Animals: - This is just a sample and may not include all topics or may
... demyelination affect the nervous system? a. slower transmission of nerve signals, causing problems with sensory perception and motor coordination b. faster transmission of nerve signals, causing increased alertness and physical activity c. reversed direction of nerve signals conduction, causing sign ...
... demyelination affect the nervous system? a. slower transmission of nerve signals, causing problems with sensory perception and motor coordination b. faster transmission of nerve signals, causing increased alertness and physical activity c. reversed direction of nerve signals conduction, causing sign ...
Teacher Guide - Cleveland Museum of Natural History
... Comparative anatomy – have students choose another non-mammal animal and look up some images of its internal anatomy. Ask them to prepare a report on what organs are similar or different in location or function compared to mammals. Check out images of bird air sacs (we have attached one image t ...
... Comparative anatomy – have students choose another non-mammal animal and look up some images of its internal anatomy. Ask them to prepare a report on what organs are similar or different in location or function compared to mammals. Check out images of bird air sacs (we have attached one image t ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... A nutrient is a substance that you get from food and that your body needs to carry out processes, such as contracting muscles. To bend a joint, one muscle contracts while another muscle returns to its original length. Tissues perform less complex jobs than organs. The skeletal system consis ...
... A nutrient is a substance that you get from food and that your body needs to carry out processes, such as contracting muscles. To bend a joint, one muscle contracts while another muscle returns to its original length. Tissues perform less complex jobs than organs. The skeletal system consis ...
Notes on Levels of Organization
... A cell, tissue, organ, system, or organism? • Found: in our brain, our nervous tissue is made up of millions of these • Function: neurons transmit signals to body parts to tell them what to do ...
... A cell, tissue, organ, system, or organism? • Found: in our brain, our nervous tissue is made up of millions of these • Function: neurons transmit signals to body parts to tell them what to do ...
Phylum : Aschelminthes - GCG-42
... nematodes). A pseudocoelom is a persistent blastocoel and is in reality a haemocoel without heart. Some smaller aschelminthes have no body cavity and are Acoelomate protostomes. (8) Digestive Tract: The digestive tract is complete, have nonmuscular wall with anterior and posterior parts are lined by ...
... nematodes). A pseudocoelom is a persistent blastocoel and is in reality a haemocoel without heart. Some smaller aschelminthes have no body cavity and are Acoelomate protostomes. (8) Digestive Tract: The digestive tract is complete, have nonmuscular wall with anterior and posterior parts are lined by ...
InvertebratesOutline..
... food. Only Deutertomes Invertebrates (Mouth develops from cells not found in the opening of the gastrula) Closest relative to chordates ...
... food. Only Deutertomes Invertebrates (Mouth develops from cells not found in the opening of the gastrula) Closest relative to chordates ...
Nerves, Hormones, and Homeostasis
... • 6.5.5-Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a nonmyelinated neuron • 6.5.6-Explain the principles of synaptic transmission. ...
... • 6.5.5-Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a nonmyelinated neuron • 6.5.6-Explain the principles of synaptic transmission. ...
Anatomy Systems summary
... • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are suited to perform a particular function. • Groups of similar cells work together to form tissues. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organs form organ sy ...
... • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Specialized cells are suited to perform a particular function. • Groups of similar cells work together to form tissues. • Groups of tissues that work together to perform complex functions are called organs. • Organs form organ sy ...
Intro to animal structure and function powerpoint
... make up organ systems Most animals are composed of specialized cells organized into tissues that have different functions ...
... make up organ systems Most animals are composed of specialized cells organized into tissues that have different functions ...
7th Grade 2nd Semester Test Chapters 14-17, 19
... b. Cerebellum c. Cerebrum d. Spinal cord 62. The brain stem a. Is associated with artistic ability and mathematical skill b. Regulates breathing c. Lies between the cerebrum and the cerebellum d. Is the second largest part of the brain 63. A concussion is a type of injury to the a. Spinal cord b. Sy ...
... b. Cerebellum c. Cerebrum d. Spinal cord 62. The brain stem a. Is associated with artistic ability and mathematical skill b. Regulates breathing c. Lies between the cerebrum and the cerebellum d. Is the second largest part of the brain 63. A concussion is a type of injury to the a. Spinal cord b. Sy ...
File - Gander biology
... Lungs: main organ of the RS : A tiny air sac where air exchange takes place Diaphragm: strong muscle below the ______ that helps in breathing ...
... Lungs: main organ of the RS : A tiny air sac where air exchange takes place Diaphragm: strong muscle below the ______ that helps in breathing ...
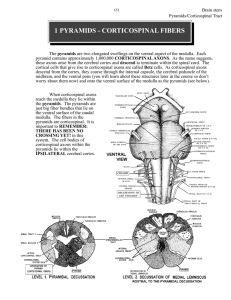
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
... At the most caudal pole of the pyramids the corticospinal axons cross over the midline and now continue their descent on the contralateral (to the cell of origin) side. This crossover point is called the PYRAMIDAL DECUSSATION. The crossing fibers enter the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord where ...
... At the most caudal pole of the pyramids the corticospinal axons cross over the midline and now continue their descent on the contralateral (to the cell of origin) side. This crossover point is called the PYRAMIDAL DECUSSATION. The crossing fibers enter the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord where ...
Simple Invertebrates – Chapter 15 – Section 1 (pages 380 – 387) I
... B. Three basic body plans 1. bilateral symmetry (insects) 2. radial symmetry (starfish) 3. asymmetrical (sponges) C. Neurons and Ganglia (the nervous system) 1. allow animals to sense their environment 2. carry messages around the body to control animal’s actions 3. nerve cords are packages of neuro ...
... B. Three basic body plans 1. bilateral symmetry (insects) 2. radial symmetry (starfish) 3. asymmetrical (sponges) C. Neurons and Ganglia (the nervous system) 1. allow animals to sense their environment 2. carry messages around the body to control animal’s actions 3. nerve cords are packages of neuro ...
Ch 29 Echinoderms and Invertebrate Chordates
... 3. Class ______________________________________________ – Sand dollars do not have rays but have a five-petal flower pattern. Sea urchins have long spines used for protection and to aid locomotion. 4. Class ______________________________________ – use tentacles to feed on the sea floor 5. Class ____ ...
... 3. Class ______________________________________________ – Sand dollars do not have rays but have a five-petal flower pattern. Sea urchins have long spines used for protection and to aid locomotion. 4. Class ______________________________________ – use tentacles to feed on the sea floor 5. Class ____ ...
file - Athens Academy
... What is olfactory neurons can only send one message at a time to the brain and/or there are feedback loops from the brain that decrease sensation after the same message is received a given number of times? ...
... What is olfactory neurons can only send one message at a time to the brain and/or there are feedback loops from the brain that decrease sensation after the same message is received a given number of times? ...
Body Systems
... Foresman, Scott. You and Your Health. Illinois: Scott Foresman and company, 1977. ...
... Foresman, Scott. You and Your Health. Illinois: Scott Foresman and company, 1977. ...
To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document.
... System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic Nervous system – Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
... System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System – Somatic Nervous system – Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
PowerPoint with notes - IRSC
... • Spinal cord: from brain downward, enclosed by bones of vertebral column, passes messages to and from the brain and acts as the center for reflex actions. • Openings between vertebrae allow nerves to join with the spinal cord. ...
... • Spinal cord: from brain downward, enclosed by bones of vertebral column, passes messages to and from the brain and acts as the center for reflex actions. • Openings between vertebrae allow nerves to join with the spinal cord. ...
Slide ()
... Diagram illustrating the relationships between the olfactory receptors in the nasal mucosa and neurons in the olfactory bulb and tract. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus are found in scattered groups caudal to the olfactory bulb. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus make immediate connectio ...
... Diagram illustrating the relationships between the olfactory receptors in the nasal mucosa and neurons in the olfactory bulb and tract. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus are found in scattered groups caudal to the olfactory bulb. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus make immediate connectio ...
Slide ()
... Diagram illustrating the relationships between the olfactory receptors in the nasal mucosa and neurons in the olfactory bulb and tract. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus are found in scattered groups caudal to the olfactory bulb. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus make immediate connectio ...
... Diagram illustrating the relationships between the olfactory receptors in the nasal mucosa and neurons in the olfactory bulb and tract. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus are found in scattered groups caudal to the olfactory bulb. Cells of the anterior olfactory nucleus make immediate connectio ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.