Fungal Lipids: The Biochemistry of Lipid Accumulation
... describe lipids as a group of naturally occurring compounds, which have in common a ready solubility in such organic solvents as hydrocarbons, chloroform, benzene, ethers and alcohols [2]–[4]. A more specific definition of lipids than one based simply on solubility is necessary, and most scientists ...
... describe lipids as a group of naturally occurring compounds, which have in common a ready solubility in such organic solvents as hydrocarbons, chloroform, benzene, ethers and alcohols [2]–[4]. A more specific definition of lipids than one based simply on solubility is necessary, and most scientists ...
PK-Focused Changes
... Classical isosteres emphasize the preservation of steric effects within a molecule. Classical isosteres, therefore, are groups that tend to have approximately the same size. A methyl group and a chlorine atom are similarly sized and are isosteres of one another. A number of classical isosteres are i ...
... Classical isosteres emphasize the preservation of steric effects within a molecule. Classical isosteres, therefore, are groups that tend to have approximately the same size. A methyl group and a chlorine atom are similarly sized and are isosteres of one another. A number of classical isosteres are i ...
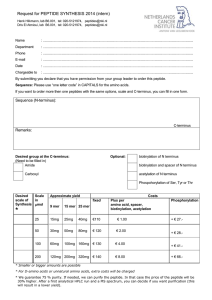
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... Request for PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS 2014 (intern) Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
... Request for PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS 2014 (intern) Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
1_Notes_Biochemistry
... The name monomer means giant molecules small units There are ____ types of macromolecules: carbs., lipids, and proteins three four ...
... The name monomer means giant molecules small units There are ____ types of macromolecules: carbs., lipids, and proteins three four ...
Option C - Human biochemistry C.1 Diet-
... • -ADRENALIN synthesized from amino acid Tyrosine:when exercise is done, impulses are sent for adrenaline to be released into the blood stream. It causes blood to be sent into areas of more active circulation. Increase in volume of blood available. Increase in rate of heart beat, stimulated respirat ...
... • -ADRENALIN synthesized from amino acid Tyrosine:when exercise is done, impulses are sent for adrenaline to be released into the blood stream. It causes blood to be sent into areas of more active circulation. Increase in volume of blood available. Increase in rate of heart beat, stimulated respirat ...
Reading Guide
... 15. Enzymes called ______________________ oppose the action of kinases, turning off glycogen degradation and turning on glycogen synthesis. 16. Liver cells respond to glucagon by _________________________. 17. Muscle does not respond to glucagon, but does respond to ______________________ by releasi ...
... 15. Enzymes called ______________________ oppose the action of kinases, turning off glycogen degradation and turning on glycogen synthesis. 16. Liver cells respond to glucagon by _________________________. 17. Muscle does not respond to glucagon, but does respond to ______________________ by releasi ...
C. Protein
... cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable complexes. Protein Structure Most proteins fold into unique 3-dimensional structures. The shape into which a protein naturally folds is known as its native conformation. Although many ...
... cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable complexes. Protein Structure Most proteins fold into unique 3-dimensional structures. The shape into which a protein naturally folds is known as its native conformation. Although many ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that is involved in energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, has physiological functions in blood glucose disposal, and is able to scavenge a number of free radicals. Alpha-lipoic acid is a fat- and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme. ...
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that is involved in energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, has physiological functions in blood glucose disposal, and is able to scavenge a number of free radicals. Alpha-lipoic acid is a fat- and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme. ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Glutathione serves as a reductant; is conjugated to drugs to make them more water soluble (detoxification). Reduces peroxides formed during oxygen transport. The resulting oxidized form of GSH consists of two molecules disulfide bonded together (abbreviated GSSG). Is involved in amino acid transport ...
... Glutathione serves as a reductant; is conjugated to drugs to make them more water soluble (detoxification). Reduces peroxides formed during oxygen transport. The resulting oxidized form of GSH consists of two molecules disulfide bonded together (abbreviated GSSG). Is involved in amino acid transport ...
Macromolecules 2015 16
... • Lipids include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. • Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms. This structure makes lipids repel water. ...
... • Lipids include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. • Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms. This structure makes lipids repel water. ...
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
... • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
Lecture 5
... residue pKi = pK1 and pKj = pK2 ; for D and E, pKi = pK1 and pKj - pKR ; For R, H and K, pKi = KR and pKj = pK2 ...
... residue pKi = pK1 and pKj = pK2 ; for D and E, pKi = pK1 and pKj - pKR ; For R, H and K, pKi = KR and pKj = pK2 ...
25-1
... • Triglycerides are split into fatty acids & glycerol by lipase – glycerol • if cell ATP levels are high, converted into glucose • if cell ATP levels are low, converted into pyruvic acid which enters aerobic pathway to ATP production ...
... • Triglycerides are split into fatty acids & glycerol by lipase – glycerol • if cell ATP levels are high, converted into glucose • if cell ATP levels are low, converted into pyruvic acid which enters aerobic pathway to ATP production ...
No Slide Title
... • Triglycerides are split into fatty acids & glycerol by lipase – glycerol • if cell ATP levels are high, converted into glucose • if cell ATP levels are low, converted into pyruvic acid which enters aerobic pathway to ATP production ...
... • Triglycerides are split into fatty acids & glycerol by lipase – glycerol • if cell ATP levels are high, converted into glucose • if cell ATP levels are low, converted into pyruvic acid which enters aerobic pathway to ATP production ...
8.1 Glycolysis Know the overall reaction: the materials that go in
... Understand how fructose is funneled into glycolysis. Reactions convert the sugars into glycolytic intermediates. 9.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Be able to recognize red-ox reactions Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Co ...
... Understand how fructose is funneled into glycolysis. Reactions convert the sugars into glycolytic intermediates. 9.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Be able to recognize red-ox reactions Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Co ...
introduction - WordPress.com
... glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by way of gluconeogenesis. In many tissues, especially heart tissue, fatty acids are broken down through a process known as beta oxidation, which results in acetylCoA, which can be used in the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of methylene ...
... glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by way of gluconeogenesis. In many tissues, especially heart tissue, fatty acids are broken down through a process known as beta oxidation, which results in acetylCoA, which can be used in the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of methylene ...
Free Form Amino Acids
... natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body must first break these molecular (pepetide) bonds for amino acid absorption to take place. Solgar's free form amino acids are already in their simplest form (no peptide bonds) and can be r ...
... natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body must first break these molecular (pepetide) bonds for amino acid absorption to take place. Solgar's free form amino acids are already in their simplest form (no peptide bonds) and can be r ...
Biochemistry 3300 More Quizzes Page:1/4 1) How many electrons
... 7) Germinating plant seeds can convert acetyl-CoA (from fatty acids stored as oils) into carbohydrates, whereas animals cannot convert fatty acids into glucose. This difference is due to the fact that: A) animals have glycogen and don’t need to make glucose from fatty acids. B) plants use the glyoxy ...
... 7) Germinating plant seeds can convert acetyl-CoA (from fatty acids stored as oils) into carbohydrates, whereas animals cannot convert fatty acids into glucose. This difference is due to the fact that: A) animals have glycogen and don’t need to make glucose from fatty acids. B) plants use the glyoxy ...
Chapter 2 Macromocules
... • Remember: “stores the most energy” • Examples: 1. Fats 2. Phospholipids 3. Oils 4. Waxes 5. Steroid hormones 6. Triglycerides ...
... • Remember: “stores the most energy” • Examples: 1. Fats 2. Phospholipids 3. Oils 4. Waxes 5. Steroid hormones 6. Triglycerides ...
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 118, pp. 7646.
... structure and dynamics. The first chapter, by Goh, gives a useful review of experimental aspects of imaging processes and applications of force microscopy to polymers, and it deals with atomic force spectroscopy of mesoscopic scales. It emphasizes instrumental details and the interpretation of patte ...
... structure and dynamics. The first chapter, by Goh, gives a useful review of experimental aspects of imaging processes and applications of force microscopy to polymers, and it deals with atomic force spectroscopy of mesoscopic scales. It emphasizes instrumental details and the interpretation of patte ...
CH 3: The Molecules of Life
... Partially denatured proteins Minor changes to active site(s) Can still function but very reduced rate ...
... Partially denatured proteins Minor changes to active site(s) Can still function but very reduced rate ...
File
... In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. Glucose from the blood is the sole or major fuel source for: • Human brain and nervous system - Brain requires 120 g/day, more than half that is stored as glycogen in muscles and liver. ...
... In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. Glucose from the blood is the sole or major fuel source for: • Human brain and nervous system - Brain requires 120 g/day, more than half that is stored as glycogen in muscles and liver. ...
Ass3_ans - The University of Sydney
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
Ass3 - The University of Sydney
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
Secondary Products
... Certain phenolics (furanocoumarins) are phototoxic - not toxic till activated by sunlight (near UV-A) Activated furanocoumarins can insert into DNA and bind to pyrimidine bases - blocks transcription and leads to cell ...
... Certain phenolics (furanocoumarins) are phototoxic - not toxic till activated by sunlight (near UV-A) Activated furanocoumarins can insert into DNA and bind to pyrimidine bases - blocks transcription and leads to cell ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.