are being unwound. ...
... DNA having a specific sequence of nucleotides. – The place where DNA replication begins. Replication fork- Y-shaped region where the parental strands of DNA are being unwound. ...
Slide 1
... • DNA polymerase – copies both strands of DNA at the same time – Needs a primer – section of DNA that starts the new strand – Always copies from 5’ -> 3’ • One strand is easy to copy because replication is moving in the same direction as DNA polymerase – this new strand formed is called the leading ...
... • DNA polymerase – copies both strands of DNA at the same time – Needs a primer – section of DNA that starts the new strand – Always copies from 5’ -> 3’ • One strand is easy to copy because replication is moving in the same direction as DNA polymerase – this new strand formed is called the leading ...
Revision BIOC 432 LAB
... (Advantage to give higher resolution to separate very small DNA fragments that are differ in a one bp and so used for DNA sequencing). ...
... (Advantage to give higher resolution to separate very small DNA fragments that are differ in a one bp and so used for DNA sequencing). ...
Homework 4
... d. O is incompletely dominant to A and B. e. A is dominant to B, and B is dominant to O. 7. The site on the chromosome occupied by a gene is called a(n) a. allele. b. region. c. locus. d. type. e. phenotype. 8. Given the following parent strand sequence, what would the daughter strand sequence look ...
... d. O is incompletely dominant to A and B. e. A is dominant to B, and B is dominant to O. 7. The site on the chromosome occupied by a gene is called a(n) a. allele. b. region. c. locus. d. type. e. phenotype. 8. Given the following parent strand sequence, what would the daughter strand sequence look ...
Genes_DNA_Test
... 16. The data in Table 2 provide evidence for which fact about DNA: a. C and T form base pairs b. the backbone of DNA is only stable with a certain base composition c. C and G form base pairs d. the percentage of each base is the same for all organisms 17. Which of these statements is NOT true? a. Wh ...
... 16. The data in Table 2 provide evidence for which fact about DNA: a. C and T form base pairs b. the backbone of DNA is only stable with a certain base composition c. C and G form base pairs d. the percentage of each base is the same for all organisms 17. Which of these statements is NOT true? a. Wh ...
coding region of DNA. o Introns – non
... o Tissue-specific transcription factors. o Repressors present in some regions and absent in others. Elongation (step 2 of transcription). o RNA polymerase breaks interactions with transcription factors and escapes the promoter region to start elongation. o RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template ...
... o Tissue-specific transcription factors. o Repressors present in some regions and absent in others. Elongation (step 2 of transcription). o RNA polymerase breaks interactions with transcription factors and escapes the promoter region to start elongation. o RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.