Name Human Body Study Guide Lesson 1 MC #14: 1. homeostasis
... d. The cardiovascular system moves more blood to the injured area to provide nutrients for cell growth. e. The endocrine system makes adrenaline, which increases your heart rate and alertness in dangerous situations to react faster. It also maintains homeostasis by controlling the metabolism and gro ...
... d. The cardiovascular system moves more blood to the injured area to provide nutrients for cell growth. e. The endocrine system makes adrenaline, which increases your heart rate and alertness in dangerous situations to react faster. It also maintains homeostasis by controlling the metabolism and gro ...
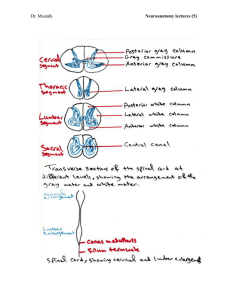
anterior spinothalamic tract.
... 3- Nucleus dorsalis of Clark: It is situated near the base of the dorsal horn and it presents only between (C8 and L3). It concerns with the posterior spinocerebellar tract. Intermediate horn: In the thoracic region, it is responsible for sympathetic output. While in the sacral region, it is respons ...
... 3- Nucleus dorsalis of Clark: It is situated near the base of the dorsal horn and it presents only between (C8 and L3). It concerns with the posterior spinocerebellar tract. Intermediate horn: In the thoracic region, it is responsible for sympathetic output. While in the sacral region, it is respons ...
best
... B. Produces and transports oxygen within the body C. Produces and excretes waste products D. Controls and coordinates body activities ...
... B. Produces and transports oxygen within the body C. Produces and excretes waste products D. Controls and coordinates body activities ...
Organ Systems and Life
... survive. The organs can be divided into reproductive and vegetative. Flower: The flower is the reproductive organ of plants. It may contain the stamen and or the carpel. The stamen contains the pollen, which is brought to the carpel by insects. The carpel contains the ovaries. The receptor of pollen ...
... survive. The organs can be divided into reproductive and vegetative. Flower: The flower is the reproductive organ of plants. It may contain the stamen and or the carpel. The stamen contains the pollen, which is brought to the carpel by insects. The carpel contains the ovaries. The receptor of pollen ...
Levels of Biological Organization
... The main role of the muscular system is to provide movement. Muscles work in pairs to move limbs and provide the organism with mobility. Muscles also control the movement of materials through some organs, such as the stomach and intestine, and the heart and circulatory system. •Major Organs: Skeleta ...
... The main role of the muscular system is to provide movement. Muscles work in pairs to move limbs and provide the organism with mobility. Muscles also control the movement of materials through some organs, such as the stomach and intestine, and the heart and circulatory system. •Major Organs: Skeleta ...
Anatomy Performance Assessment
... Urinary (be sure to include the kidneys, absorption and cleaning of blood) Brain (be sure to include all the parts of brain that are working) (unless it is directly related to your movement you can skip excretory and lymphatic) Tissue You must choose 3 of your systems to provide tissue detail in. Ac ...
... Urinary (be sure to include the kidneys, absorption and cleaning of blood) Brain (be sure to include all the parts of brain that are working) (unless it is directly related to your movement you can skip excretory and lymphatic) Tissue You must choose 3 of your systems to provide tissue detail in. Ac ...
Anatomy Physiology
... produces sex cells, fertilizes, nurtures and protects embryo and developing fetus ...
... produces sex cells, fertilizes, nurtures and protects embryo and developing fetus ...
File - Biology with Ms. Murillo
... 3 Types: Sensory neurons; motor neurons; interneurons 41. Label the parts of the brain. 42. How does the nervous system work with the other systems to maintain homeostasis? Bones of the skeletal system protect the spinal cord and brain. The brain controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing vi ...
... 3 Types: Sensory neurons; motor neurons; interneurons 41. Label the parts of the brain. 42. How does the nervous system work with the other systems to maintain homeostasis? Bones of the skeletal system protect the spinal cord and brain. The brain controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing vi ...
Human Body Systems - Warren County Schools
... 3) Respiratory System (get oxygen) – Uses the lungs – Air brought in when you breathe through the trachea ...
... 3) Respiratory System (get oxygen) – Uses the lungs – Air brought in when you breathe through the trachea ...
The Human Body - bakerbiologykingdoms
... the follicle to rupture. The corpus leteum produces progesterone and some estrogen and prevents the release of LH. If fertilization does not occur then the rising levels of progesterone and estrogen inhibit the release of FSH and LH and the uterine ...
... the follicle to rupture. The corpus leteum produces progesterone and some estrogen and prevents the release of LH. If fertilization does not occur then the rising levels of progesterone and estrogen inhibit the release of FSH and LH and the uterine ...
The Human Body - mrsblythesclass
... We will discuss/learn some of the systems of the body. 1. The skin system covers the body, and includes the skin, hair, and nails. 2. The skeletal system supports the body, and includes the bones. 3. The muscular system makes it possible for the body and its parts to move. 4. The digestive system d ...
... We will discuss/learn some of the systems of the body. 1. The skin system covers the body, and includes the skin, hair, and nails. 2. The skeletal system supports the body, and includes the bones. 3. The muscular system makes it possible for the body and its parts to move. 4. The digestive system d ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... • The cortex is much larger in mammals than in species that evolved earlier, such as fish and amphibians. • The cross section of the human brain shows how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
... • The cortex is much larger in mammals than in species that evolved earlier, such as fish and amphibians. • The cross section of the human brain shows how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
Human Body Systems Review
... 4. The nervous system controls the 5 senses which are: Sight, Touch, Taste, Smell, Hearing ...
... 4. The nervous system controls the 5 senses which are: Sight, Touch, Taste, Smell, Hearing ...
File - Fifth Grade!
... -bicep: muscle at the front of the upper arm -cardiac muscle: heart muscle -contract: to draw together -endurance: ability or strength to continue or last without becoming tired -exertion: activity of using muscles in various ways to keep fit -extend: to increase in length -flex: to bend -involuntar ...
... -bicep: muscle at the front of the upper arm -cardiac muscle: heart muscle -contract: to draw together -endurance: ability or strength to continue or last without becoming tired -exertion: activity of using muscles in various ways to keep fit -extend: to increase in length -flex: to bend -involuntar ...
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Surface Topography
... On the inferior surface of the brain, the frontal, temporal, and occipital poles should be identified, as well as the prominent medial bulge of the temporal lobe known as the uncus. Note the relationship of the medial surface of the temporal lobe to the brain stem. The inferior surface of the fronta ...
... On the inferior surface of the brain, the frontal, temporal, and occipital poles should be identified, as well as the prominent medial bulge of the temporal lobe known as the uncus. Note the relationship of the medial surface of the temporal lobe to the brain stem. The inferior surface of the fronta ...
Science Study Guide
... 1. system – a group of body parts that work together to perform a job 2. organ – a body part that does a special job within a body system 3. tissue – a group of cells that look alike and work together to do a certain job 4. cell – the basic unit of all living things, including the human body 5. cart ...
... 1. system – a group of body parts that work together to perform a job 2. organ – a body part that does a special job within a body system 3. tissue – a group of cells that look alike and work together to do a certain job 4. cell – the basic unit of all living things, including the human body 5. cart ...
Reflex Arcs
... (optional step) Interneurons in the CNS (a reflex center) to Motor neurons to Effector ...
... (optional step) Interneurons in the CNS (a reflex center) to Motor neurons to Effector ...
The Human Body
... – The wave of blood through the arteries formed when the left ventricle contracts – Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a bone • Blood pressure – Amount of force exerted against walls of arteries – Systole: Left ventricle contracts – Diastole: Left ventricle relaxes • P ...
... – The wave of blood through the arteries formed when the left ventricle contracts – Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a bone • Blood pressure – Amount of force exerted against walls of arteries – Systole: Left ventricle contracts – Diastole: Left ventricle relaxes • P ...
doc - Virtual Homeschool Group
... The lobes that coordinate vital functions, such as those of the circulatory and respiratory systems, and transport signals from the brain to the spinal cord ...
... The lobes that coordinate vital functions, such as those of the circulatory and respiratory systems, and transport signals from the brain to the spinal cord ...
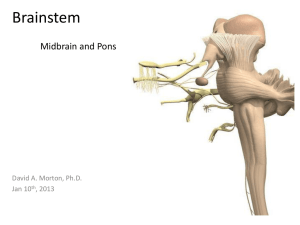
Brainstem (Midbrain/Pons) PP
... Name all the cranial nerves and know their components and functions Identify and locate the CN’s associated with the medulla, pons and midbrain Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a gross or stained cro ...
... Name all the cranial nerves and know their components and functions Identify and locate the CN’s associated with the medulla, pons and midbrain Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a gross or stained cro ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.