Chapter 9
... B) It attaches and detaches phosphate groups. C) It uses glucose and generates pyruvate. D) It shifts molecules from cytosol to mitochondrion. E) It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP. Answer: E Topic: Concept 9.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension Use the following information to answ ...
... B) It attaches and detaches phosphate groups. C) It uses glucose and generates pyruvate. D) It shifts molecules from cytosol to mitochondrion. E) It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP. Answer: E Topic: Concept 9.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension Use the following information to answ ...
Short-Term Overexpression of a Constitutively Active Form of AMP
... increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle, both directly and indirectly, via the hypothalamic-sympathetic nervous system axis (2). Adiponectin activates AMPK in skeletal muscle, stimulating glucose utilization, glycogen synthesis, and fatty acid oxidation and, in the liver, increasing fatty ...
... increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle, both directly and indirectly, via the hypothalamic-sympathetic nervous system axis (2). Adiponectin activates AMPK in skeletal muscle, stimulating glucose utilization, glycogen synthesis, and fatty acid oxidation and, in the liver, increasing fatty ...
Microbial Metabolism
... atoms, ions, or molecules must collide. The collision theory explains how chemical reactions occur and how certain factors affect the rates of those reactions. The basis of the collision theory is that all atoms, ions, and molecules are continuously moving and are thus continuously colliding with on ...
... atoms, ions, or molecules must collide. The collision theory explains how chemical reactions occur and how certain factors affect the rates of those reactions. The basis of the collision theory is that all atoms, ions, and molecules are continuously moving and are thus continuously colliding with on ...
Sex-specific alterations in glucose homeostasis and metabolic
... Sex-specific alterations in fasting-induced lipolysis of adipose tissue in Casp2−/− mice Glucose homeostasis can be related to body composition. As a leaner phenotype has been previously observed in aged Casp2−/− mice,8,9 we wanted to investigate this further and focus on the role of caspase-2 in lip ...
... Sex-specific alterations in fasting-induced lipolysis of adipose tissue in Casp2−/− mice Glucose homeostasis can be related to body composition. As a leaner phenotype has been previously observed in aged Casp2−/− mice,8,9 we wanted to investigate this further and focus on the role of caspase-2 in lip ...
University of Groningen Fructosyltransferases of Lactobacillus
... of cellulose, starch, sucrose (Fig. 3A), raffinose (Fig. 3B), lactose, glucans, and α,αtrehalose. It is also found in a free state in a number of materials such as honey, grapes, and raisins. Glucose plays an important role in the blood of all animals, where it serves as an immediate source of energ ...
... of cellulose, starch, sucrose (Fig. 3A), raffinose (Fig. 3B), lactose, glucans, and α,αtrehalose. It is also found in a free state in a number of materials such as honey, grapes, and raisins. Glucose plays an important role in the blood of all animals, where it serves as an immediate source of energ ...
Bio1A - Lec 9 slides File
... Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy / making ATP ...
... Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy / making ATP ...
Lecture 9 – Cellular Respiration
... • Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen • Anaerobic respiration – takes place in the absence of oxygen – Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration where sugars are partially degraded – Consumes compounds other than oxygen Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and ana ...
... • Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen • Anaerobic respiration – takes place in the absence of oxygen – Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration where sugars are partially degraded – Consumes compounds other than oxygen Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and ana ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
View/Open - VUW research archive - Victoria University of Wellington
... Conditions for extraction and two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins were established. One hundred and seventy nine proteins were identified by MALDI mass spectrometry of tryptic digests of protein spots excised from Coomassie stained gels. All of the enzymes for conversion of glucose to ethano ...
... Conditions for extraction and two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins were established. One hundred and seventy nine proteins were identified by MALDI mass spectrometry of tryptic digests of protein spots excised from Coomassie stained gels. All of the enzymes for conversion of glucose to ethano ...
Citric acid cycle
... ATP synthesis • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle produce only 4 ATP molecules per glucose, all by substrate-level phosphorylation: 2 net ATP from glycolysis and 2 ATP from the citric acid cycle. • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via o ...
... ATP synthesis • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle produce only 4 ATP molecules per glucose, all by substrate-level phosphorylation: 2 net ATP from glycolysis and 2 ATP from the citric acid cycle. • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via o ...
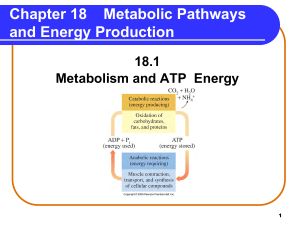
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
The Regulation of Energy Metabolism Pathways
... noted that to our knowledge, an acute mildronate treatment does not induce any metabolic or gene expression changes, and therefore, long-term treatment (at least 10-14 days) is necessary to achieve regulatory effects. In addition, all changes induced by mildronate are highly related to the decrease ...
... noted that to our knowledge, an acute mildronate treatment does not induce any metabolic or gene expression changes, and therefore, long-term treatment (at least 10-14 days) is necessary to achieve regulatory effects. In addition, all changes induced by mildronate are highly related to the decrease ...
Mammalian Cell Culture: High Throughput Applications of
... has been in the production of proteins for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The main advantage of using these and other mammalian cell lines for production is their ability to produce proteins with the correct conformation and post-translational modifications. CHO cells are also routinely used f ...
... has been in the production of proteins for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The main advantage of using these and other mammalian cell lines for production is their ability to produce proteins with the correct conformation and post-translational modifications. CHO cells are also routinely used f ...
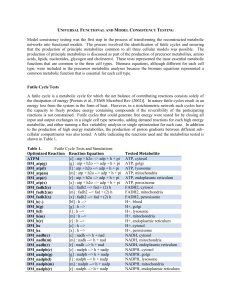
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... that the production of principle metabolites common to all three cellular models was possible. The production of principle metabolites is discussed as part of the production of precursor metabolites, amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, glycogen and cholesterol. These tests represented the most essenti ...
... that the production of principle metabolites common to all three cellular models was possible. The production of principle metabolites is discussed as part of the production of precursor metabolites, amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, glycogen and cholesterol. These tests represented the most essenti ...
Carbohydrates & Lipids - mvhs
... – Fibers form parallel chains – How would the structure of cellulose & chitin support their functions? ...
... – Fibers form parallel chains – How would the structure of cellulose & chitin support their functions? ...
Glycogen branches out: new perspectives on the role of glycogen
... kinase in the cell is found at the sarcoplasmic reticulum bound to glycogen (32, 39, 63), allowing for the coupling of contraction, calcium release, and glycogen breakdown. Glycogen phosphorylase is also allosterically activated by increased [Pi] within the cell, which rises as ATP levels fall, refl ...
... kinase in the cell is found at the sarcoplasmic reticulum bound to glycogen (32, 39, 63), allowing for the coupling of contraction, calcium release, and glycogen breakdown. Glycogen phosphorylase is also allosterically activated by increased [Pi] within the cell, which rises as ATP levels fall, refl ...
respiration in plants
... The term respiration was first used by animal physiologists to describe breathing movements of animals, but was subsequently extended to include the chemical reactions by which complex organic -ve substances like carbohydrates, fats and proteins are broken down to release CO2, water and energy. In p ...
... The term respiration was first used by animal physiologists to describe breathing movements of animals, but was subsequently extended to include the chemical reactions by which complex organic -ve substances like carbohydrates, fats and proteins are broken down to release CO2, water and energy. In p ...
Biochemistry of Ensiling - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... and are generally found as activated sugars. Flux through this pool can be quite high, especially during times of high metabolic activity. Plant monosaccharides are classified according to the type of functional group they contain. Most contain an aldehyde group and are referred to as aldoses (e.g., ...
... and are generally found as activated sugars. Flux through this pool can be quite high, especially during times of high metabolic activity. Plant monosaccharides are classified according to the type of functional group they contain. Most contain an aldehyde group and are referred to as aldoses (e.g., ...
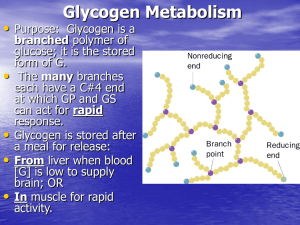
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... d) PP1 has a much higher affinity for GP-P than for GS, GPK, etc, so it must first “work its way through” nearly all the GP-P, dephosphorylating it, before it has much effect on GS. ...
... d) PP1 has a much higher affinity for GP-P than for GS, GPK, etc, so it must first “work its way through” nearly all the GP-P, dephosphorylating it, before it has much effect on GS. ...
Pentose Phosphate Shunt
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis Or, if NADPH or ribose-5-P ...
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis Or, if NADPH or ribose-5-P ...
Reactions of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Energy and Electron Balance Sheets Gluconeogenesis Coordinated Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis Entry of Other Sugars into the Glycolytic Pathway ...
... Energy and Electron Balance Sheets Gluconeogenesis Coordinated Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis Entry of Other Sugars into the Glycolytic Pathway ...
09_Lectures_PPT
... • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.