2 H2(g)
... 9. Calculate the number of moles of water needed to make 20 g of glucose during photosynthesis. 10. Calculate what mass of calcium hydroxide reacts with 0.257 moles of hydrogen chloride. 11. Calculate the number of moles of oxygen reacting with 250 g of hydrogen to form water. 12. What`s the volume ...
... 9. Calculate the number of moles of water needed to make 20 g of glucose during photosynthesis. 10. Calculate what mass of calcium hydroxide reacts with 0.257 moles of hydrogen chloride. 11. Calculate the number of moles of oxygen reacting with 250 g of hydrogen to form water. 12. What`s the volume ...
Document
... Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
... Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
The Chemicals of Living Things
... Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
... Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
Chem Sheets to Memorize
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
Chem Sheets to Memorize
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
Chem Sheets to Memorize SOLUBILITY CHART
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
... Please write net ionic balanced reactions (with states of matter included) for the following questions on a separate piece of paper. You’ll have reactions that are classified as precipitation, acid-base, or redox (reduction-oxidation…like, synthesis, decomposition, and single displacement/replacemen ...
I. Introduction
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
Week 5, Muscles, Feb 12, student version
... Types of muscles- smooth • Internal organs/tubes • Involuntary • Lack striations ...
... Types of muscles- smooth • Internal organs/tubes • Involuntary • Lack striations ...
Non-competitive
... Apoenzyme – the polypeptide portion of an enzyme Cofactor – non protein portion of an enzyme May be a metal ion such as Zn2+ of Mg2+ May also be an organic molecule such as vitamin B or heme – called a coenzyme Substrate – the molecule an enzyme acts on Activation – any process that initiates or in ...
... Apoenzyme – the polypeptide portion of an enzyme Cofactor – non protein portion of an enzyme May be a metal ion such as Zn2+ of Mg2+ May also be an organic molecule such as vitamin B or heme – called a coenzyme Substrate – the molecule an enzyme acts on Activation – any process that initiates or in ...
Chapter 19: Respiratory System
... C. Carbon Dioxide Transport 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. ...
... C. Carbon Dioxide Transport 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. ...
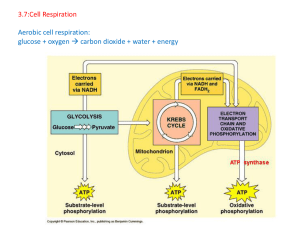
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
I. Introduction
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
Moles and Equations
... We won't manage to balance them by multiplying just one side by something - there's no whole number we can multiply 2 by to get 3. So we have 3 lots of O2 and 2 lots of Fe2O3 - so we end with 6 oxygens on each side (this is a bit like the cross-over rule) ...
... We won't manage to balance them by multiplying just one side by something - there's no whole number we can multiply 2 by to get 3. So we have 3 lots of O2 and 2 lots of Fe2O3 - so we end with 6 oxygens on each side (this is a bit like the cross-over rule) ...
I. Introduction
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
16Notes-Answer Key - Brimm Medical Arts High School
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
I. Introduction
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
... 1. Blood flowing through capillaries gain carbon dioxide because the tissues have a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide is transported to lungs in one of the following three forms: bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or as bicarbonate ions. 3. Hemoglobin can carry oxygen ...
Physiological effects of exercise
... muscles is readily supplied from the oxidative metabolism of glucose and fatty acids. However, at the onset of exercise there is an immediate requirement for increased supply of energy and there is only enough ATP stored for 1–2 seconds of work and therefore rapid ways to resynthesize ATP are requir ...
... muscles is readily supplied from the oxidative metabolism of glucose and fatty acids. However, at the onset of exercise there is an immediate requirement for increased supply of energy and there is only enough ATP stored for 1–2 seconds of work and therefore rapid ways to resynthesize ATP are requir ...
Physiological effects of exercise
... muscles is readily supplied from the oxidative metabolism of glucose and fatty acids. However, at the onset of exercise there is an immediate requirement for increased supply of energy and there is only enough ATP stored for 1–2 seconds of work and therefore rapid ways to resynthesize ATP are requir ...
... muscles is readily supplied from the oxidative metabolism of glucose and fatty acids. However, at the onset of exercise there is an immediate requirement for increased supply of energy and there is only enough ATP stored for 1–2 seconds of work and therefore rapid ways to resynthesize ATP are requir ...
Analysis of Mathematical Models of the Human Lung
... system responsible for this process is the respiratory system, shown in Figure (1.1). To begin the process, air enters through the oral cavity or nasal vestibule and moves through the nasal cavity due to compression of the diaphragm. First, after entering the nose, the air is warmed and large partic ...
... system responsible for this process is the respiratory system, shown in Figure (1.1). To begin the process, air enters through the oral cavity or nasal vestibule and moves through the nasal cavity due to compression of the diaphragm. First, after entering the nose, the air is warmed and large partic ...
Biology_Chapter 8_Cellular_Respiration
... Grapes are crushed and the sugar they contain is fermented by yeasts to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide usually escapes but if the wine is bottled before fermentation is complete, the carbon dioxide dissolves and escapes as bubble when the bottle is opened This is the case wit ...
... Grapes are crushed and the sugar they contain is fermented by yeasts to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide usually escapes but if the wine is bottled before fermentation is complete, the carbon dioxide dissolves and escapes as bubble when the bottle is opened This is the case wit ...
Formulae and equations
... The number of atoms or groups of atoms in a formula is given by putting a small number just below and behind the symbol(s). As the appearance of a symbol indicates one atom is present, a 1 isn’t written (you put NaCl not Na1Cl1). In some formulae brackets are used to avoid ambiguity. Aluminium sulph ...
... The number of atoms or groups of atoms in a formula is given by putting a small number just below and behind the symbol(s). As the appearance of a symbol indicates one atom is present, a 1 isn’t written (you put NaCl not Na1Cl1). In some formulae brackets are used to avoid ambiguity. Aluminium sulph ...
Thesis A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
... system responsible for this process is the respiratory system, shown in Figure (1.1). To begin the process, air enters through the oral cavity or nasal vestibule and moves through the nasal cavity due to compression of the diaphragm. First, after entering the nose, the air is warmed and large partic ...
... system responsible for this process is the respiratory system, shown in Figure (1.1). To begin the process, air enters through the oral cavity or nasal vestibule and moves through the nasal cavity due to compression of the diaphragm. First, after entering the nose, the air is warmed and large partic ...
cellular respiration
... process that: – Primarily occurs in mitochondria – Harvests energy stored in organic molecules ...
... process that: – Primarily occurs in mitochondria – Harvests energy stored in organic molecules ...
Respiratory A&P and Assessment PN 132
... - To simulate the sound of Crackles ○ Take a few strands of hair between your fingers ○ Hold it up to your ear ○ Rub back and forth ...
... - To simulate the sound of Crackles ○ Take a few strands of hair between your fingers ○ Hold it up to your ear ○ Rub back and forth ...
WJEC Biology / Human Biology BY4 Question
... experiment are shown below. The growth media was the same in all tubes. ...
... experiment are shown below. The growth media was the same in all tubes. ...