Fatty acid synthesis
... Production of cytoplasmic Acetyl CoA Mitochondrial acetyl CoA is produced from • Oxidation of pyruvate •Degradation of fatty acids •Degradation of ketones bodies •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot cross mitochondrial membrane Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate to ...
... Production of cytoplasmic Acetyl CoA Mitochondrial acetyl CoA is produced from • Oxidation of pyruvate •Degradation of fatty acids •Degradation of ketones bodies •Degradation of amino acids Coenzyme A portion of acetyl Co A cannot cross mitochondrial membrane Acetyl CoA combines with Oxaloacetate to ...
(PDF format, 1.73MB)
... (saliva, small intestine) Monosacharides: transported across intestinal wall: glycogen or metabolism Glycolysis 1 glucose molecule - 2 ATP (~30 from OXPHOS) ...
... (saliva, small intestine) Monosacharides: transported across intestinal wall: glycogen or metabolism Glycolysis 1 glucose molecule - 2 ATP (~30 from OXPHOS) ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... Although palmitate, a 16-carbon, fully saturated long-chain length fatty acid (16:0), is the primary end product of fatty acid synthase activity, it can be further elongated by the addition of two-carbon units in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the mitochondria. ...
... Although palmitate, a 16-carbon, fully saturated long-chain length fatty acid (16:0), is the primary end product of fatty acid synthase activity, it can be further elongated by the addition of two-carbon units in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the mitochondria. ...
Thursday, September 4 Bell Work: Predict the outcome of slight
... at all, with water Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids ...
... at all, with water Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids ...
Chapter 5 - Missouri State University
... Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis (continued) _______________________________ cannot leak out of the cell. ___________________________ generate glucose-6-phosphate for ...
... Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis (continued) _______________________________ cannot leak out of the cell. ___________________________ generate glucose-6-phosphate for ...
Stable Isotope and Metabolomics Core Facility
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
BIOCHEMISTRY WEBQUEST
... 1) Based on what you can see in their structure, why do you suppose these molecules are known as “triglycerides”? (hint: what does “tri-“ mean? What do they have three of?) 1 pt ...
... 1) Based on what you can see in their structure, why do you suppose these molecules are known as “triglycerides”? (hint: what does “tri-“ mean? What do they have three of?) 1 pt ...
Biochemistry Chp 3
... When H2O is created because two monomers are united, this is called a condensation reaction. The opposite, when water is added to break a polymer apart, it is called hydrolysis. ...
... When H2O is created because two monomers are united, this is called a condensation reaction. The opposite, when water is added to break a polymer apart, it is called hydrolysis. ...
Protein Nomenclature
... • Peptides 2 – 50 amino acids • Proteins >50 amino acids • Amino acid with free α-amino group is the amino-terminal or N-terminal residue • Amino acid with free α-carboxyl group is the carboxyl-terminal or C-terminal residue ...
... • Peptides 2 – 50 amino acids • Proteins >50 amino acids • Amino acid with free α-amino group is the amino-terminal or N-terminal residue • Amino acid with free α-carboxyl group is the carboxyl-terminal or C-terminal residue ...
Metabolism of lipids
... • The FAs are built by sequential addition of two-carbon units derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of the two-carbon units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elonga ...
... • The FAs are built by sequential addition of two-carbon units derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of the two-carbon units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elonga ...
Chapter 3 Biological Molecules
... Most lipids are therefore hydrophobic and water insoluble Lipids are diverse in structure and serve in a variety of functions ...
... Most lipids are therefore hydrophobic and water insoluble Lipids are diverse in structure and serve in a variety of functions ...
CH03_Lecture
... All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
... All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
CHEM 214 Elementary Biochemistry
... There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of ...
... There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of ...
3. Related Pathways
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
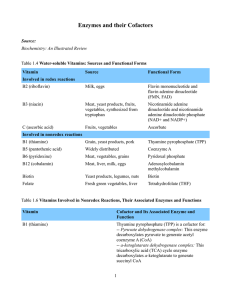
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... -- a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: This tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzyme decarboxylates a-ketoglutarate to generate succinyl CoA ...
... -- a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: This tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzyme decarboxylates a-ketoglutarate to generate succinyl CoA ...
Chapter 8 Summary
... (NAD+, FAD, and NADP+) and reduced (NADH + H+, FADH2, and NADPH + H+) forms. Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways are regulated primarily by hormones. The hormone insulin promotes energy storage, whereas the hormone glucagon promotes energy mobilization. The hormones cortisol and epinephrine also ...
... (NAD+, FAD, and NADP+) and reduced (NADH + H+, FADH2, and NADPH + H+) forms. Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways are regulated primarily by hormones. The hormone insulin promotes energy storage, whereas the hormone glucagon promotes energy mobilization. The hormones cortisol and epinephrine also ...
Mouse anti- Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 1
... for long-chain fatty acetyl-CoA, LCFA-CoA) from acetyl-CoA by a 256 kDa protein called Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC-1).1 The translocation of LCFA-CoA from cytosol to mitochondria is catalyzed by two carnitine palmitoyl transferases (CPT-1 & CPT-2) and regulated by ACC-2, the rate limiting step of ...
... for long-chain fatty acetyl-CoA, LCFA-CoA) from acetyl-CoA by a 256 kDa protein called Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC-1).1 The translocation of LCFA-CoA from cytosol to mitochondria is catalyzed by two carnitine palmitoyl transferases (CPT-1 & CPT-2) and regulated by ACC-2, the rate limiting step of ...
ch_9 - WordPress.com
... (c) Phosphoric Acids : It contains a phosphate group. It combines two nucleotides together by formation of phosphodiester bond. ...
... (c) Phosphoric Acids : It contains a phosphate group. It combines two nucleotides together by formation of phosphodiester bond. ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... and fruits of plants. Animals (and humans) store excess glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles. ...
... and fruits of plants. Animals (and humans) store excess glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles. ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis: Source of Acetyl-CoA and
... acetyl-CoA-generating genes (acetyl-CoA synthetase, pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, plastidic pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and ATP-citrate lyase), and compared these with the expression of acetyl-CoA-metabolizing genes (heteromeric and homomeric acetylCoA carboxylase). These co ...
... acetyl-CoA-generating genes (acetyl-CoA synthetase, pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, plastidic pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and ATP-citrate lyase), and compared these with the expression of acetyl-CoA-metabolizing genes (heteromeric and homomeric acetylCoA carboxylase). These co ...
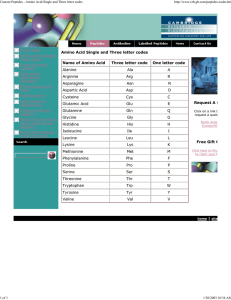
Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.