Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... acetyl-CoA is formed as an intermediate in this process, first entering the citric acid cycle followed by complete conversion of its chemical energy to ATP in oxidative phosporylation. When the body has excess carbohydrates available, some glucose is fully metabolized, and some of it is stored by us ...
... acetyl-CoA is formed as an intermediate in this process, first entering the citric acid cycle followed by complete conversion of its chemical energy to ATP in oxidative phosporylation. When the body has excess carbohydrates available, some glucose is fully metabolized, and some of it is stored by us ...
Document
... 10. Know the sources of carbon and nitrogen for amino acid biosynthesis. How are amino groups transferred to acids to make amino acids? 11. Understand the role of folic acid in nucleotide biosynthesis. 12. How does sulfanilamide inhibit the growth of microorganisms? 13. Humans do not make their own ...
... 10. Know the sources of carbon and nitrogen for amino acid biosynthesis. How are amino groups transferred to acids to make amino acids? 11. Understand the role of folic acid in nucleotide biosynthesis. 12. How does sulfanilamide inhibit the growth of microorganisms? 13. Humans do not make their own ...
Ch. 3 Vocabs
... hundreds or thousands of atoms condensation reaction: a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule hydrolysis: a chemical reaction between water and another substance to form two or more new substances; a reaction between water and a salt ...
... hundreds or thousands of atoms condensation reaction: a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule hydrolysis: a chemical reaction between water and another substance to form two or more new substances; a reaction between water and a salt ...
answers to study guide
... poly – many, cellulose, starch, chitin starch vs. cellulose why can’t humans digest cellulose polymers of glucose starch stores energy, alpha glycosidic linkages cellulose used for structural purposes, beta glycosidic linkages can’t digest b/can’t break down beta glycosidic linkages facts about lipi ...
... poly – many, cellulose, starch, chitin starch vs. cellulose why can’t humans digest cellulose polymers of glucose starch stores energy, alpha glycosidic linkages cellulose used for structural purposes, beta glycosidic linkages can’t digest b/can’t break down beta glycosidic linkages facts about lipi ...
SLIB biochemistry homework
... 23) Describe two dietary factors that are thought to increase levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood and explain why this might be dangerous to the individual. 24) Describe the difference in structure between linoleic and linolenic acid and explain why it is important in include these two acids in ...
... 23) Describe two dietary factors that are thought to increase levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood and explain why this might be dangerous to the individual. 24) Describe the difference in structure between linoleic and linolenic acid and explain why it is important in include these two acids in ...
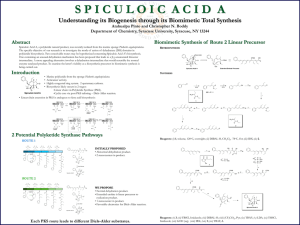
Total Synthesis of Spiculoic Acid A
... Spiculoic Acid A, a polyketide natural product, was recently isolated from the marine sponge Plakortis angulospiculatus. The specific objective of our research is to investigate the mode of action of dehydratase (DH) domains in polyketide biosynthesis. Two conceivable routes may be hypothesized conc ...
... Spiculoic Acid A, a polyketide natural product, was recently isolated from the marine sponge Plakortis angulospiculatus. The specific objective of our research is to investigate the mode of action of dehydratase (DH) domains in polyketide biosynthesis. Two conceivable routes may be hypothesized conc ...
Acids and Bases
... Most solutions of both acids and bases are clear and colourless. We need an indicator to tell them apart. An indicator is a chemical which changes colour as the concentration of H+ (aq) and OH- (aq) changes. Two common indicators are litmus and phenolpthalein ...
... Most solutions of both acids and bases are clear and colourless. We need an indicator to tell them apart. An indicator is a chemical which changes colour as the concentration of H+ (aq) and OH- (aq) changes. Two common indicators are litmus and phenolpthalein ...
Sample Exam 1
... a. They act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions. b. They are the molecules of instruction and inheritance. c. They provide structure to the body by holding it together. d. They provide the primary source of fuel for a cell to make energy. e. They allow polar molecules to move through a cell me ...
... a. They act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions. b. They are the molecules of instruction and inheritance. c. They provide structure to the body by holding it together. d. They provide the primary source of fuel for a cell to make energy. e. They allow polar molecules to move through a cell me ...
投影片 1
... Alcohols, carbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids: REDUCTION Reduction: Addition of H2 (or H-), loss of O or O2; loss of X2 ...
... Alcohols, carbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids: REDUCTION Reduction: Addition of H2 (or H-), loss of O or O2; loss of X2 ...
Review over Glucose Metabolism
... glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _____1. Most of the ATP is made _____2. Occurs only under anaerobic conditions _____3. Occurs onl ...
... glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _____1. Most of the ATP is made _____2. Occurs only under anaerobic conditions _____3. Occurs onl ...
Review of Glucose Metabolism File
... glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _____1. Most of the ATP is made _____2. Occurs only under anaerobic conditions _____3. Occurs onl ...
... glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _____1. Most of the ATP is made _____2. Occurs only under anaerobic conditions _____3. Occurs onl ...
Name
... 1) Give the following formula for: a) chlorite ion d) perchlorate ion b) chloride ion e) hypochlorite ion c) chlorate ion 2) Name the following ionic compounds. Where applicable, name the compound two ways: a) AlF3 ...
... 1) Give the following formula for: a) chlorite ion d) perchlorate ion b) chloride ion e) hypochlorite ion c) chlorate ion 2) Name the following ionic compounds. Where applicable, name the compound two ways: a) AlF3 ...
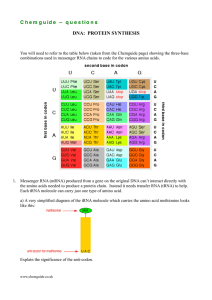
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Hydrophobic (“hydro”=water; “phobic” = fearing) Consist mostly of hydrocarbons Do NOT consist of polymers ...
... Hydrophobic (“hydro”=water; “phobic” = fearing) Consist mostly of hydrocarbons Do NOT consist of polymers ...
EPA/DHA Vegetarian - Pure Encapsulations
... product. At this time, there are no known side effects or precautions. Consult your physician for more information. ...
... product. At this time, there are no known side effects or precautions. Consult your physician for more information. ...
Lecture 9 - Fatty Acid Metabolism - chem.uwec.edu
... Even though the citric acid cycle intermediate oxaloacetate can be used to synthesize glucose, Acetyl–CoA cannot be used to synthesize oxaloacetate. The two carbons that enter the citric acid cycle as Acetyl–CoA leave as CO2. ...
... Even though the citric acid cycle intermediate oxaloacetate can be used to synthesize glucose, Acetyl–CoA cannot be used to synthesize oxaloacetate. The two carbons that enter the citric acid cycle as Acetyl–CoA leave as CO2. ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Option C
... When fat is used as a source of energy, it yields more than 1 g of water for each 1 g of fat converted, making it ideal for a camel in very dry conditions. Fat is split into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol is phosphorylated and converted to pyruvate and enters the Krebs cycle. Fatty acids are con ...
... When fat is used as a source of energy, it yields more than 1 g of water for each 1 g of fat converted, making it ideal for a camel in very dry conditions. Fat is split into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol is phosphorylated and converted to pyruvate and enters the Krebs cycle. Fatty acids are con ...
Name 1 Bio 451 17th November 2000 EXAM III KEY
... A. Noji et al (1997) performed an elegant experiment that allowed the direct observation of the rotation of the ((gamma) subunit of F1-ATPase relative to " 3$3. [A b/w figure illustrating the experimental setup was included in Handout 12 and one of the links provided in the announcement of this ques ...
... A. Noji et al (1997) performed an elegant experiment that allowed the direct observation of the rotation of the ((gamma) subunit of F1-ATPase relative to " 3$3. [A b/w figure illustrating the experimental setup was included in Handout 12 and one of the links provided in the announcement of this ques ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (aka Hexose monophosphate shunt)
... A second transketolase catalyzes the transfer of C2 from Xu-5-P to E-4-P forming a second F-6-P and GAP. Requires TPP as cofactor Goes through a TPP-Xu5-P adduct as intermediate ...
... A second transketolase catalyzes the transfer of C2 from Xu-5-P to E-4-P forming a second F-6-P and GAP. Requires TPP as cofactor Goes through a TPP-Xu5-P adduct as intermediate ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.