Neuron [or Nerve Cell]
... structure in the soma of the neuron that contains the chromosomes. The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found. Most of the protein production and energy storage is performed at this point in the cell. A layer of fatty cells that covers many axons and helps speed neural impulses The portion of ...
... structure in the soma of the neuron that contains the chromosomes. The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found. Most of the protein production and energy storage is performed at this point in the cell. A layer of fatty cells that covers many axons and helps speed neural impulses The portion of ...
1. Jointed appendages have a variety of specialized functions 2. The
... 2. The body is covered by an exoskeleton made of chitin Advantage: good protection, muscles attach to it for strength Disadvantage: heavy and does not grow & animal must molt ...
... 2. The body is covered by an exoskeleton made of chitin Advantage: good protection, muscles attach to it for strength Disadvantage: heavy and does not grow & animal must molt ...
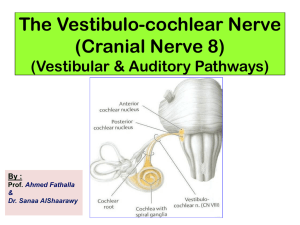
9-Cranial nerve 8 (Vestibulo
... • Type: Special sensory (SSA) • Conveys impulses from inner ear to nervous system. • Components: Vestibular part: conveys impulses associated with body posture and balance coordination of head & eye movement. ...
... • Type: Special sensory (SSA) • Conveys impulses from inner ear to nervous system. • Components: Vestibular part: conveys impulses associated with body posture and balance coordination of head & eye movement. ...
2/13 Human Organ System
... Impulse Nerve Impulse: the electrical discharge that travels along a nerve fiber ...
... Impulse Nerve Impulse: the electrical discharge that travels along a nerve fiber ...
Body Systems Work Together
... 3. Nervous and Muscle work together by sending signals based on the senses to contract muscles and move. 4. Nervous and Endocrine work together by reacting to a stimulus in the body, and signaling a response, like sugar level, water level, calcium level, growth, or sleep. ...
... 3. Nervous and Muscle work together by sending signals based on the senses to contract muscles and move. 4. Nervous and Endocrine work together by reacting to a stimulus in the body, and signaling a response, like sugar level, water level, calcium level, growth, or sleep. ...
Neuro Anatomy Lec.6 د.عبد الجبار الحبي طي The Pons Is the middle
... It lies in the posterior cranial fossa, behind the Pons and medulla oblongata and encloses with them the 4th ventricle. It has two surfaces (sup. and inf.), two notches (the ant. and pos. – the anterior one receives the back of the brain stem, while the posterior receives the falx cerebelli). It con ...
... It lies in the posterior cranial fossa, behind the Pons and medulla oblongata and encloses with them the 4th ventricle. It has two surfaces (sup. and inf.), two notches (the ant. and pos. – the anterior one receives the back of the brain stem, while the posterior receives the falx cerebelli). It con ...
organs and organ systems: introdaction
... Organs are composed of multiple tissue types organized to carry out a specific function. Examples of organs include the heart, the brain, the pancreas, blood vessels, bones, and skin. Groups of multiple organs working together to carry out a major bodily function are called organ systems. Any animal ...
... Organs are composed of multiple tissue types organized to carry out a specific function. Examples of organs include the heart, the brain, the pancreas, blood vessels, bones, and skin. Groups of multiple organs working together to carry out a major bodily function are called organ systems. Any animal ...
The Neuron - MsHughesPsychology
... also contains the nucleus, which keeps the neuron functioning. 3. Axon: a long tube-like structure that transmits information away from the Soma and to the next neuron in the neural pathway. 4. Axon Terminals: branches extend out from the axon and end in knob-like structures called ...
... also contains the nucleus, which keeps the neuron functioning. 3. Axon: a long tube-like structure that transmits information away from the Soma and to the next neuron in the neural pathway. 4. Axon Terminals: branches extend out from the axon and end in knob-like structures called ...
Chapter 43
... • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connective, muscle, and nerve tissue ...
... • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connective, muscle, and nerve tissue ...
anatomi sistem saraf dan indera a
... • Based on number of processes found on cell body – multipolar = several dendrites & one axon • most common cell type in the brain and SC ...
... • Based on number of processes found on cell body – multipolar = several dendrites & one axon • most common cell type in the brain and SC ...
Given sufficient input, neurons “fire action potentials”
... Given sufficient input, neurons “fire action potentials” – fast voltage transients …which are communicated to downstream neurons via synapses INPUT ...
... Given sufficient input, neurons “fire action potentials” – fast voltage transients …which are communicated to downstream neurons via synapses INPUT ...
Amphibian (Frog)
... They can see light and colors these go to the visual part of the brain and then is processed in the cerebellum of the brain. ...
... They can see light and colors these go to the visual part of the brain and then is processed in the cerebellum of the brain. ...
No Slide Title
... atrium then pumped to ventricle, then to lungs • from lungs high O2 blood enters left atrium, then to ventricle and rest of body or back to lungs ...
... atrium then pumped to ventricle, then to lungs • from lungs high O2 blood enters left atrium, then to ventricle and rest of body or back to lungs ...
NEURO ANATOMY
... Nuclei of trigeminal nerve ( 4 nuclei ) : Motor nucleus: - gives motor fibers that join the mandibular nerve to supply the muscles of mastication, mylohyoid & ant. Belly of digastric. in addition to the nerves to the tensor palati & tensor tympani muscles Main sensory nucleus : it receive touch sens ...
... Nuclei of trigeminal nerve ( 4 nuclei ) : Motor nucleus: - gives motor fibers that join the mandibular nerve to supply the muscles of mastication, mylohyoid & ant. Belly of digastric. in addition to the nerves to the tensor palati & tensor tympani muscles Main sensory nucleus : it receive touch sens ...
Anatomy - study of the structures of the human body visible with the
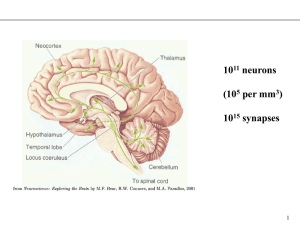
... Nervous System: *coordinates all body activities *100 billion nerve cells aka neurons *study of nerves is Neurology *3 principal components nerves spinal cord brain *3 main subdivisions Central - controls senses & voluntary muscle actions Peripheral - connects the outer parts of body to stem Au ...
... Nervous System: *coordinates all body activities *100 billion nerve cells aka neurons *study of nerves is Neurology *3 principal components nerves spinal cord brain *3 main subdivisions Central - controls senses & voluntary muscle actions Peripheral - connects the outer parts of body to stem Au ...
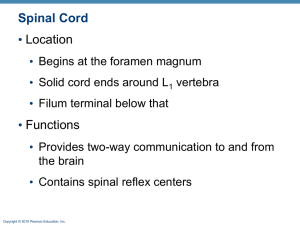
Spinal Cord
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
Investigation into the network basis of ‘signal-to-noise’ processing in hippocampus using high throughput in vivo electrophysiological recording
... The successful conclusion of the study will help establish the newer technology as a significant electrophysiological recording tool and bring out the role of the entorhinal cortex in pain. B. The proposal will test the hypothesis that a network of related structures is a basis of both acute and chr ...
... The successful conclusion of the study will help establish the newer technology as a significant electrophysiological recording tool and bring out the role of the entorhinal cortex in pain. B. The proposal will test the hypothesis that a network of related structures is a basis of both acute and chr ...
TERMINOLOGY, BODY CAVITIES, AND ORGAN SYSTEM
... 1. What are the two types of sections can be cut through the body that will reveal both the lungs and the heart in each section ? 2. What position does the tongue occupy with respect to the palate ? 3. What position do the cheeks occupy with respect to the tongue ? 4. What term would best describe t ...
... 1. What are the two types of sections can be cut through the body that will reveal both the lungs and the heart in each section ? 2. What position does the tongue occupy with respect to the palate ? 3. What position do the cheeks occupy with respect to the tongue ? 4. What term would best describe t ...
Human Body Systems
... coordinates the functions throughout the body by transmitting electrical signals or impulses via neurons • Responds to internal and external stimuli in order to maintain homeostasis ...
... coordinates the functions throughout the body by transmitting electrical signals or impulses via neurons • Responds to internal and external stimuli in order to maintain homeostasis ...
YOUR AMAZING BODY
... system is to be the boss of the rest of the body! Your brain tells each of the other systems what to do. Your thinking and emotions take place in the brain, as well. ...
... system is to be the boss of the rest of the body! Your brain tells each of the other systems what to do. Your thinking and emotions take place in the brain, as well. ...
Resp, Circ and Nerv Test review answers
... sensory neuron- Carry messages towards the central nervous system (CNS) ...
... sensory neuron- Carry messages towards the central nervous system (CNS) ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.
![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-300x300.png)