Ch21 Conversion of Amino Acids to Specialized Products
... 1. Formation of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA): All the carbon and nitrogen atoms of the porphyrin molecule are provided by two simple building blocks: ...
... 1. Formation of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA): All the carbon and nitrogen atoms of the porphyrin molecule are provided by two simple building blocks: ...
Muscle alanine synthesis and hepatic gluconeogenesis
... Hanson & Parsons, 1977). Of these sources, skeletal muscle is undoubtedly the most significant contributor to circulating alanine, because it represents such a large fraction of the total body mass compared with other tissues and, moreover, contains almost 60% of the total body protein. Muscle prote ...
... Hanson & Parsons, 1977). Of these sources, skeletal muscle is undoubtedly the most significant contributor to circulating alanine, because it represents such a large fraction of the total body mass compared with other tissues and, moreover, contains almost 60% of the total body protein. Muscle prote ...
Amino acid utilisation and deamination of glutamine and asparagine
... Several potential virulence factors have been identified, including a vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) [5], a cytotoxin-associated gene product (CagA) [6], acid and alkaline phosphatases and urease [7]. The urease enzyme of H. pylori is constitutively produced at high levels accounting for up to 6% of t ...
... Several potential virulence factors have been identified, including a vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) [5], a cytotoxin-associated gene product (CagA) [6], acid and alkaline phosphatases and urease [7]. The urease enzyme of H. pylori is constitutively produced at high levels accounting for up to 6% of t ...
Translocation of Photosynthate - Academic Resources at Missouri
... 4 ATPs Gained + 2 NADH2s Pyruvic Acid (C3) intermediates ...
... 4 ATPs Gained + 2 NADH2s Pyruvic Acid (C3) intermediates ...
Propionate stimulates pyruvate oxidation in the - AJP
... myocardial ischemia inhibits production of hyperpolarized (HP) [13C]bicarbonate derived from HP [1-13C]pyruvate (8, 9, 36). Because the appearance of HP [13C]bicarbonate is due to metabolism in functioning mitochondria, the appearance of HP [1-13C]bicarbonate may provide evidence of viable myocardiu ...
... myocardial ischemia inhibits production of hyperpolarized (HP) [13C]bicarbonate derived from HP [1-13C]pyruvate (8, 9, 36). Because the appearance of HP [13C]bicarbonate is due to metabolism in functioning mitochondria, the appearance of HP [1-13C]bicarbonate may provide evidence of viable myocardiu ...
Carnitine: A Review - Society of Education~Agra
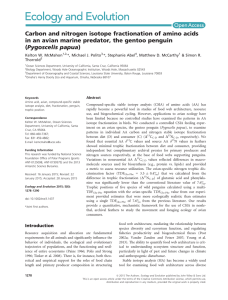
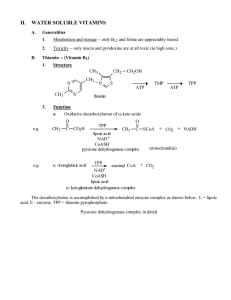
... Vitamins are defined as a group of complex organic compounds present in minute amounts in natural foodstuffs that are essential to normal mal metabolism and lack of which in the diet causes deficiency diseases. Vitamins consist of a mixed group of chemical compounds a n d are not related to each oth ...
... Vitamins are defined as a group of complex organic compounds present in minute amounts in natural foodstuffs that are essential to normal mal metabolism and lack of which in the diet causes deficiency diseases. Vitamins consist of a mixed group of chemical compounds a n d are not related to each oth ...
Student notes in ppt
... from six C5 isoprenoids Prenyl transferase catalyzes a condensation reaction in which isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate condense in a head to tail fashion to form the C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate. The same enzyme adds a second isopentenyl pyrophosphate to generate farne ...
... from six C5 isoprenoids Prenyl transferase catalyzes a condensation reaction in which isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate condense in a head to tail fashion to form the C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate. The same enzyme adds a second isopentenyl pyrophosphate to generate farne ...
Fatty acid synthase inhibitors of phenolic constituents
... compounds 7 and 9, respectively, indicating that the phenolic hydroxyl groups are required for the activity. The more phenolic hydroxyl groups in the compound, the higher activity. However, the acute function loss of compounds 4 and 7 compared to c-mangostin (3) and compound (8) suggested that the n ...
... compounds 7 and 9, respectively, indicating that the phenolic hydroxyl groups are required for the activity. The more phenolic hydroxyl groups in the compound, the higher activity. However, the acute function loss of compounds 4 and 7 compared to c-mangostin (3) and compound (8) suggested that the n ...
The Enzymes of Ammonia Assimilation and their
... Continuous cultures. The media contained (mmol 1-1 in distilled water) : for ammonia-limited conditions, D-glucose, 67; MgS04.7&0, 4.1 ; NaCI, 8.6; KH2P04,15; NH,CI, 7.2; and for ammonia-excess (glucoselimited) conditions, D-glucose, 14; MgS04.7Hz0,4.1 ; NaCI, 8.6; KH2P04,15; NH,Cl, 36. The media we ...
... Continuous cultures. The media contained (mmol 1-1 in distilled water) : for ammonia-limited conditions, D-glucose, 67; MgS04.7&0, 4.1 ; NaCI, 8.6; KH2P04,15; NH,CI, 7.2; and for ammonia-excess (glucoselimited) conditions, D-glucose, 14; MgS04.7Hz0,4.1 ; NaCI, 8.6; KH2P04,15; NH,Cl, 36. The media we ...
linolenic acid prevent insulin resistance but have divergent impacts
... (⬍8%) (44, 54). Therefore, it is conceivable that ALA and EPA/DHA have divergent effects on insulin sensitivity, although this remains to be shown. In contrast, n-6 PUFA have traditionally been viewed as detrimental to insulin sensitivity in part because they serve as precursors for the production o ...
... (⬍8%) (44, 54). Therefore, it is conceivable that ALA and EPA/DHA have divergent effects on insulin sensitivity, although this remains to be shown. In contrast, n-6 PUFA have traditionally been viewed as detrimental to insulin sensitivity in part because they serve as precursors for the production o ...
Standard PDF - Wiley Online Library
... underlying mechanisms (McMahon et al. 2010; Newsome et al. 2011). With respect to d15N, individual AAs are commonly divided into trophic and source AAs (after Popp et al. 2007), based on their relative fractionation with trophic transfer (D15NC-D). Trophic AAs, most commonly repre- ...
... underlying mechanisms (McMahon et al. 2010; Newsome et al. 2011). With respect to d15N, individual AAs are commonly divided into trophic and source AAs (after Popp et al. 2007), based on their relative fractionation with trophic transfer (D15NC-D). Trophic AAs, most commonly repre- ...
Effects of Amino Acids Replacing Nitrate on Growth - dl.edi
... (Gly), serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), cysteine (Cys), tyrosine (Tyr), asparagine (Asn), and glutamine (Gln). All treatments had the same total 12.5 mmol L−1 N concentration in nutrient solutions. During the experiment, pH in nutrient solutions was maintained at about 6.0 by addition of either 1 mmol ...
... (Gly), serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), cysteine (Cys), tyrosine (Tyr), asparagine (Asn), and glutamine (Gln). All treatments had the same total 12.5 mmol L−1 N concentration in nutrient solutions. During the experiment, pH in nutrient solutions was maintained at about 6.0 by addition of either 1 mmol ...
A Loop Unique to Ferredoxin-Dependent Glutamate Synthases is
... delete the entire 27 amino acid-long loop in the ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. The specific activity of the resulting loopless variant of this glutamate synthase, when reduced ferredoxin serves as the electron donor, is actually significa ...
... delete the entire 27 amino acid-long loop in the ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. The specific activity of the resulting loopless variant of this glutamate synthase, when reduced ferredoxin serves as the electron donor, is actually significa ...
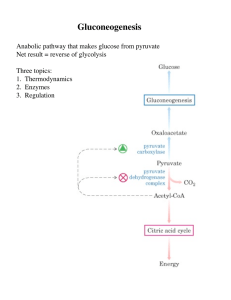
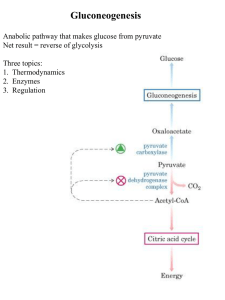
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
No Slide Title
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
Document
... substance P cholecystokinin neurotensin Antibiotics: tachikinin gramicidine S Toxins: conotoxins spider toxins snake toxins ionchanel blockers Enzymes and enzyme inhibitors: Ribonuclease A ...
... substance P cholecystokinin neurotensin Antibiotics: tachikinin gramicidine S Toxins: conotoxins spider toxins snake toxins ionchanel blockers Enzymes and enzyme inhibitors: Ribonuclease A ...
Luminaries - Oxford Academic
... Krebs observed a rapid oxidation of citrate, but interestingly, he identified that citrate was never fully consumed as a substrate, suggesting a capacity for citrate synthesis in this system (Figure 1). In addition, hypoxic conditions (low oxygen) resulted in large amounts of citrate formation in mi ...
... Krebs observed a rapid oxidation of citrate, but interestingly, he identified that citrate was never fully consumed as a substrate, suggesting a capacity for citrate synthesis in this system (Figure 1). In addition, hypoxic conditions (low oxygen) resulted in large amounts of citrate formation in mi ...
Amino Acid Sequences Containing Cysteine or Cystine Residues in
... the other close to the region of the hen ovalbumin molecule which is susceptible to limited proteolysis by subtilisin which results in plakalbumin (Thompson et al. 1971). It has been reported by Smith and Back (1970) that the S-peptide (a 33-residue C-terminal fragment), which is formed during limit ...
... the other close to the region of the hen ovalbumin molecule which is susceptible to limited proteolysis by subtilisin which results in plakalbumin (Thompson et al. 1971). It has been reported by Smith and Back (1970) that the S-peptide (a 33-residue C-terminal fragment), which is formed during limit ...
Organic Molecules chapt03
... Some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain. Each of these polypeptides has its own unique tertiary structure. ...
... Some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain. Each of these polypeptides has its own unique tertiary structure. ...
Vitamins in cosmetics
... aminomethyl group belong to the vitamin B6. The three compounds show the same vitamin activity as they can be transformed into each other. Yeast extract, milk, seeds and nuts are typical sources of this vitamin. Pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme of numerous enzymes of the amino acid metabolism. Vita ...
... aminomethyl group belong to the vitamin B6. The three compounds show the same vitamin activity as they can be transformed into each other. Yeast extract, milk, seeds and nuts are typical sources of this vitamin. Pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme of numerous enzymes of the amino acid metabolism. Vita ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.