writing chemical equations
... periodic table, fluorine being the most reactive. Consider the following example: ...
... periodic table, fluorine being the most reactive. Consider the following example: ...
KCSE ONLINE REVISION Biology Notes Form 2
... the mineral ions in sap and those in soil solution active transport involves energy in form of ATP due to respiration which forces mineral salts through a plant against a concentration gradient water moves by osmosis through a semi-permeable membrane of root hairs and between cells of stem in stem ...
... the mineral ions in sap and those in soil solution active transport involves energy in form of ATP due to respiration which forces mineral salts through a plant against a concentration gradient water moves by osmosis through a semi-permeable membrane of root hairs and between cells of stem in stem ...
Biology Form 2
... the mineral ions in sap and those in soil solution active transport involves energy in form of ATP due to respiration which forces mineral salts through a plant against a concentration gradient water moves by osmosis through a semi-permeable membrane of root hairs and between cells of stem in stem ...
... the mineral ions in sap and those in soil solution active transport involves energy in form of ATP due to respiration which forces mineral salts through a plant against a concentration gradient water moves by osmosis through a semi-permeable membrane of root hairs and between cells of stem in stem ...
PHY3072 - MUSCLE AND EXERCISE LECTURE 2: Introduction to
... Muscle pH is reduced during exercise in an intensity dependent matter Implications for metabolism: E.g. pH drop inhibits fatty acid oxidation enzymes and may cause the decrease in fat metabolism seen during intense aerobic exercise ...
... Muscle pH is reduced during exercise in an intensity dependent matter Implications for metabolism: E.g. pH drop inhibits fatty acid oxidation enzymes and may cause the decrease in fat metabolism seen during intense aerobic exercise ...
QA1
... The wire is then ready to be used. If a sample solution is being tested, immerse the wire into the solution and then put the wire into a colourless flame and note the colour of the flame. Caution should be made not to burn the glass part of the platinum wire; otherwise, it will be broken. Sodium com ...
... The wire is then ready to be used. If a sample solution is being tested, immerse the wire into the solution and then put the wire into a colourless flame and note the colour of the flame. Caution should be made not to burn the glass part of the platinum wire; otherwise, it will be broken. Sodium com ...
No Slide Title
... Which of the following organisms use alcoholic fermentation to allow glycolysis to continue to produce ATP? ...
... Which of the following organisms use alcoholic fermentation to allow glycolysis to continue to produce ATP? ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... their prey by drowning them. How do crocodile's tissues get O2 while submerged? Unlik e deep diving whales, which use myoglobin to store O2 in muscle, crocodil es rely on a unique allo steric effector of Hb to ensure deliv ery of O2 to tissues. While submerged, metabolism produces CO2, which is conv ...
... their prey by drowning them. How do crocodile's tissues get O2 while submerged? Unlik e deep diving whales, which use myoglobin to store O2 in muscle, crocodil es rely on a unique allo steric effector of Hb to ensure deliv ery of O2 to tissues. While submerged, metabolism produces CO2, which is conv ...
Cellular respiration photosynthesis
... Which of the following organisms use alcoholic fermentation to allow glycolysis to continue to produce ATP? ...
... Which of the following organisms use alcoholic fermentation to allow glycolysis to continue to produce ATP? ...
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with
... The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond. These bonds can occur between molecules (intermolecularly), or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecularly). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, ...
... The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond. These bonds can occur between molecules (intermolecularly), or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecularly). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, ...
1MBO Lopez kin
... release free iron and is not utilized as a source of cellular heme3. While the traditional textbook roles for heme as a cofactor include hemo- and myoglobins, cytochromes and a handful of enzymes, considerable evidence has emerged that demonstrates a central role for heme in regulation of gene trans ...
... release free iron and is not utilized as a source of cellular heme3. While the traditional textbook roles for heme as a cofactor include hemo- and myoglobins, cytochromes and a handful of enzymes, considerable evidence has emerged that demonstrates a central role for heme in regulation of gene trans ...
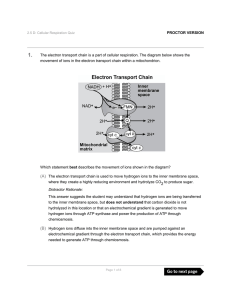
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
Respiratory System
... This region contains no alveoli, so no gas exchange takes place in this area. Consequently, it is also referred to as anatomical dead space. The conducting airways carry out two major functions. The first is to lead inspired air to the more distal gas-exchanging regions of the lungs. The second is t ...
... This region contains no alveoli, so no gas exchange takes place in this area. Consequently, it is also referred to as anatomical dead space. The conducting airways carry out two major functions. The first is to lead inspired air to the more distal gas-exchanging regions of the lungs. The second is t ...
Answer Key
... A) copper sulfate acid. B) copper sulfate pentahydrate. C) copper(II) sulfate acid. D) copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. E) copper(V) sulfate hydrate. ...
... A) copper sulfate acid. B) copper sulfate pentahydrate. C) copper(II) sulfate acid. D) copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. E) copper(V) sulfate hydrate. ...
Structures and Bonding
... 2) However, if temperature was INCREASED the rate of reaction in both directions would ________ causing the ammonia to form faster 3) If pressure was INCREASED the amount of ammonia formed would INCREASE because there are less molecules on the right hand side of the equation ...
... 2) However, if temperature was INCREASED the rate of reaction in both directions would ________ causing the ammonia to form faster 3) If pressure was INCREASED the amount of ammonia formed would INCREASE because there are less molecules on the right hand side of the equation ...
UN1001: Section 11: Hydrogen Effects
... High temperature process - C or carbide in steels can react with gaseous hydrogen . . . C + 2H2 CH4 Note that the reaction can occur with atomic H in the metal lattice . . . C + 4H CH4 May crack the steel from high internal pressure. ...
... High temperature process - C or carbide in steels can react with gaseous hydrogen . . . C + 2H2 CH4 Note that the reaction can occur with atomic H in the metal lattice . . . C + 4H CH4 May crack the steel from high internal pressure. ...
10/7 N cycle notes - Cornell Geological Sciences
... 5) NH4+ may react to form NH3 and be lost as the gas phase (“volatilization”). NH4+ + OH- NH3(gas)↑ + H2O. This process is obviously favored at high pH. It is also favored at high T, and fires cause significant N losses. The net NH4+ and NO3- produced (total minus that taken up – immobilized- by b ...
... 5) NH4+ may react to form NH3 and be lost as the gas phase (“volatilization”). NH4+ + OH- NH3(gas)↑ + H2O. This process is obviously favored at high pH. It is also favored at high T, and fires cause significant N losses. The net NH4+ and NO3- produced (total minus that taken up – immobilized- by b ...
Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms
... Use alternate terminal electron acceptor other that oxygen ...
... Use alternate terminal electron acceptor other that oxygen ...
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 14. In the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, electrons are commonly transferred from one molecule to another. In one such reaction a Fe3+ ion in a cytochrome is converted to a Fe2+ ion. This is known as a) isomer formation b) hydrolysis c) reduction d) oxidation 15. Where in the electron ...
... 14. In the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, electrons are commonly transferred from one molecule to another. In one such reaction a Fe3+ ion in a cytochrome is converted to a Fe2+ ion. This is known as a) isomer formation b) hydrolysis c) reduction d) oxidation 15. Where in the electron ...
Chemical Equation Reactions
... periodic table, fluorine being the most reactive. Consider the following example: ...
... periodic table, fluorine being the most reactive. Consider the following example: ...
Alternative Pathways to Cellular Respiration!
... calvin cycle When pyruvate is left after the CO2 breaks off the malate, it takes ATP to rearrange the pyruvate into PEP. ...
... calvin cycle When pyruvate is left after the CO2 breaks off the malate, it takes ATP to rearrange the pyruvate into PEP. ...
2. Pyruvate Oxidation
... is the step-wise release of energy from carbohydrates and other molecules Energy from these reactions is used to synthesize ATP molecules This is an aerobic process—it requires oxygen ...
... is the step-wise release of energy from carbohydrates and other molecules Energy from these reactions is used to synthesize ATP molecules This is an aerobic process—it requires oxygen ...
Question 2
... 9. When this expression is balanced, 2C3H6 + O2 CO2 + 6H2O what is the coefficient of oxygen, O2? a) 6 ...
... 9. When this expression is balanced, 2C3H6 + O2 CO2 + 6H2O what is the coefficient of oxygen, O2? a) 6 ...
Class: X Subject: Biology Topic: Life processes No. of
... Ans. B Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a ...
... Ans. B Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a ...