lecture_ch05_2014 honors biology_website
... mRNA strand copied from the DNA strand below? TATTAGTAGGTTA 1. UAUUACUACCUUA 2. AUAAUCAUCCAAU 3. ATTGGATGATTAT 4. ATAATCATCCAAT ...
... mRNA strand copied from the DNA strand below? TATTAGTAGGTTA 1. UAUUACUACCUUA 2. AUAAUCAUCCAAU 3. ATTGGATGATTAT 4. ATAATCATCCAAT ...
Chapter 4: DNA, RNA, and the Flow of Genetic Information
... The double-helical model of DNA and the presence of specific base pairs immediately suggested how the genetic material might replicate. The sequence of bases of one strand of the double helix precisely determines the sequence of the other strand; a guanine base on one strand is always paired with a ...
... The double-helical model of DNA and the presence of specific base pairs immediately suggested how the genetic material might replicate. The sequence of bases of one strand of the double helix precisely determines the sequence of the other strand; a guanine base on one strand is always paired with a ...
No Slide Title
... Low Mutation Rates are Necessary for the Evolution of Complexity 1. Because most mutations are deleterious, there are limits to the number of mutations that an organism can afford to accumulate in its somatic body, e.g., a) given mean eukaryotic rates, genomes can accommodate 60,000 genes without i ...
... Low Mutation Rates are Necessary for the Evolution of Complexity 1. Because most mutations are deleterious, there are limits to the number of mutations that an organism can afford to accumulate in its somatic body, e.g., a) given mean eukaryotic rates, genomes can accommodate 60,000 genes without i ...
Biology STAAR EOC Fall 2011
... TEK 11C: Summarize the role of microorganisms in both maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. (Supporting Standard) 38. Microorganisms, such as bacteria, play a vital role in maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. Bacteria live symbio ...
... TEK 11C: Summarize the role of microorganisms in both maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. (Supporting Standard) 38. Microorganisms, such as bacteria, play a vital role in maintaining and disrupting the health of both organisms and ecosystems. Bacteria live symbio ...
8.4 Transcription
... • RNA Polymerase • Enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of a complementary strand of RNA from a DNA template. • Enzymes that bond nucleotides together in a chain to make a new RNA molecule. • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Form of RNA that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where ...
... • RNA Polymerase • Enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of a complementary strand of RNA from a DNA template. • Enzymes that bond nucleotides together in a chain to make a new RNA molecule. • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Form of RNA that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where ...
An Interesting Saga of Simple Sequence Repeats in
... ECIL Road, Nacharam, Hyderabad-500076, Andhra Pradesh, India. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) or microsatellites are the repetitive nucleotide sequences of motifs of length 1-6bp. They are scattered throughout the genomes of all the known organisms ranging from viruses to eukaryotes. Microsatellites ...
... ECIL Road, Nacharam, Hyderabad-500076, Andhra Pradesh, India. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) or microsatellites are the repetitive nucleotide sequences of motifs of length 1-6bp. They are scattered throughout the genomes of all the known organisms ranging from viruses to eukaryotes. Microsatellites ...
Cytoplasmic inheritance
... 5. ORFs (open reading frames) sequences capable of encoding proteins but no product has been identified ...
... 5. ORFs (open reading frames) sequences capable of encoding proteins but no product has been identified ...
Restriction Enzymes
... information about a piece of DNA • We can use restriction enzymes to find out – The size of a plasmid – If there are any restriction sites for a particular enzyme on a piece of DNA (ex. EcoRI) – How many restriction sites for a particular enzyme – Where the restriction sites are located ...
... information about a piece of DNA • We can use restriction enzymes to find out – The size of a plasmid – If there are any restriction sites for a particular enzyme on a piece of DNA (ex. EcoRI) – How many restriction sites for a particular enzyme – Where the restriction sites are located ...
01. PCR and QPCR2
... spermatozoan to be amplified and analyzed DNA sequences as short as 50-100bp and as long as 10kb can be amplified As few as 20 cycles would yield ~106 times the amount of target DNA initially present ...
... spermatozoan to be amplified and analyzed DNA sequences as short as 50-100bp and as long as 10kb can be amplified As few as 20 cycles would yield ~106 times the amount of target DNA initially present ...
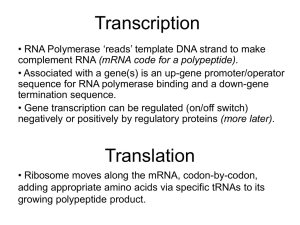
Transcription & Translation
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...
Final Exam Review
... 4. A cell with only one set of chromosomes is said to be ______________ (n). 5. A cell with two sets of chromosomes is said to be _______________ (2n). 6. In a heterozygous individual the ________________ allele is expressed. 7. The ________________ allele is only expressed when both alleles are low ...
... 4. A cell with only one set of chromosomes is said to be ______________ (n). 5. A cell with two sets of chromosomes is said to be _______________ (2n). 6. In a heterozygous individual the ________________ allele is expressed. 7. The ________________ allele is only expressed when both alleles are low ...
chapter 17 and 18 study guide
... Promoter? A specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA that binds RNA polymerase, positioning it to start transcribing RNA at the appropriate place Repressor? A protein that inhibits gene transcription; in prokaryotes repressors bind to the DNA in or near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind ...
... Promoter? A specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA that binds RNA polymerase, positioning it to start transcribing RNA at the appropriate place Repressor? A protein that inhibits gene transcription; in prokaryotes repressors bind to the DNA in or near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind ...
KOD -Plus
... Use of this product is covered by one or more of the following US patents and corresponding patent claims outside the US: 5,079,352, 5,789,224, 5,618,711, 6,127,155 and claims outside the US corresponding to US Patent No. 4,889,818. The purchase of this product includes a limited, non-transferable i ...
... Use of this product is covered by one or more of the following US patents and corresponding patent claims outside the US: 5,079,352, 5,789,224, 5,618,711, 6,127,155 and claims outside the US corresponding to US Patent No. 4,889,818. The purchase of this product includes a limited, non-transferable i ...
Lecture 5
... Eukaryotic chromosomal organization • Many eukaryotes are diploid (2N) • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins ...
... Eukaryotic chromosomal organization • Many eukaryotes are diploid (2N) • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins ...
Section 8.1 Power point
... • Results identified DNA as the transforming principle • Still these conclusions were questioned – “Maybe there was some protein in sample” “Maybe DNA is the genetic matter only in bacteria” • Much skepticism was due to many believing the the all important proteins had to be the genetic material. ...
... • Results identified DNA as the transforming principle • Still these conclusions were questioned – “Maybe there was some protein in sample” “Maybe DNA is the genetic matter only in bacteria” • Much skepticism was due to many believing the the all important proteins had to be the genetic material. ...
Rosalind Franklin
... the hidden atomic structure of matter in its crystalline form. 7. Franklin joined the war effort doing research on __________. 8. Her experiments led to a better _______ _____________, a valuable contribution to England under attack. 9. Her research was not without its risks so lab workers were peri ...
... the hidden atomic structure of matter in its crystalline form. 7. Franklin joined the war effort doing research on __________. 8. Her experiments led to a better _______ _____________, a valuable contribution to England under attack. 9. Her research was not without its risks so lab workers were peri ...
BF#10987 DNA Mutation Consequences
... Mutations are changes in a DNA sequence. A point mutation is a change in a single base pair of a gene. Point mutations, or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), involve only one nitrogen base change of the three nitrogen bases in a codon. Perform this activity and witness the change a single poin ...
... Mutations are changes in a DNA sequence. A point mutation is a change in a single base pair of a gene. Point mutations, or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), involve only one nitrogen base change of the three nitrogen bases in a codon. Perform this activity and witness the change a single poin ...
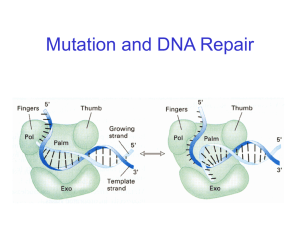
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.