C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... Major topics include: ammonia fixing pathway, glutamine synthetase, transamination mechanism, essential/nonessential amino acids, carbon sources of nonessential amino acids, role of THF, compare/contrast purine-pyrimidine biosynthesis, role and inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase, ketogenic/gluco ...
... Major topics include: ammonia fixing pathway, glutamine synthetase, transamination mechanism, essential/nonessential amino acids, carbon sources of nonessential amino acids, role of THF, compare/contrast purine-pyrimidine biosynthesis, role and inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase, ketogenic/gluco ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 4 cellular physiology click here
... -vesicle sacs that contain powerful enzymes to breakdown substances into their component parts e.g. nucleases = breakdown RNA & DNA into nucleotides proteases = breakdown proteins into amino acids -over 60 kinds of enzymes within the lysosome -these enzymes are collectively known as acid hydrolases ...
... -vesicle sacs that contain powerful enzymes to breakdown substances into their component parts e.g. nucleases = breakdown RNA & DNA into nucleotides proteases = breakdown proteins into amino acids -over 60 kinds of enzymes within the lysosome -these enzymes are collectively known as acid hydrolases ...
Mechanisms
... Reactions with target molecules Cellular deregulation Repair mechanisms “Essentials of Toxicology” by Klaassen Curtis D. and Watkins John B ...
... Reactions with target molecules Cellular deregulation Repair mechanisms “Essentials of Toxicology” by Klaassen Curtis D. and Watkins John B ...
3. G-protein-coupled receptors
... catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from a donor, such as ADP or ATP, to an acceptor. Phosphatase: Any of numerous enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of esters of phosphoric acid and are important in the absorption and metabolism of carbohydrates, nucleotides, and phospholipids and in the c ...
... catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from a donor, such as ADP or ATP, to an acceptor. Phosphatase: Any of numerous enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of esters of phosphoric acid and are important in the absorption and metabolism of carbohydrates, nucleotides, and phospholipids and in the c ...
Fall Semester Review - mychandlerschools.org
... (a) Cell junctions. Both animals and plants have cell junctions that allow molecules to pass readily between adjacent cells without crossing plasma membranes. ...
... (a) Cell junctions. Both animals and plants have cell junctions that allow molecules to pass readily between adjacent cells without crossing plasma membranes. ...
Chapter 11
... A signal relayed by a signal transduction pathway may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second messengers ...
... A signal relayed by a signal transduction pathway may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second messengers ...
5 - edl.io
... KEY CONCEPT #5 The endocrine system produces hormones that affect growth, development, and homeostasis. ...
... KEY CONCEPT #5 The endocrine system produces hormones that affect growth, development, and homeostasis. ...
New Product Highlights Monoclonal Anti
... Isotype: rat IgG2a Species Cross Reactivity: Human and mouse Shh Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is an important cell signaling molecule expressed during embryonic development. Shh is involved in the patterning of the developing embryonic nervous system, somite and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is releas ...
... Isotype: rat IgG2a Species Cross Reactivity: Human and mouse Shh Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is an important cell signaling molecule expressed during embryonic development. Shh is involved in the patterning of the developing embryonic nervous system, somite and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is releas ...
Slide 1
... Alternately, mutations can induce “loss of function” by mutating the hormone binding site so that the receptor does not significantly bind the hormone at normal activating concentrations. In other words, some mutations lower the activation equilibrium constant dramatically, making the receptor unres ...
... Alternately, mutations can induce “loss of function” by mutating the hormone binding site so that the receptor does not significantly bind the hormone at normal activating concentrations. In other words, some mutations lower the activation equilibrium constant dramatically, making the receptor unres ...
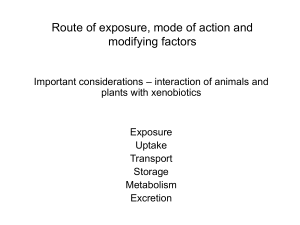
Route of exposure, mode of action and modifying factors
... histidine -> histamine (in Mast cells through decarboxylation) Released to trigger immune response Histamine is a powerful vasodialator Increases permeability of blood vessels Reduce blood pressure and lead to anaphylactic shock Most extreme is vascular collapse Antihistamines inhibit the function o ...
... histidine -> histamine (in Mast cells through decarboxylation) Released to trigger immune response Histamine is a powerful vasodialator Increases permeability of blood vessels Reduce blood pressure and lead to anaphylactic shock Most extreme is vascular collapse Antihistamines inhibit the function o ...
RECOMBINANT HUMAN INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR I
... Order Confirmation: Sales order confirmations are sent out upon the receipt of all orders. Please contact GenWay if you do not receive a confirmation within 1 business day of submitting your order. Precautions: IGF1 protein is for in vitro research use only. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutic ...
... Order Confirmation: Sales order confirmations are sent out upon the receipt of all orders. Please contact GenWay if you do not receive a confirmation within 1 business day of submitting your order. Precautions: IGF1 protein is for in vitro research use only. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutic ...
AP Biology Unit 1- The Chemistry of Life
... Life’s little compartments: Types of cells and how they work After the last unit, this one may be a little refreshing, since almost all you need to know about this unit can be summarized in a few tables and figures. This unit is about cells Define cell:_______________________________________________ ...
... Life’s little compartments: Types of cells and how they work After the last unit, this one may be a little refreshing, since almost all you need to know about this unit can be summarized in a few tables and figures. This unit is about cells Define cell:_______________________________________________ ...
Molecular Biology of the Cell
... plasma membrane (Fig 10-3, Fig 10-16) Marker for apoptosis Signal to neighboring cells, macrophages (“Eat me” signal) ...
... plasma membrane (Fig 10-3, Fig 10-16) Marker for apoptosis Signal to neighboring cells, macrophages (“Eat me” signal) ...
Metabolic Pathways - University of California, Santa Barbara
... Metabolic Pathways – Ch. 26 10. Stage 4 of catabolism is _________________________ in which 1 molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle _________ ...
... Metabolic Pathways – Ch. 26 10. Stage 4 of catabolism is _________________________ in which 1 molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle _________ ...
HTRF phospho-IKKβ is more sensitive than Western-Blot
... The HTRF cellular kinase platform has been optimized for the investigation of site-specific phosphorylation of endogenous proteins in whole cells. With 12 phosphospecific assays, it covers key targets implicated in diverse signaling pathways, and enables an accurate and sensitive determination of ph ...
... The HTRF cellular kinase platform has been optimized for the investigation of site-specific phosphorylation of endogenous proteins in whole cells. With 12 phosphospecific assays, it covers key targets implicated in diverse signaling pathways, and enables an accurate and sensitive determination of ph ...
a-Catulin, a Rho signalling component, can regulate NF
... induced by transfected a-catulin (Figure 6d); however, cyclin D1, which has been previously reported to be inhibited by a-catulin (Merdek et al., 2004), was not affected. Together, these results demonstrate that a-catulin has anti-apoptotic properties, but that at least in this cell type and at earl ...
... induced by transfected a-catulin (Figure 6d); however, cyclin D1, which has been previously reported to be inhibited by a-catulin (Merdek et al., 2004), was not affected. Together, these results demonstrate that a-catulin has anti-apoptotic properties, but that at least in this cell type and at earl ...
Systems Biology Study Group Chapter 3
... • Conformational changes in enzyme molecule • Example: Hexokinase – Catalyzes phosphorylation of glucose – Inhibited by ATP, product of glycolysis – Stimulated by ADP, product of ATP stored energy consumption ...
... • Conformational changes in enzyme molecule • Example: Hexokinase – Catalyzes phosphorylation of glucose – Inhibited by ATP, product of glycolysis – Stimulated by ADP, product of ATP stored energy consumption ...
Bios90: Defining the mechanisms that regulate
... cause the short fin phenotype The short fin mutant exhibits less connexin43 activity, which leads to less growth and shorter bony segments ...
... cause the short fin phenotype The short fin mutant exhibits less connexin43 activity, which leads to less growth and shorter bony segments ...
Allosteric Function(s) of Proteins
... academia. Specifically, ideas from molecular dynamics have reshaped receptor theory from the rigid single-active state concepts prevalent historically into a modern view of dynamic protein ensembles of multiple receptor active states. Second, the technology of pharmacological assays has exploded to ...
... academia. Specifically, ideas from molecular dynamics have reshaped receptor theory from the rigid single-active state concepts prevalent historically into a modern view of dynamic protein ensembles of multiple receptor active states. Second, the technology of pharmacological assays has exploded to ...
AP Biology Summer Session Lecture 6
... Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway. One strategic point occurs in the third step of ...
... Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway. One strategic point occurs in the third step of ...
Differential expression of genes involved in
... Analysis of gene expression data agrees with certain findings of Berney et al. (2010) • Berney et al. (2010) shows up-regulation of NAD+/NADH independent enzymes coupled with down regulation of NAD+/NADH dependent enzymes • Berney et al. (2010) shows differential regulation of ferredoxin usage and ...
... Analysis of gene expression data agrees with certain findings of Berney et al. (2010) • Berney et al. (2010) shows up-regulation of NAD+/NADH independent enzymes coupled with down regulation of NAD+/NADH dependent enzymes • Berney et al. (2010) shows differential regulation of ferredoxin usage and ...
Gene Section LPAR1 (lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Figure of the LPAR1, a G protein-coupled receptor, spanning the plasma membrane seven times. The receptor has three numbered extracellular and intracellular loops that are involved in signal transduction. Also shown are the amino terminus and carboxyl terminal tail. Three regions of the carboxyl ter ...
... Figure of the LPAR1, a G protein-coupled receptor, spanning the plasma membrane seven times. The receptor has three numbered extracellular and intracellular loops that are involved in signal transduction. Also shown are the amino terminus and carboxyl terminal tail. Three regions of the carboxyl ter ...
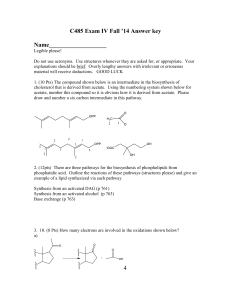
C485 Exam I
... cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this pathway. ...
... cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this pathway. ...
SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION The applied Hi3 approach relies
... determined the stoichiometry of Escherichia coli proteins belonging to selected wellcharacterized protein complexes. Accordingly, we calculated the stoichiometry of representative Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein complexes (i.e. ATP synthase F1 and soluble part of the succinate dehydrogenase) as well ...
... determined the stoichiometry of Escherichia coli proteins belonging to selected wellcharacterized protein complexes. Accordingly, we calculated the stoichiometry of representative Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein complexes (i.e. ATP synthase F1 and soluble part of the succinate dehydrogenase) as well ...