Genetics, Heredity, and Biotechnology
... • Stem Cells are the group of cells produced in the very early stages of embryonic growth; they are similar to the original zygote. • When the embryo reaches 20 – 150 cells in size, this group begins to produce specialized cells that later become tissues. • Stem cells can become any type of cell. Th ...
... • Stem Cells are the group of cells produced in the very early stages of embryonic growth; they are similar to the original zygote. • When the embryo reaches 20 – 150 cells in size, this group begins to produce specialized cells that later become tissues. • Stem cells can become any type of cell. Th ...
Spermatogenesis: sperm formation
... • These eggs begin meiosis (before birth) and stop just before the first division. • Puberty: ovulation once a month, egg completes it’s first division and is released from the ovary • It begins the second division, but does not complete the process unless fertilized! • On average, a woman will ovul ...
... • These eggs begin meiosis (before birth) and stop just before the first division. • Puberty: ovulation once a month, egg completes it’s first division and is released from the ovary • It begins the second division, but does not complete the process unless fertilized! • On average, a woman will ovul ...
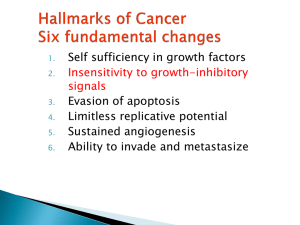
The 2 alleles on chromosome 13q14 must be inactivated
... The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by Rb gene ...
... The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by Rb gene ...
Lesson Overview
... Cell differentiation in mammals is controlled by a number of interacting factors in the embryo. Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
... Cell differentiation in mammals is controlled by a number of interacting factors in the embryo. Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
Lesson Overview
... Cell differentiation in mammals is controlled by a number of interacting factors in the embryo. Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
... Cell differentiation in mammals is controlled by a number of interacting factors in the embryo. Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
Cell odling/Cell culturing There is no mandatory book for this course
... Manipulating the mouse embryo A laboratory manual third ed Authors: Andras Nagy, Marina Gertsenstein, Kristina Vintersten, Richard Behringer , Cold spring Harbor Laboratory Press 2003, ISBN 0-87969-574-9 ...
... Manipulating the mouse embryo A laboratory manual third ed Authors: Andras Nagy, Marina Gertsenstein, Kristina Vintersten, Richard Behringer , Cold spring Harbor Laboratory Press 2003, ISBN 0-87969-574-9 ...
Nucleus - Control Center of cell
... DNA is stored in Chromatin Chromatin is a substance that contains • Each strand of chromatin is of DNA in the nucleus. •During cell growth and creates •Chromatin coils into (x shaped structure) when cells ready to Relationship between DNA-->Chromatin-->Chromosomes ...
... DNA is stored in Chromatin Chromatin is a substance that contains • Each strand of chromatin is of DNA in the nucleus. •During cell growth and creates •Chromatin coils into (x shaped structure) when cells ready to Relationship between DNA-->Chromatin-->Chromosomes ...
Pressemitteilung Excellent Stem Cell Researchers
... doi:10.1038/nature13804), the lab was able to identify key new properties of naïve state human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). These cells constitute only five percent of hESC cultures. In the search for distinctive key properties of the naïve cells, the authors detected a sequence originally derived ...
... doi:10.1038/nature13804), the lab was able to identify key new properties of naïve state human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). These cells constitute only five percent of hESC cultures. In the search for distinctive key properties of the naïve cells, the authors detected a sequence originally derived ...
VI. Genetic Engineering or Recombinant DNA Technology
... V. Tissue Culture and Mericloning A. Tissue Culture 1. Defined • a mass of callus tissue growing on an artificial medium 2. Techniques a. Isolate plant tissues from meristems or pith b. Place in sterile growth medium c. Rapid multiplication of cells occurs d. Tissue may differentiate into roots, sh ...
... V. Tissue Culture and Mericloning A. Tissue Culture 1. Defined • a mass of callus tissue growing on an artificial medium 2. Techniques a. Isolate plant tissues from meristems or pith b. Place in sterile growth medium c. Rapid multiplication of cells occurs d. Tissue may differentiate into roots, sh ...
Document
... • Stem cells are defined by their ability to: – Continue to grow and divide – Given the right signals (e.g. hormones or growth/differentiation factors), to differentiate into a specialized cell type ...
... • Stem cells are defined by their ability to: – Continue to grow and divide – Given the right signals (e.g. hormones or growth/differentiation factors), to differentiate into a specialized cell type ...
Quiz 2 Q3 Review Sheet 3/8/11
... 22. Compare embryonic stems cells to adult stem cells. Give an example of each. Which are more useful to us and why? 23. If I contracted a virus that destroyed my motor neurons, explain how you would generate new neurons that are genetically identical to me so that my immune system does not reject t ...
... 22. Compare embryonic stems cells to adult stem cells. Give an example of each. Which are more useful to us and why? 23. If I contracted a virus that destroyed my motor neurons, explain how you would generate new neurons that are genetically identical to me so that my immune system does not reject t ...
Developmental Gene Expression Part II
... expression of many genes. The gene bicoid is a transcriptional repressor of a second gene, giant, and is expressed early at the anterior end of the embryo during development (see diagram below). Explain ...
... expression of many genes. The gene bicoid is a transcriptional repressor of a second gene, giant, and is expressed early at the anterior end of the embryo during development (see diagram below). Explain ...
Cell Growth and Division
... • Asexual – Making genetically identical offspring to a single parent. – Ex: bacteria, many multicellular organisms. ...
... • Asexual – Making genetically identical offspring to a single parent. – Ex: bacteria, many multicellular organisms. ...
Cell Division
... • Then a second division occurs without duplication of Chromosomes • Resulting in 4 gametes (sex cells) • These contain ½ the DNA of parent • Crossing over of genetic material can also occur, this process is responsible for the variation amongst the different chromosomes (switch genes) ...
... • Then a second division occurs without duplication of Chromosomes • Resulting in 4 gametes (sex cells) • These contain ½ the DNA of parent • Crossing over of genetic material can also occur, this process is responsible for the variation amongst the different chromosomes (switch genes) ...
Glover-presentation - Oslo University Hospital
... What is the differentiation potential of somatic stem cells? Organ-restricted (multipotent), or broader (pluripotent)? Much circumstantial evidence. Requirement for definitive studies proving full differentiation to specific cell types in vivo. ...
... What is the differentiation potential of somatic stem cells? Organ-restricted (multipotent), or broader (pluripotent)? Much circumstantial evidence. Requirement for definitive studies proving full differentiation to specific cell types in vivo. ...
EOC Vocab Review Terms
... 1. ___Part of the experiment that does not contain the variable 2. ___Testable explanation for a problem 3. ___The factor in the experiment to be tested ...
... 1. ___Part of the experiment that does not contain the variable 2. ___Testable explanation for a problem 3. ___The factor in the experiment to be tested ...
D E V E L O P M E N T
... that ECs undergo slow turnover and that lost cells are replaced by self-duplication rather than by stem cell division. Using fluorescent markers, they show that ECs extend elaborate cellular processes that interact with differentiated germ cells and that these processes are missing when GSC differen ...
... that ECs undergo slow turnover and that lost cells are replaced by self-duplication rather than by stem cell division. Using fluorescent markers, they show that ECs extend elaborate cellular processes that interact with differentiated germ cells and that these processes are missing when GSC differen ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... differences in genotype, and are potentially reversible, but are generally stably maintained during cell division. Examples: imprinting, twins, cancer vs. normal cells, differentiation, ... The narrow interpretation of this concept is that of stable differential states of gene expression. A much mor ...
... differences in genotype, and are potentially reversible, but are generally stably maintained during cell division. Examples: imprinting, twins, cancer vs. normal cells, differentiation, ... The narrow interpretation of this concept is that of stable differential states of gene expression. A much mor ...
N E W S A N D ...
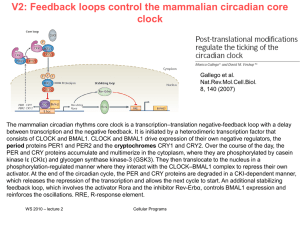
... from immunology to synthetic and systems biology. From an immunological and evolutionary standpoint, cells that show bistability can have a distinct advantage over those that are monostable, especially in highly variable environments4,5 Mulitstability not based on feedback could also be a useful too ...
... from immunology to synthetic and systems biology. From an immunological and evolutionary standpoint, cells that show bistability can have a distinct advantage over those that are monostable, especially in highly variable environments4,5 Mulitstability not based on feedback could also be a useful too ...
WENJUN GUO, Ph.D. Positions: Research interests:
... heterogeneous subtypes of breast cancer arise remains largely unclear. Addressing this question is important for breast cancer prevention and treatment. Distinct stem/progenitor cell populations have recently been identified in the mammary gland. It is likely that accumulation of genetic/epigenetic ...
... heterogeneous subtypes of breast cancer arise remains largely unclear. Addressing this question is important for breast cancer prevention and treatment. Distinct stem/progenitor cell populations have recently been identified in the mammary gland. It is likely that accumulation of genetic/epigenetic ...
A New Stem Cell Line for HD
... development of drugs for others," Daley said. The stem cell line for Huntington’s Disease provides a welcome new model to study the development of the disease within a single cell. It could also be used to screen for and test potential new treatments. The authors note, however, that these cells coul ...
... development of drugs for others," Daley said. The stem cell line for Huntington’s Disease provides a welcome new model to study the development of the disease within a single cell. It could also be used to screen for and test potential new treatments. The authors note, however, that these cells coul ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... Parents transmit genes to their offspring. Some medical conditions and diseases are genetic in origin. The processes involved in sorting and recombining parents' genetic material create potential variation among offspring. Chromosomes contain genetic information which can be categorized as r ...
... Parents transmit genes to their offspring. Some medical conditions and diseases are genetic in origin. The processes involved in sorting and recombining parents' genetic material create potential variation among offspring. Chromosomes contain genetic information which can be categorized as r ...
Cell - Cloudfront.net
... • Zygote: fertilized cell created by the union of the egg and sperm • Embryonic stem cells – Created during earliest divisions – Potential to become any type of cell ...
... • Zygote: fertilized cell created by the union of the egg and sperm • Embryonic stem cells – Created during earliest divisions – Potential to become any type of cell ...
Prof. Dinko Mitrecic, MD, PhD Laboratory for Stem Cells
... https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28033684 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26730404 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26019332 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23990976 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23140086 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22490338 ...
... https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28033684 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26730404 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26019332 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23990976 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23140086 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22490338 ...