* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Central nervous system wikipedia , lookup
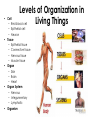
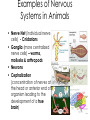
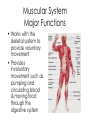
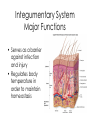
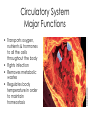
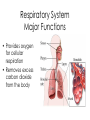
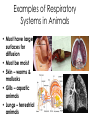
Body Systems A Brief Overview • • • • • Levels of Organization in Cell Living Things – Red blood cell – Epithelial cell – Neuron Tissue – Epithelial tissue – Connective tissue – Nervous tissue – Muscle tissue Organ – Skin – Brain – Heart Organ System – Nervous – Integumentary – Lymphatic Organism Nervous System Major Functions • Controls and coordinates the functions throughout the body by transmitting electrical signals or impulses via neurons • Responds to internal and external stimuli in order to maintain homeostasis Examples of Nervous Systems in Animals • Nerve Net (individual nerve cells) - Cnidarians • Ganglia (more centralized nerve cells) – worms, mollusks & arthropods • Neurons • Cephalization (concentration of nerves at the head or anterior end of organism leading to the development of a true brain) Skeletal System Major Functions • Supports the body • Protects the internal organs • Serves as muscle attachment for movement Examples of Skeletal Systems in Animals • Hydrostatic Skeleton: fluid filled body cavity that supports the muscles found in some worms & cnidarians • Exoskeleton: external skeleton made of chitin found in arthropods • Endoskeleton: internal skeleton made of calcium found in echinoderms & vertebrates Muscular System Major Functions • Works with the skeletal system to provide voluntary movement • Provides involuntary movement such as pumping and circulating blood & moving food through the digestive system Integumentary System Major Functions • Serves as a barrier against infection and injury • Regulates body temperature in order to maintain homeostasis Examples of Integumentary Systems in Animals • Skin • Hair & Fur • Nails • sweat & oil glands • Feathers • Scales Circulatory System Major Functions • Transports oxygen, nutrients & hormones to all the cells throughout the body • Fights infection • Removes metabolic wastes • Regulates body temperature in order to maintain homeostasis Examples of Circulatory Systems in Animals • Open Circulatory System: Blood is not completely contained in vessels (blood found in sinuses or open cavities) –Most Mollusks & Arthropods • Closed Circulatory System: Blood is contained in vessels some worms & mollusks and vertebrates • More complex systems & hearts develop as organisms move up the evolutionary ladder Respiratory System Major Functions • Provides oxygen for cellular respiration • Removes excess carbon dioxide from the body Examples of Respiratory Systems in Animals • Must have large surfaces for diffusion • Must be moist • Skin – worms & mollusks • Gills – aquatic animals • Lungs – terrestrial animals Digestive System Major Functions • Breaks down large molecules of food into simpler, smaller molecules to be used by the cells of the body – glucose for cellular respiration • Absorbs nutrients • Eliminates wastes • Food moves through the digestive system thru a muscle action called peristalsis Examples of Digestive Systems in Animals Intracellular vs. Extracellular Digestion: Food digested within cells as opposed to food digested outside of the cells in a digestive cavity or a digestive tract (more complex animals) Excretory System Major Functions • Eliminates metabolic wastes from the body in order to maintain homeostasis • Regulates water also to maintain homeostasis Examples of Excretory Systems in Animals • Flame cells (eliminates excess water from flatworms) • Skin & Gills (aquatic organisms) • Nephridia (annelids & mollusks • Malpighian Tubules (arthropods such as insects & arachnids) • Kidneys (vertebrates) Reproductive System: General • Most invertebrates reproduce SEXUALLY during at least part of their life cycle. • Depending on environmental conditions, many invertebrates may also reproduce ASEXUALLY REMEMBER… THERE ARE ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES TO BOTH External vs. Internal Fertilization Eggs are fertilized OUTSIDE of the FEMALE’S BODY as opposed to INSIDE the FEMALE’S BODY Reproductive System Major Functions - Female • Produces reproductive cells called eggs or ova in the ovaries • Nurtures and protects developing embryo Reproductive System Major Functions - Male • Produces reproductive cells called sperm in the testes